- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Social Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Social Science
Municipality :
The cities with a population of more than twenty thousand are managed by Municipalities or Municipal Committees. The members of Municipal Committee, who generally number between 15 to 60, are also elected in the same way as the members of a Corporation. These members elect a Chairman and a Deputy Chairman. Their duties are the same as of the Mayor and the Deputy Mayor. The Chairman of a Municipal Committee presides over the meetings and carries out the functions with the help of the executive members in accordance with the policies approved by the elected members.
Differences between a Municipal Corporation and a Municipality :
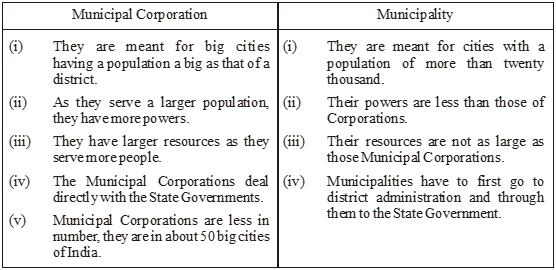
Sources of Income :
To discharge all these functions properly, the local bodies need money which they get from the following sources :
(i) Octroi duty on goods brought into the city or taken out of the city.
(ii) Taxes on property, i.e., houses, shops and lands .
(iii) Taxes on vehicles.
(iv) Income from water and electricity supplied to houses and factories.
Key Terms
1. Municipal Corporation: also called nagar nigam, is a local government body that governs a city which has a population of over 10 lakhs
2. Municipal Committee: also called nagar palika, is a local government body that governs a smaller city with a population between 20,000 and 10 lakhs
3. Wards : small units in which a city is divided for governing purposes
4. Ward Councillor: elected member of municipal corporation or municipality who represents a ward
5. Mayor: head of the municipal corporation
6. Municipal Commissioner: head of the administrative staff of the municipal corporation
7. Sub-Contracting : hiring private contractors to undertake government jobs
8. Tax: money collected from the people in return for the facilities and services given to them by the government
9. Vat: value added tax is the indirect tax on the consumption of the goods

 Param Publication
Param Publication
