- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Science
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
(i) In this kind of reproduction two opposite sexes i.e. male and female are required.
(ii) The flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant. The stamens are the male reproductive part and the carpel or pistil is the female reproductive part.
(iii) The flowers which contain either only the pistil or only the stamens are called unisexual flowers.
(iv) The flowers which contain both stamens and pistil are called bisexual flowers.
(v) Corn, papaya and cucumber produce unisexual flowers, whereas mustard, rose and petunia have bisexual flowers. Both the male and the female unisexual flowers may be present in the same plant or in different plants.
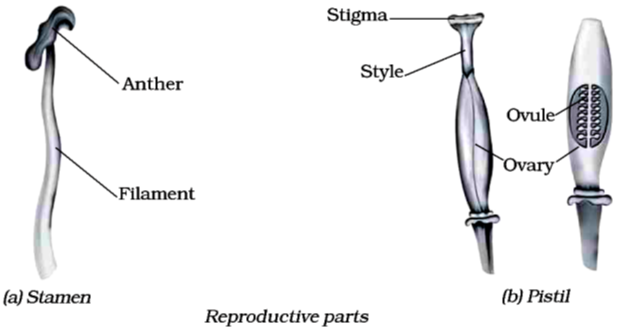
(vi) Anther contains pollen grains which produce male gametes.
(vii) A pistil consists of stigma, style and ovary. The ovary contains one or more ovules. The female gamete or the egg is formed in an ovule. In sexual reproduction, a male and a female gamete fuse to form a zygote.
1. Pollination
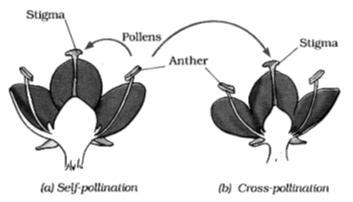
The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination.
Types of pollination:
(a) Self pollination
(b) Cross-pollination
(a) If the pollen lands on the stigma of the same flower it is called self-pollination.
(b) When the pollen of a flower lands on the stigma of another flower of the same plant, or that of a different plant of the same kind, it is called cross-pollination. In plants pollination is followed by fertilization.
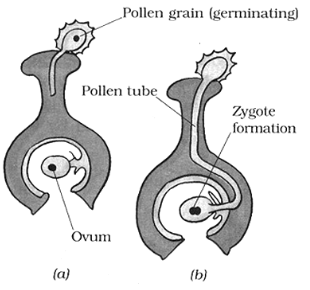
2. Fertilisation
The process of fusion of male and female gametes (to form a zygote) is called fertilisation. The zygote develops into an embryo.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
