1. Proper and Improper fractions
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, we will study :
- What are fractions
- Types of fractions-
(a) Comparison of fractions
(b) Operation on fractions
FRACTIONS
Fraction is a part of whole.

Denominator tells us about into how many equal parts the whole is divided.
Numerator tells us how many parts are considered of the whole
Types of Fractions
1. Decimal fractions : Any fraction whose denominator is in the form of 10n, n ∈ N as i.e.10,100, 1000 etc. is called a decimal fraction.
![]()
2. Vulgar fraction : Any fraction other than decimal fraction is called vulgar fraction.
![]()
3. Proper fraction : Any fraction having its numerator less than its denominator is called a proper fraction.
![]()
4. Improper Fraction : Any fraction whose numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator is called an Improper fraction.
![]()
5. Mixed Fraction : When an improper fraction is expresed as sum of a natural number and a proper fraction is called mixed fraction.
![]()
6. Equivalent Fractions : The fractions obtained by multiplying the numerator and denominator both by the same number are called Equivalent fractions.
![]()
7. Like Fractions : Those fractions which have same denominator but different numerator are called like fractions.
![]()
8. Unlike Fractions : Fractions which do not have common denominator are unlike fractions.
![]()
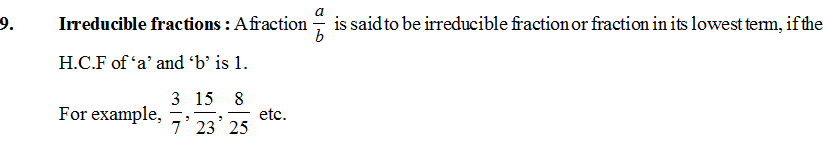
2. Operations in Fractions
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Comparison of Fractions
1. Method for comparison of two fractions:
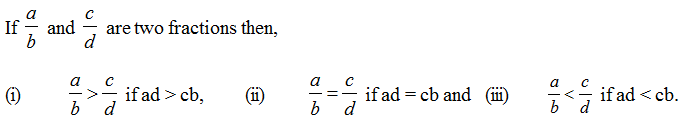
2. Method for comparison of more than 2 fractions:
1st Step : Find the L.C.M. of denominator of all the given fractions.
2nd Step : Convert all the given fractions into like fractions by dividing the L.C.M. with individual denominators and multiplying the result obtained with denominator and numerator, of each fractions.
3rd Step : On comparison of numerator the fraction with smaller numerator is smaller fraction.
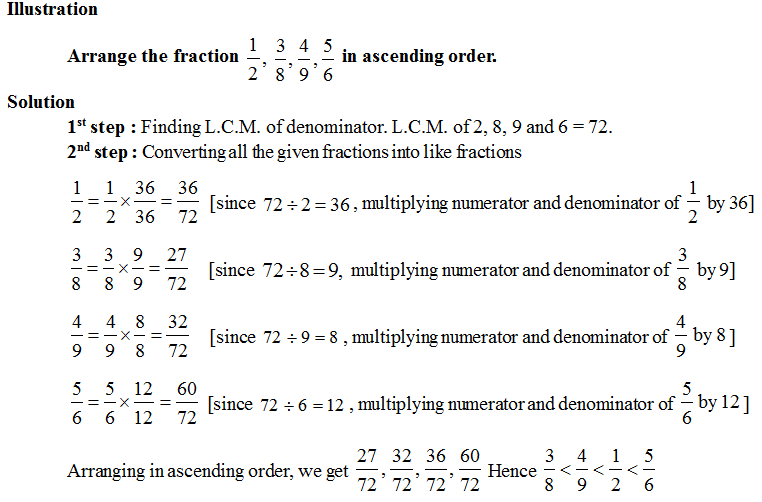
Operations on Fractions:
1. Addition of fractions:
Rule 1: In case of like fractions, add the numerators, keeping the denominator same.
![]()
Rule 2: For unlike fractions, addition is done by first converting the fractions into like fractions and then adding. In practice, the addition of unlike fractions is done by using L.C.M.
![]()
Rule 3: Two mixed numbers can be added by adding whole numbers and fractions separately.
![]()
2. Subtraction of Fractions:
Rules for subtraction of fractions is similar to that of addition
(i) Like fractions are subtracted by finding the difference of numerators.
![]()
(ii) Unlike fractions are converted to like fractions and then subtracted.
![]()
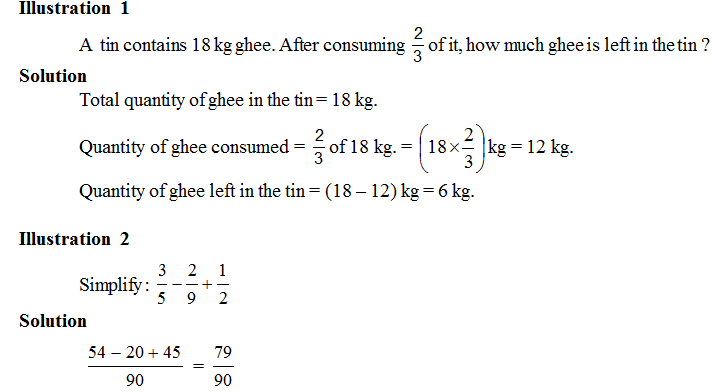
3. Decimal Numbers
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
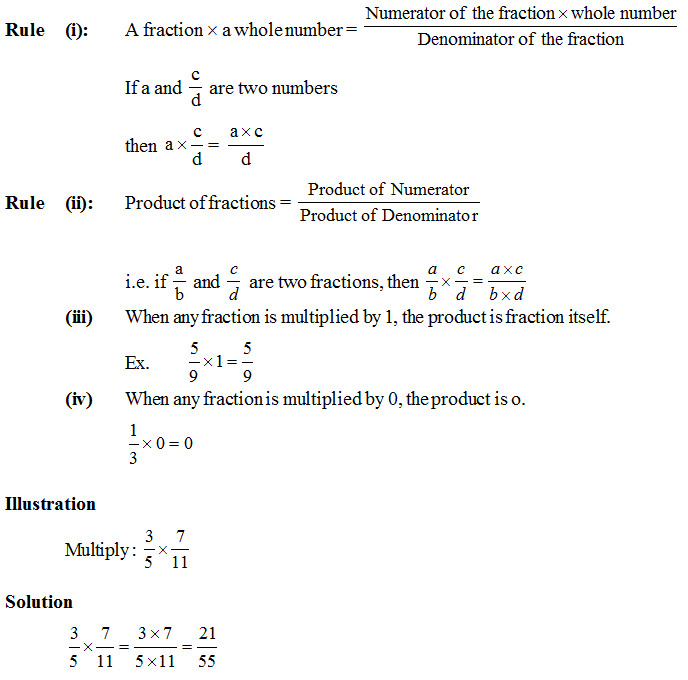
3. Multiplication of Fractions :
4. Basic operations on decimal numbers
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
4. Division of Fractions
Fraction as an operator “of”
To know the fractional part of a quantity fraction and the number (quantity) are multiplied.
![]()
Before understanding the division of fractions, we must know , what is inverse of a fraction.
Inverse of a fraction or reciprocal of fraction: A fraction is said to be inverse of itself, if the places of

5. Multiplication of decimal numbers
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
DECIMALS
Numbers of the form 12.4, 362.49, 148.3672 etc. are said to be in decimal form.
A decimal number can be expressed into two parts
1. The whole number
2. The decimal part in a decimal number.
The parts are seperated by a point (.) called the decimal point.
In a decimal number the number on left hand side of the decimal is called the whole number part and the number on the right hand side of the point is called the decimal part.
For example, In the number 13.436, 13 is the whole number part and 436 is the decimal part.
Decimal Places - The number of digits in the decimal part give the number of decimal places.
For example, 140.034 has 3 decimal places
Like Decimals - Decimal numbers having same number of decimal places are called like fractions.
For example, 12.32, 143.93, 160.04 etc. are like decimals having two decimals places each.
Unlike Decimals - Decimal numbers having different number of decimal places are called unlike decimals.
For example, 1.362, 3.43, 16.1 etc.
Note: Placing any number of zeroes at the extreme right of the last digit of the decimal place does not change its value. Thus 44.083 = 44.08300 = 44.083000 etc.
Comparison of Decimals numbers
Steps for comparison of decimal numbers :
(i) Convert the decimal number into like decimals by placing zeroes to the right of the decimal.
(ii) Compare the whole number part. The number with greater whole number part is greater.
(iii) If the whole number parts are equal, compare the first digit after decimal. The number with the larger digit in the place right to decimal will be greater.
(iv) If the digit to the right of the decimal is equal then compare the 2nd digit from the right of decimal then the 3rd digit to the right of decimal and so on.
Illustration
Write the following decimal number in ascending order: 6.3, 5.3, 6.03, 4.308, 5.45
Solution
Convert the given fractions into like fraction.
6.300, 5.300, 6.030, 4.308, 5.450 arranging in ascending order after comparison of digits we get,
4.308 < 5.300 < 5.450 < 6.030 < 6.300
Conversion of decimal number into fraction
In order to convert a decimal number into fraction, the digits of the decimal number are kept as numerator without the decimal, and the denominator is kept as 1 followed by the same number of zeroes as there were digits after decimal.
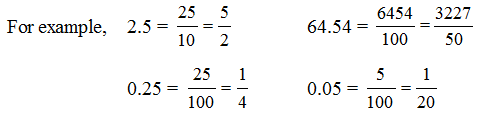
Operation of Decimals
Addition and Subtraction of Decimal Numbers
Steps to add or subtract decimal numbers:
(i) Convert all the decimal number into like decimals
(ii) Add or subtract as required, as per rules of addition or subtraction of whole numbers.
(iii) Place the decimal under decimal point in the given numbers.
Illustration 1
Add : 13.46, 219.54, 2.084
Solution
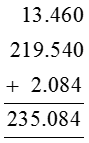
Illustration 2
Subtract : 148.23 – 30.018
Solution
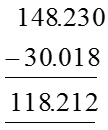
6. Division of decimal numbers
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Multiplication of Decimal Numbers
Multiplication of a decimal numbers by 10 or its factors
Rule: Shift the decimal point to the right place equivalent to numbers of zeros followed by 1.
For example, 5.23 x10 = 52.3
13.438 x 100 = 1343.8 (since in 100 one is followed by 2 zeroes hence the decimal point is shifted to two places to the right)
Multiplication of a decimal by a whole number or by decimal number .
Rule: Multiply the decimal numbers by the whole number or another decimal number as per rules of multiplication.
Rule: Place the decimal in the result at such a place from the left most digit, which is equal to the sum of the places from the left, of the decimal number or whole number and the decimal number which is multiplied.
Illustration 1
Multiply : 0.534 by 2
Solution
The product must contain 3 places of decimal hence 0.534 x 2 = 1.068.
Illustration 2
Multiply : 2.054 x 4.32
Solution
Multiply : 2.054 and 4.32 without putting decimal i.e. 2054 x 432 = 887328
The product must contain 3 + 2 = 5 decimal places. Since sum of the decimal places of the two
numbers = 5 hence 2.054 x 4.32 = 8.87328
Illustration 3
Multiply : 2 × 0.2 × 0.002
Solution
2 × 2 × 2 = 8
Sum of the decimal places of the given numbers = 4 hence the product must contain 4 places of decimals
So 2 × 0.02 × 0.002 = 0.0008
Division of Decimal Numbers
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Divisions of Decimals
1. Division of a decimal number by factors of 10
Rule: On dividing a decimal number by 10 or its factors, the decimal point is shifted towards left by as many places as are zeroes followed by 1.
For example, 12.75 ÷10 = 1.275 (decimal point is shifted towards left by 1 decimal place as there is 1 zero after 1 in 10.)
For example, 12480.03 ÷ 1000 = 12.48003 (decimal point is shifted towards left by 3 decimal place as there are 3 zeroes followed by 1.
Division of a decimal number by a whole number
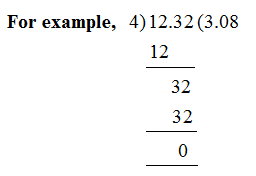
Step - 1: Perform the division by considering the dividend (the decimal number to be divided) as a whole number.
Step - 2: The decimal would be placed in the quoteint once the whole number part of the dividend is complete. Continue the division as in case of whole numbers.
Remark: On dividing the decimal number of a whole number, we can place as many zeroes to the right end of the decimal point of the interval as required to make the remainder zero.
2. Division of a decimal by a decimal:
Step-1: First convert the divisor into a whole number by multiplying the dividend and divisor by suitable factor of 10.
Step-2: Follow the rules of divisions as discussed earlier
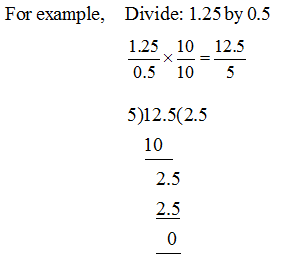
Illustration 1
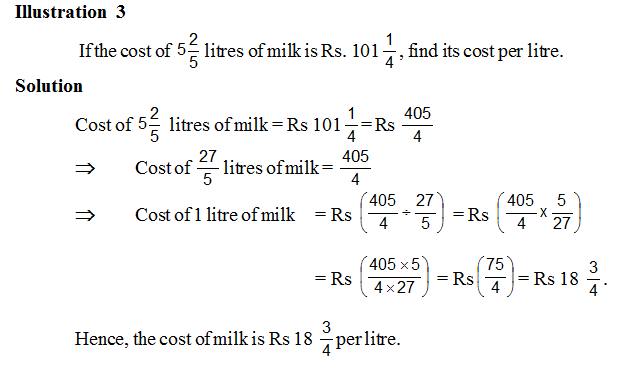
The cost of 28 toys of the same kind is Rs 3462.20. Find the cost of each toy.
Solution
Cost of 28 toys = Rs 3462.20.
Cost of 1 toy = Rs (3462.20 ÷ 28)
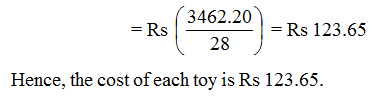
Illustration 2
The product of two decimals is 1.5008 . If one of them is 0.56, find the other.
Solution
Product of given decimals = 1.5008; One decimal = 0.56.
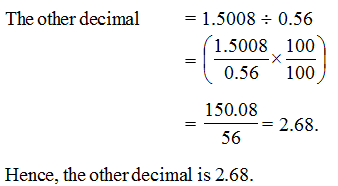

 ReginaTagebücher
ReginaTagebücher
 Param Publication
Param Publication
