Introduction
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Social Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Social Science
ADMINISTRATION IN A VILLAGE
Two rural government officials play an important role in administering the villagers during conflicts: the patwari and the police. The patwari is the land record officer, whose job is to visit agricultural lands and maintain record of ownership and yield. The local police solve the quarrels and are in charge of maintaining law and order in the village.
The Police
Villages are divided into areas and put under different police stations. Each police station is responsible for maintenance of law and order of that area. The people of that particular area can report cases of burglary, quarrels and accidents in the police station. The SHO or the Station House Officer is in charge of the police station. He has many police constables under him. The SHO registers a case by taking a written statement of the complaint. This is called the FIR or the First Information Report. Then as per procedure the police begin an investigation on the matter and takes appropriate legal action.
The Patwari
The chief duties of the patwari include :
1. visiting agricultural lands and preparing land maps
2. maintaining records of land owner, that is, the number of people who own that land.
3. maintaining records of the crop grown at every harvest.
4. collecting land revenue irrigation dues, etc. from the farmers.
The patwari regularly updates his record when there are changes, such as when a fanner rents out his land, buys more land, changes the crop grown or divides his land among family members. The patwari also provides a copy of his records to the villagers on the payment of a small fee when they need it to apply for a loan, land transfer, etc.
Administration of a District
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Social Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Social Science
Administration of a District
For the purpose of administration, district is the most important unit in India. It is in the charge of a Collector or Deputy Commissioner who is the highest officer in a district. He belongs to the cadre of the Indian Administrative Service (I.A.S.) and is appointed by the State Government. He is, generally an experienced person who knows about all aspects of the district administration. In his work, he is assisted by numerous other officers who look after different aspects of administration in the district. The officers include Tehsildars, Naib Tehsildars, Kanungos, Lekhpals or Patwaris, Superintendents of Police, Inspectors, District Judge and Additional Judges, Munsif, Chief Medical Officer, Inspector of Education and several other officers.
Functions of the District Collector or the Eputy Commissioner
As the head of the district administration, a District collector has to perform various functions
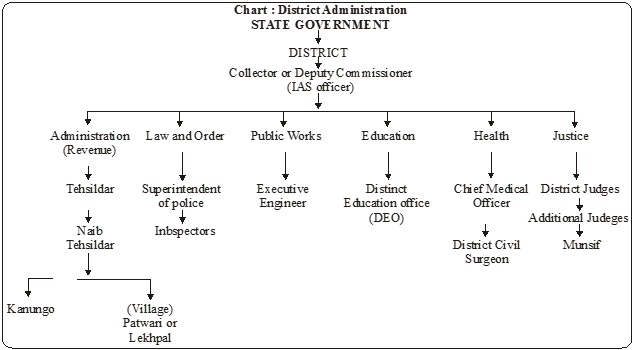
which can broadly be placed under the following heads :
1. Maintenanc of law and order.
2. Maintenance of land records and realisation of land revenue.
3. Civic amenities and public services.
4. General development of the district and coordination of work at different levels.
5. Supervision of the Panchayati Raj.
Judicial Administration
The Judicial Administration at the district level deals with two types of law suits-civil and criminal. The civil courts decide civil cases pertaining to property and money matters while the criminal courts hear criminal cases regarding such crimes as thefts, murders and threat to life or property. The court of the Sessions judge is the highest court of justice in a district
Administration
The most important responsibility of the District Magistrate is to maintain law and order in the district. He can pass orders to check lawlessness and rioting. In this task he is assisted by the Superintendent of Police (SP).
• The Superintendent of Police, selected from the Indian Police Service (IPS) maintains law and order of the district.
• The Deputy Conservator of Forests elected from the Indian Forest Service (IFS) manages the environment, forest and wildlife in the district.
• District Civil Surgeon is the officer in charge of health services in a district. He supervises the working of hospitals and dispensaries of the district.
• District inspector of schools or the District Education Officer inspects schools and supervises the work of the department of education.
• Public Works Department is in charge of construction and maintenance of roads and government buildings. The Executive Engineer is the head of this department.
• District administration also provides relief to the affected people during emergencies like famines, floods, fire, epidemics and earthquakes.
Key Terms
1. Patwari : the village accountant who maintains land records.
2. SHO : the Station House Officer-the in charge at the police station.
3. FIR : First Information Report-a written statement given as a complaint to the police.
4. Tehsildar : the revenue officer of a tehsil.
5. Jamabandi: the patwari's land records for all villages within a tehsil.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
