Soil Teeming with Life
Chapter 9: Soil

Soil science is the study of soil as a natural resource on the surface of the Earth including soil formation, classification and mapping; physical, chemical, biological, and fertility properties of soils; and these properties in relation to the use and management of soils.
Soil teeming with life

Soil is teemed with life.” The statement states that the soil contains different types of living organisms that help in sustaining life. Soil comprises millions and billions of living organisms that form a complex ecosystem and is the most precious resource to humans
Soil Profile
Soil profile

A soil horizon is a layer parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Horizons are defined in many cases by obvious physical features, mainly colour and texture. These may be described both in absolute terms (particle size distribution for texture, for instance) and in terms relative to the surrounding material, i.e. ‘coarser’ or ‘sandier’ than the horizons above and below.
Soil Types
Soil types

Sandy Soil
The first type of soil is sand. It consists of small particles of weathered rock. Sandy soils are one of the poorest types of soil for growing plants because it has very low nutrients and poor water holding capacity, which makes it hard for the plant’s roots to absorb water. This type of soil is very good for the drainage system. Sandy soil is usually formed by the breakdown or fragmentation of rocks like granite, limestone and quartz.
Silt Soil
Silt, which is known to have much smaller particles compared to sandy soil and is made up of rock and other mineral particles, which are smaller than sand and larger than clay. It is the smooth and fine quality of the soil that holds water better than sand. Silt is easily transported by moving currents and it is mainly found near the river, lakes and other water bodies. The silt soil is more fertile compared to the other three types of soil. Therefore, it is also used in agricultural practices to improve soil fertility.
Clay Soil
Clay is the smallest particle among the other two types of soil. The particles in this soil are tightly packed together with each other with very little or no airspace. This soil has very good water storage qualities and makes it hard for moisture and air to penetrate into it. It is very sticky to the touch when wet but smooth when dried. Clay is the densest and heaviest type of soil which does not drain well or provide space for plant roots to flourish.
Loamy Soil
Loam is the fourth type of soil. It is a combination of sand, silt and clay such that the beneficial properties of each are included. For instance, it has the ability to retain moisture and nutrients; hence, it is more suitable for farming. This soil is also referred to as agricultural soil as it includes an equilibrium of all three types of soil materials, being sandy, clay, and silt, and it also happens to have humus. Apart from these, it also has higher calcium and pH levels because of its inorganic origins.
Properties of Soil
Properties of soil
All soil contain mineral particles, organic matter, water and air. The combinations of these determine the soil’s properties – its texture, structures is made up of different-sized particles. Soil texture refers to the size of the particles that make up the soil and depends on the proportion of sand, silt and clay-sized particles and organic matter in the soil. Sandy soils feel gritty when rubbed between your fingers. Silts feel smooth – a little like flour. Most clays are sticky and mouldable. If you’ve ever used pottery clay, you’ll know the feelinge, porosity, chemistry and colour.
Moisture in Soil
Moisture in soil

Soil moisture is the water stored in the soil and is affected by precipitation, temperature, soil characteristics, and more. These same factors help determine the type of biome present, and the suitability of land for growing crops.
Absorption of Water by Soil
Absorption of water by soil
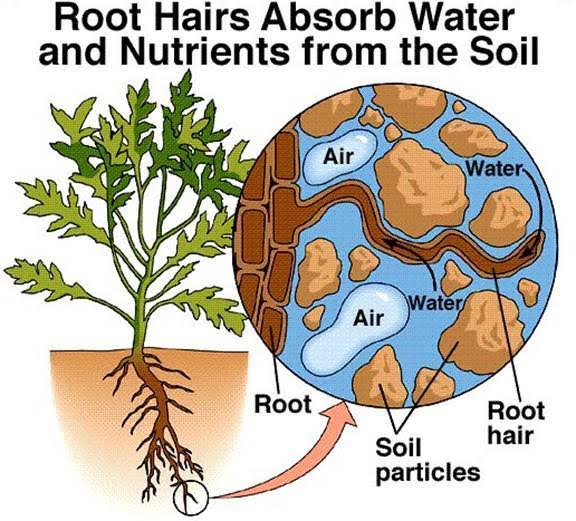
A combination of sand, silt, and clay particles, this soil absorbs water readily and is able to store it for use by plants. Loam absorbs water at a rate between ¼ and 2 inches per hour. Sandy Soil, because it has very large spaces, absorbs water at a rate of more than 2 inches per hour.
Soil and Crops.
Soil and crops

Agriculture is the backbone of Indian economy, and soil plays a very important in it. Different types of crops requires suitable soils for their growth and cultivation. Soil is a significant natural resource. Soil can be categorised into different types, each with distinct characteristics that provide crop growing benefits and limitations.
Various types of soil are present in distinct parts of India. Soil is mostly affected by wind, rainfall, temperature, light and humidity. Several climatic factors also affect the soil profile and bring transitions in the soil structure. The factors mentioned above that affect the soil influence vegetation in an area. Vegetation area can be forest, grassland, tundra, desert, and ice sheet. Vegetation is mostly in the fertile upper soil of the earth and covers the soil like a green sheet spread on its surface

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
 Param Publication
Param Publication
