- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Division of algebraic expressions
Division is the inverse process of multiplication.
When we divide one expression by another, we find a third expression which when multiplied by the second gives the first , i.e., if a ÷ b = x then a = bx. In a ÷ b = x, ‘a’ is called the Dividend, ‘b’ the Divisor and ‘x’ is called the Quotient.
Rules of Signs in Division :
(i) When the dividend and the divisor have the same signs, the quotient has the plus sign.
(ii) When the dividend and the divisor have opposite signs, the quotient has the negative sign.
Division of a Monomial by another Monomial :
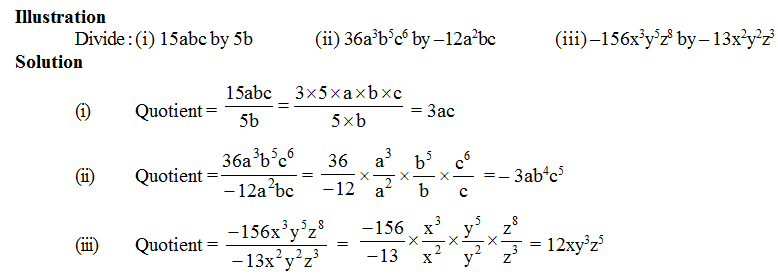
Division of a Polynomial by a Monomial :
Divide each term of the polynomial by the monomial and then write the resulting quotients.
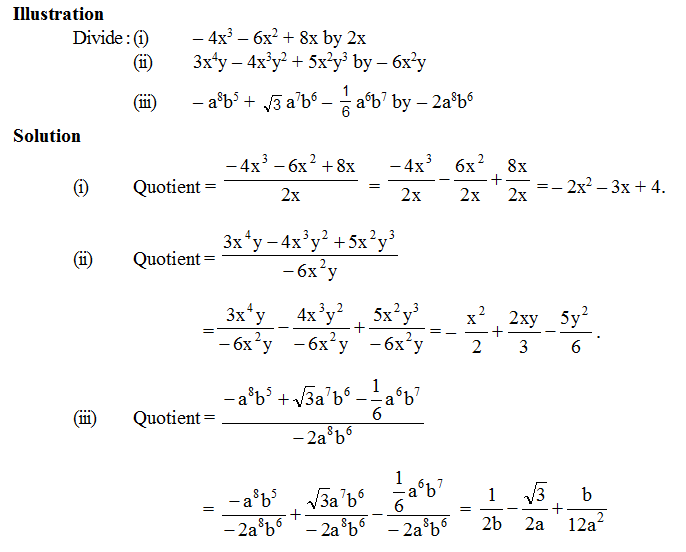
Algebraic identities
An identity is an equality, which is true for all values of the variables. The following three identities are very important.
Identity 1 : (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
Proof : we have :
(a + b)2 = (a + b) (a + b)
= a (a + b) + b(a + b)
= a2 + ab + ba + b2
= a2 + 2ab + b2 [Since ba = ab]
∴ (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2.
Identity 2 : (a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab + b2.
Proof : we have
(a – b)2 = (a – b) (a – b)
= a(a – b) – b(a – b)
= a2 – ab – ba + b2
= a2 – ab – ab + b2 [Since ba = ab]
= a2 – 2ab + b2.
= (a2 – 2ab + b2)
Identity 3 : (a + b)(a – b) = a2 – b2
Proof We have :
(a + b) (a – b) = a (a – b) + b(a – b)
= a2 – ab + ba – b2
= a2 – b2 [Since ba = ab]
∴ (a + b)(a–b) = a2 – b2.
Applications of the above identities :
Illustration
Find each of the following products :
(i) (3x +2y) (3x +2y) (ii) (4x2 + 5) (4x2 + 5)
(iii) (2x – 5y)2 (iv) (3x2 +2y2) (3x2 – 2y2)
Solution
(i) (3x +2y)(3x +2y) = (3x +2y)2
= (3x)2 + (2y)2 + 2 (3x) (2y) [Using (a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab]
= 9x2 +4y2 + 12xy.
∴ (3x + 2y) (3x + 2y) = 9x2 + 4y2 + 12xy.
(ii) (4x2 + 5)(4x2 + 5) = (4x2 + 5)2
= (4x2)2 + 52 + 2 (4x2) 5 [Using (a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab]
= 16x4 +25 + 40x2.
(iiii) (2x – 5y)2 = (2x)2 + (5y)2 – 2 (2x) (5y) [Using (a – b)2 = a2 + b2 – 2ab]
= 4x2 + 25y2 – 20xy.
(iv) (3x2 + 2y2 )(3x2 – 2y2) = (3x2)2 – (2y2)2 [∴ (a + b) (a – b) = (a2 – b2)]
= (9x4 – 4y4).

 Param Publication
Param Publication
