Modes of Reproduction
Chapter 12: Reproduction in Plants
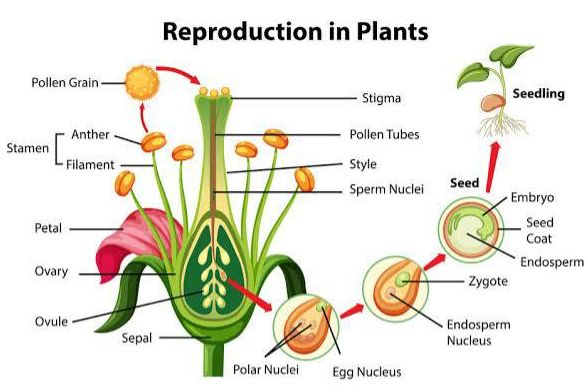
Plant reproduction is the production of new offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from either parent. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, resulting in clonal plants that are genetically identical to the parent plant and each other, unless mutations occur. Asexual reproduction does not involve the production and fusion of male and female gametes. Asexual reproduction may occur through budding, fragmentation, spore formation, regeneration and vegetative propagation.
Modes of reproduction
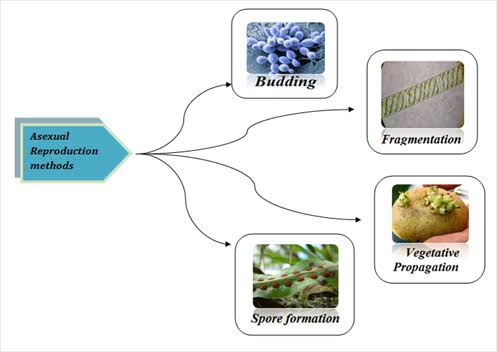
Depending on the number of parents involved, there are different modes of reproduction. Every living organism reproduces by either of the two modes i.e. sexual reproduction or asexual reproduction. The different modes of reproduction in animals and plants are explained below.
Sexual reproduction
It is the mode of reproduction in which gamete cells from two organisms, one male and one female, combine to form a singular zygote. This zygote shares half of its genetic information with the father and the other half with the mother.
Asexual Reproduction
It is the mode of reproduction which involves only one organism. The offspring that is produced is genetically identical to the mother and almost always has the same number of chromosomes. Hence, they are called clones. Moreover, they are exact copies of their parent cell.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction
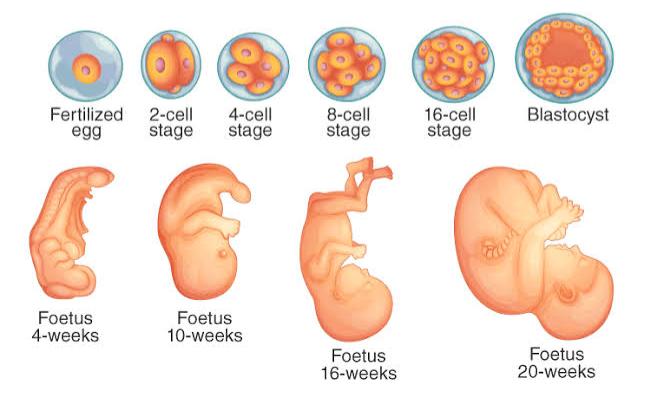
Humans reproduce sexually by the fusion of sperm with the egg (ovum) to produce a zygote called fertilization. Fertilization is the crucial stage of sexual reproduction. Without fertilization, sexual reproduction will not be complete.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Plants that reproduce sexually have sex parts which we know as flowers. The process of reproduction involves the fusion of male gametes, namely, pollen with the female gamete, also known as ovules. This fusion results in the formation of a zygote and an endosperm nucleus, which grow into seeds and fruits respectively.
Sexual Reproduction in Animals
Among the different modes of reproduction in animals, sexual reproduction is the most common one. Most animals reproduce sexually, though in a variety of different ways.
Sexual reproduction in animals involves the union of a haploid sperm and a haploid egg to form a diploid zygote, which shares its DNA with both the parent cells.
Fruits and Seed Formation
Fruits and seeds formation
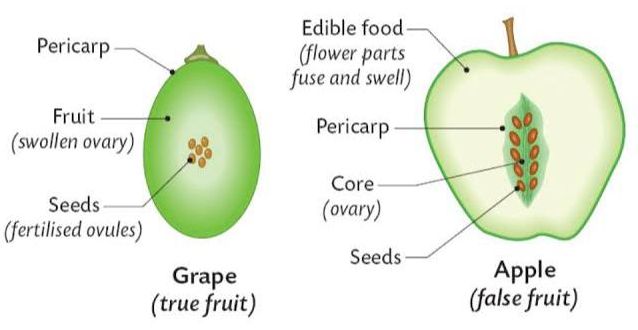
Seeds and fruits are formed by fertilization. In angiosperms, two structures are formed as a result of double fertilization – a diploid zygote and a triploid primary endosperm cell. The zygote develops into an embryo, whereas, the endosperm cell gives rise to endosperm. It provides nourishment to the growing embryo.
Seed Dispersal
Seed dispersal
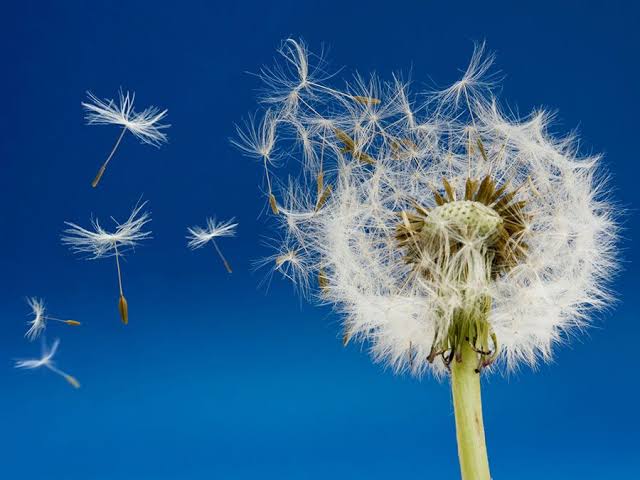

Seed dispersal is the mechanism by which plant seeds are transported to new sites for germination and the establishment of new individuals. Animals commonly mediate this process, and consequently, the ultimate fate of seeds depends on their effectiveness as seed dispersers.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
