1. Linear Equations in One Variable
- Books Name
- class 8 th Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Linear Equations in One Variable
Introduction to linear equations,
An equation is called linear equation if it has only one degree i.e., the highest power of the variable appearing in equation is 1, and the form of linear equation is
P(x) = ax + b = 0
e.g., x + 5 = 0,
x/2 – 7 = 15
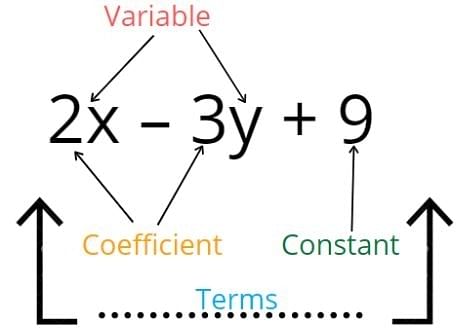
Rules for linear equation
A linear equation may have any rational number, as its solution.
An equation may have a linear expression on both sides of the equation.
A number which satisfies an equation is called the solution of the equation.
Example:
Let us assume an equation 4x−5=35.
That is x=10 is the solution of this equation 4x−5=35.
To verify this, substitute x=10 in the equation, and you find LHS and RHS are equal.
LHS=(4×10)−5=40−5=35=RHS.
Transposition method,
A term may be transposed from one side of the equation to the other side, but its sign will be changed.
We can use the following steps to find a solution using transposition method:
Step 1) Identify the variables and constants in the given linear equation.
Step 2) Simplify the equation in LHS and RHS.
Step 3) Transpose the term on the other side to solve the equation further simplest.
Step 4) Simplify the equation using arithmetic operation as per required that is mentioned in rule1 or rule2 of linear equations.
Step 5) Then the final will be the solution for given linear equatio
Example:
Solve: 2x+8=20
The given linear equation is 2x+8=20.
To solve the given linear equation, we can use the linear equation rules.
Step 1) Transposing 8 to RHS side.
2x=20−82x=12
Step 2) Divide both sides by 2.
2x2=122x=6
Thus x= 6.
Linear equation - Variable on both sides
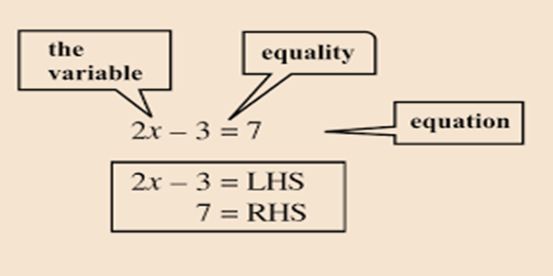
An equation essentially contains a sign of equality (=).
Also, the expression we use to form a linear equation is linear only, i.e., the highest power of the variable occurring in the expression is 1 and that too only in one variable.
The expression on the left of the sign of equality is called the Left-Hand Side whereas the expression on the right of the sign of equality is called the Right Hand Side.
The value of the variable for which LHS = RHS is called a solution of the linear equation.
To find the solution of a linear equation in one variable, we assume that the two sides of the equation are balanced.
For example
Solve: 2x+6=x+14
This linear equation consists of the variable on both sides.
LHS= 2x+6.
RHS= x−14.
Now we see a couple of steps to solve the equation.
Step I)
The equation is 2x+6=x+14.
Now transpose the 6 to RHS side and transpose the variable x in RHS to LHS respect to the given equation.
2x−x=14−61x=8
Step II)
Divide by 1 on both side.
1x=81x1=81x=8
Cross multiplication method
If the given equation is not in a linear polynomial form, we use the cross multiplication method of solving.
Let's understand this concept with an example.
Steps for cross multiplication:
1. Multiply the numerator in LHS by the denominator in RHS.
2. After multiply the RHS numerator by the LHS denominator.
3. Simplify both the sides of the equation.
4. Transpose the constant and variable to RHS and LHS respect to the simplified equation.
5. Now use the linear equation rules (Addition, Subtraction, Multiply, Divide - to both sides) to find the solution of the given equation.
Solve: 2x+42=x+410
The given equation is 2x+42=x+410. This is not in linear polynomial form and also the equation contains variable on both sides. Now apply the cross multiplication rule in this equation.
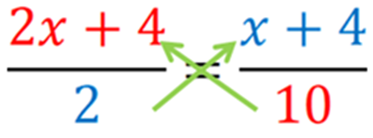
the solution for the equation 2x+42=x+410 is x=−2.

 Carrier Point
Carrier Point
 ReginaTagebücher
ReginaTagebücher
