- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Science
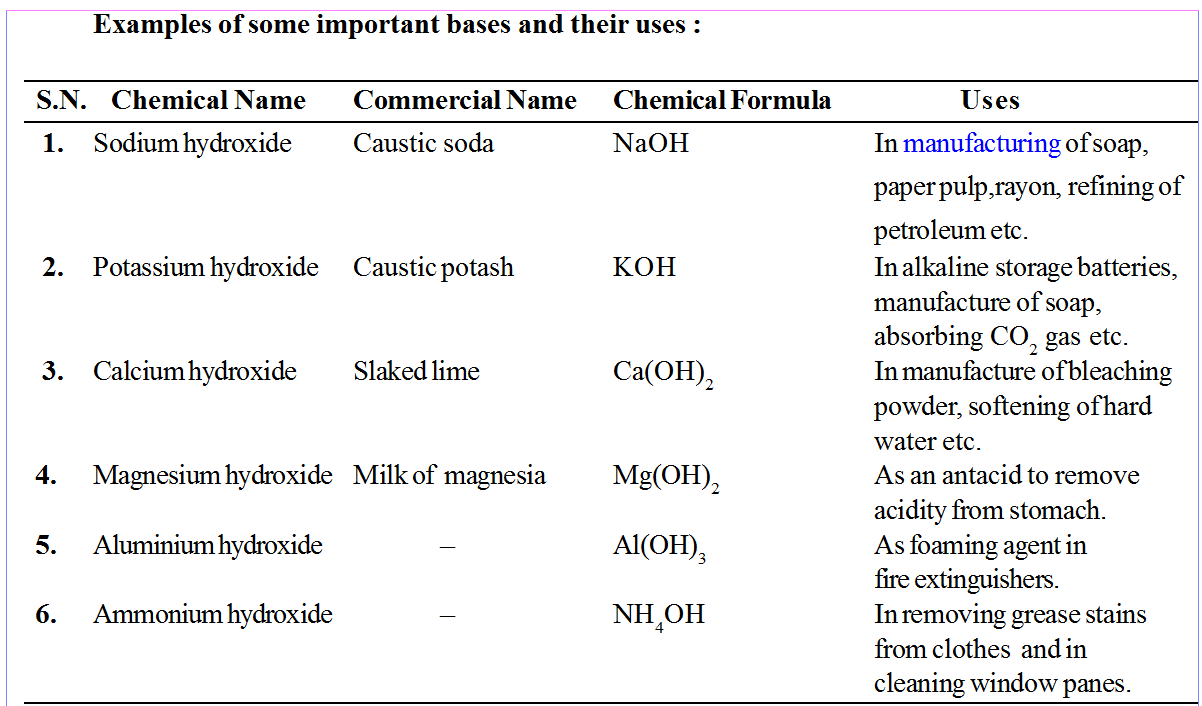
2.3 BASES
These chemical substances are bitter in taste and soapy to touch . The chemical nature of such substances is basic.
Definition :
A base is a compound which gives hydroxyl group (OH–) on dissolution in water are known as bases.
e.g.
Sodium hydroxide NaOH
Calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2
Aluminium hydroxide Al(OH)3
Remember
• Alkalis :
Bases which dissolves in water are called alkalis. e.g. KOH, NaOH.
All alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis. e.g. Al(OH)3 is a base, but not an alkali.

Remember
• Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is commonly called Washing soda.
• Sodium bicarbonate(NaHCO3) is commonly called baking soda.
• CaO is used to neutralize acidic nature of soil.
• Ca(OH)2 is used to prepare mortar, bleaching powder and to neutralize acid in water supplies.
• KOH (caustic potash) is used to conduct electricity between two electrodes.
Advance Learning
• Both NaOH and KOH are deliquescent in nature which means that they absorb moisture from air.
Classification of Bases :
(i) On the basis of strength :
(1) Strong Bases : Bases which are almost completely dissociated in water are known as strong bases.
e.g. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), barium hydroxide Ba(OH)2 etc .
![]()
(2) Weak Bases : Bases which dissolve in water only slightly and produce a low concentration of hydroxide ions are called weak bases.
e.g. Ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH), silver hydroxide (AgOH) etc.
(ii) On the Basis of their Concentration :
By the term concentration, we mean the amount of water present in the given sample of alkali solution in water. On the basis of concentration, the alkalis can be classified as under :
(1) Concentrated alkali :
A solution of alkali having a relatively high percentage of alkali in its aqueous solution is known as concentrated alkali.
(2) Dilute alkali :
A solution of alkali having a relatively low percentage of alkali in its aqueous solution is known as a dilute alkali.
If the concentration of alkali in the solution is less than 1 mole per litre, then it is considered to be a dilute alkali.
(iii) On the Basis of their Acidity :
The number of hydroxide (OH–) ions produced by one molecule of an alkali on complete dissociation in water or the number of hydrogen ions (of an acid) with which a molecule of that alkali reacts to produce salt and water only is known as acidity of an alkali.
For water insoluble hydroxides, acidity of the base is equal to the number of OH– ions present in one molecule of that base.
On the basis of acidity, the bases can be classified as under :
(1) Monoacidic Bases (or alkalis) :
When one molecule of the base on complete ionisation produces one hydroxide (OH–) ion in aqueous solution, the base or alkali is said to be monoacidic base.
OR
A monoacidic base (or alkali) may be defined as one whose one molecule reacts with one hydrogen (H+) ion completely to form salt and water as the only products.
Examples of Monoacidic Bases (or alkalis) :
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), Potassium hydroxide (KOH), Ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH). All these substances produce only one hydroxyl ion on complete ionisation in aqueous solution.
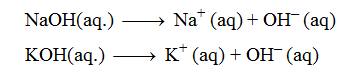
The dissociation of monoacidic bases or alkalis takes place in a single step.
(2) Diacidic Bases (or alkalis) :
When one molecule of a base or alkali on complete ionisation produces two hydroxide (OH–) ions in aqueous solution, the base or alkali is said to be diacidic.
Examples of Diacidic Bases
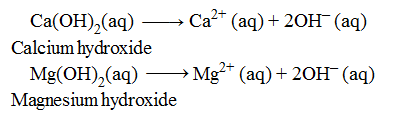
One molecule of both the bases are producing 2OH– ions in aqueous solution, therefore, these are termed as diacidic bases .
(3) Triacidic Bases :
When one molecule of a base or alkali on complete ionisation produces three hydroxide (OH–) ions in aqueous solution, the base or alkali is said to be triacidic base.
Examples of Triacidic Bases :
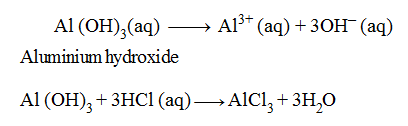
In the above equations, one molecule of Al (OH)3 is producing three OH– ions and one molecule of Al (OH)3 is reacting with three hydrogen (H+) ions to form salt and water only, therefore, it is termed as a triacidic base.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
