Light Travels Along A Straight Line
Chapter 15: Light
What is light in physics? Light is electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation occurs over an extremely wide range of wavelengths, from gamma rays with wavelengths less than about 1 × 10−11 metres to radio waves measured in metres.
Light travels along a straight line

Light travels in a straight line because the diffraction effect is least due to the small wavelength of light. So the small wavelength of light produces negligible diffraction and therefore light travels along a straight line.
Reflection of Light
Reflection of light
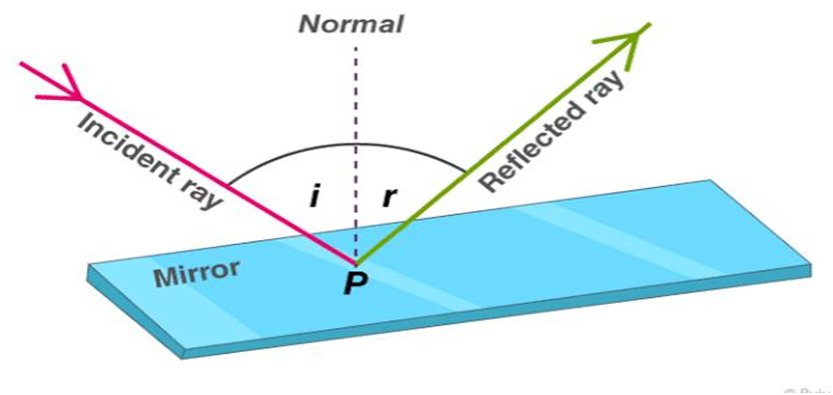
When a ray of light approaches a smooth polished surface and the light ray bounces back, it is called the reflection of light. The incident light ray that land on the surface is reflected off the surface. The ray that bounces back is called the reflected ray
Right or Left!
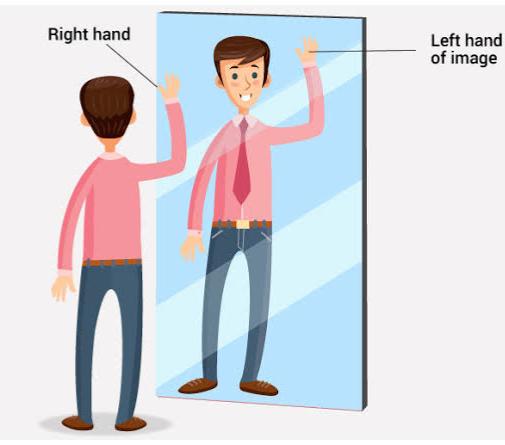
Right or left
When Barack Obama promised in his 2009 inaugural address that “we will restore science to its rightful place,” he invoked not so much a debate as a set of widely shared assumptions. According to conventional wisdom, liberals and Democrats are the party of reason and science; conservatives and Republicans are the party of religion and patriotic symbols. As Drew Westen, a psychotherapist, recently expressed it in a New York Times op-ed, “Whereas Democrats have carried forward the belief in the role of science and knowledge in improving our lives, Republicans have moved in increasingly anti-intellectual directions.” This way of stating the division, needless to say, is itself liberal and Democratic. While many conservatives (with notable exceptions) agree that religion is an important source of beliefs and public policies, probably few consider themselves anti-intellectual. Yet the impression that the physical and social sciences are to liberalism what religion is to conservatism goes mostly unquestioned on either side.
Playing with Spherical Mirrors
Playing with spherical mirrors
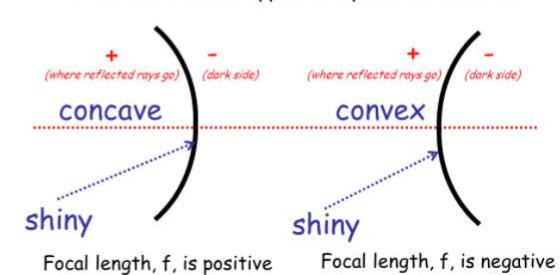
Spherical mirrors are used by all in day-to-day life. It is important that students have a better understanding of the application of spherical mirrors so that they grasp the concept properly. Students often find problems when dealing with the concept because it can prove to be complicated. A spherical mirror is a mirror that has the shape of a piece cut out of a spherical surface. There are two types of spherical mirrors: concave and convex mirror.
Images Formed by Lenses
Images formed by lenses
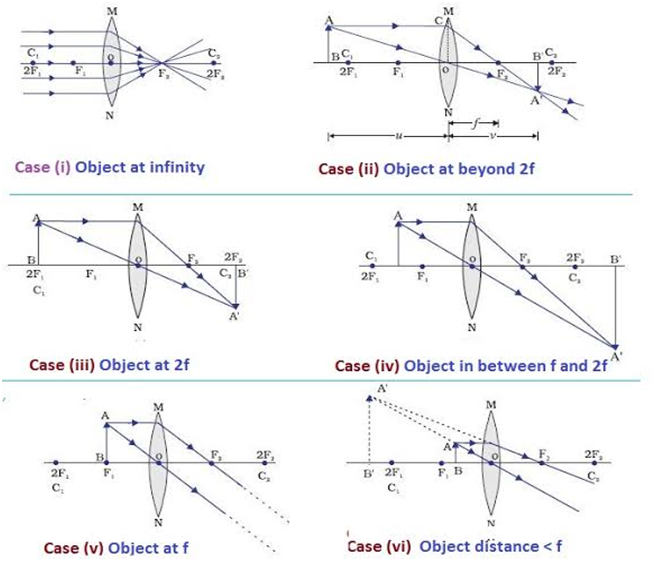
A lens is a part of a transparent thick glass which is bounded by two spherical surfaces. It is an optical device through which the rays of light converge or diverge before transmitting.
A convex lens is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges. A convex lens is also known as a “biconvex lens” because of two spherical surfaces bulging outwards.
A concave lens is thicker at the edges and thinner in the middle. A concave lens is also known as a “biconcave lens” because of two spherical surfaces bulging inwards.
Sunlight — White Or Coloured?.
Sunlight - white or coloured ?
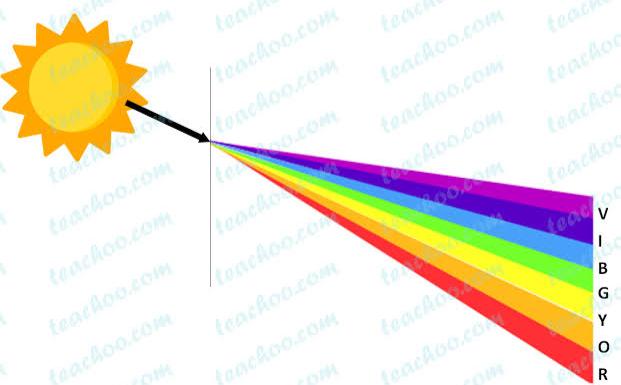
The colour of the sun is white. The sun emits all colours of the rainbow more or less evenly and in physics, we call this combination “white”. That is why we can see so many different colours in the natural world under the illumination of sunlight.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
