Photosynthesis – food making process in plants
The plants use the energy in sunlight to prepare food in the presence of a green colour matter called “chlorophyll” present in the leaves of a green plant. The process by which green plants make their own food (like glucose) from carbon dioxide and water by using sunlight energy (in the presence of chlorophyll) is called photosynthesis.
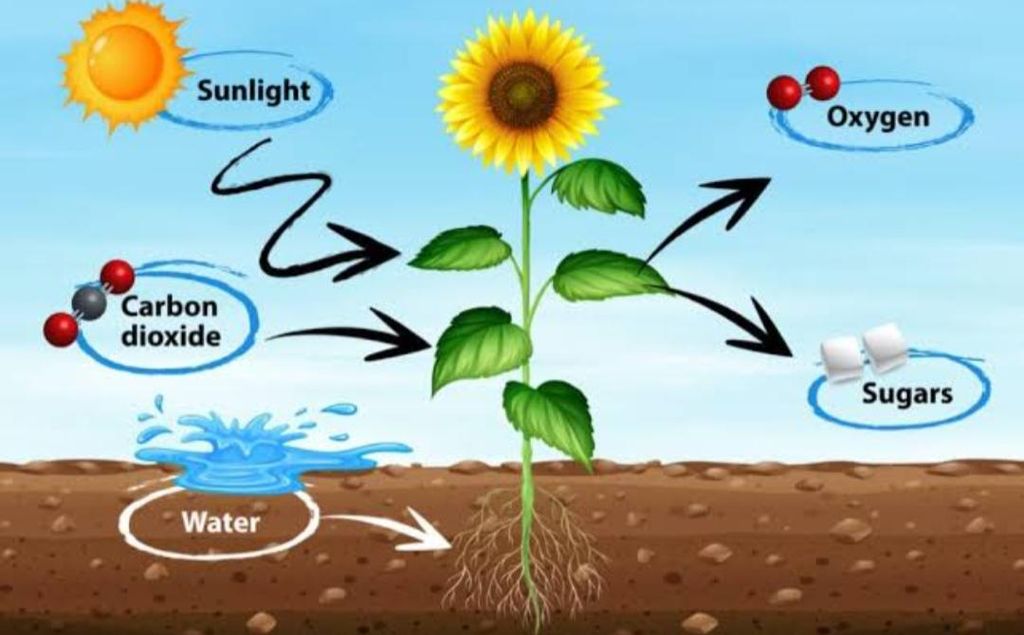
Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen The process of photosynthesis takes place in the leaves of a plant. Oxygen gas is produced during photosynthesis which is utilised by all the living organisms for their survival. The process of photosynthesis first produces a simple carbohydrate called ‘glucose’ as food. The glucose carbohydrate then gets converted into a complex carbohydrate called Starch. Starch gets stored as food in the various parts of plant including leaves. Some of the glucose is also converted into other types of plant foods such as fats and oils, proteins as well as vitamins. The synthesis of food (or making of food) occurs in the leaves of a plant, so leaves are the food factories of a plant. The leaves of a plant can synthesise food because they contain a green pigments chlorophyll (which is necessary for making food). Other parts of a plant usually cannot synthesise food because they do not contain chlorophyll.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
