The Living Organisms Characteristics and Habitats
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
The Living Organisms Characteristics and Habitats
Introduction: Different regions in the world have various types of living creatures called organisms. Even the openings of volcanoes have tiny living organisms. Even our homes are not devoid of these tiny organisms. List some of the tiny organisms which you have encountered at home!
Environment: Everything that we see surrounding us; living, non-living, physical, chemical etc. is called as environment
Organisms and The Surroundings Where They Live
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Organisms And The Surroundings Where They Live

Biotic Components: These are the living components of the ecosystem. e.g. flora and fauna
Abiotic Components: The non-living components of the ecosystem like soil, water, air etc. are called abiotic components.
We all are surrounded by plants, trees, animals, birds, microbes, and other living and nonliving things based on certain parameters. Scientists were able to differentiate between:
- Living things
- Non-living things
Organisms and the surroundings where they live
The table shows some common organisms and their place to live
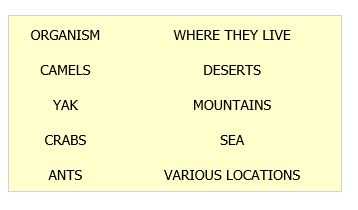
Habitat and adaption
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Habitat And Adaptation

Animals benefit a lot from their habitats. For example, rabbits live in a forest habitat by building a burrow in the soil; they get food from the plant products; they obtain fresh air they breathe. Habitat provides air, food, water and shelter to an animal.
The place where an organism naturally lives and reproduces is called a habitat.
The soil and climate conditions on land are varied in different parts of the earth. Organisms tend to adjust to the conditions and environment they live in. The unique characteristics of plants and animals that enable them to successfully survive in a particular environment are called as adaptation.
Light :
- The sunlight is essential for the survival of the biotic components as the sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living things.
- The sunlight affects growth, flowering, seed germination and in many other ways in plants. Indoor plants put in the shade for a long time grow faster but become delicate and weak.
- Light also affects animals. Animals living in caves and burrows where sunlight cannot reach have very much reduced eyes e.g., Proteus. Amblyopsis do not have eyes.
- Nocturnal animals: Some animals like bats, cockroaches and owls are called nocturnal as they are active during the night.
Temperature :
- Temperature regulates growth, movement, reproduction, morphology and other aspects of life.
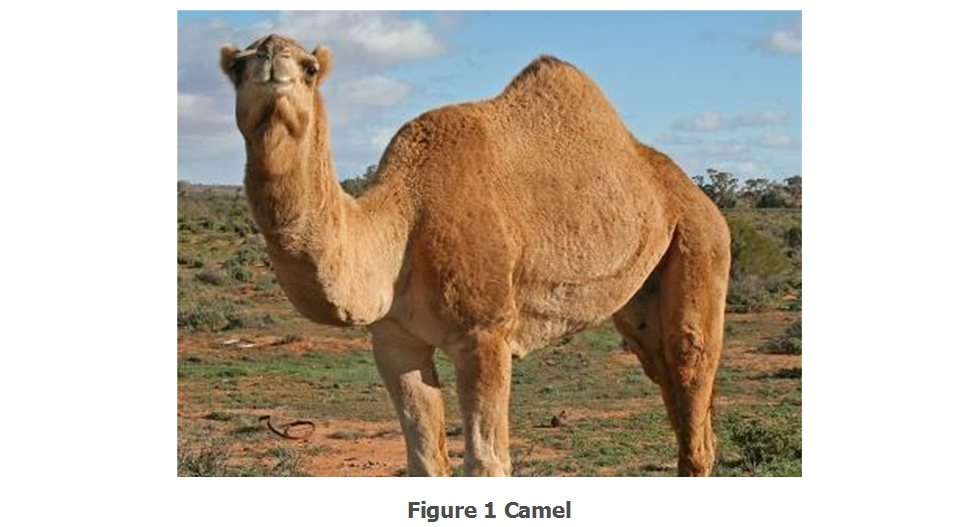
- Animals living in hot areas e.g., snakes, desert rats and lizards are not able to get sufficient water. They have thick skin and do not sweat.
- Desert animals e.g., camels have long legs. Long legs help them to lift their body above the ground. Thus, they can avoid direct contact with the hot ground.
Water :
All living organisms need water for their survival.
Aquatic plants:
Aquatic plants have the following adaptations:
- The root system is poorly developed.
- Air-filled cavities found inside the body make them spongy and buoyant.
- Leaves in submerged plants are thin and narrow; while in floating plants, they are big and flat with a waxy coating.
Desert plants:
Desert plants carry the following adaptations:
- Well-developed root systems.
- Stem is succulent and spongy which helps in storage of water. It is also green and performs photosynthesis.
- Stomata (sunken) are less in number.
- Leaves are either very small or converted into spines.
Habitat and Adaptation
The region or place where an organism lives is termed as its habitat. Habitat provides an organism everything it needs to survive like food, shelter, proper weather conditions such as rainfall, heat etc. to breed and flourish.


Fish
- Their streamline shape helps to move easily in water
- Presence of slippery scales
Gills help in respiration.
- Flat fins and tail help in changing direction in the water
- Tapering ends.
A journey through different habitats
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
A Journey Through Different Habitats

Aquatic habitat
When organisms live in water, this place of living is known as aquatic habitat.
- Ponds, lakes, rivers, oceans, etc., are examples of aquatic habitats.
- Water is a medium in aquatic habitats.

Marine Habitat
- Marine Habitat comprises of oceans and seas, and both have saltwater.
- They are home to a wide variety of creatures like the most part of fish population is found here.
- Marine creatures are found in Estuaries – where rivers and oceans meet and the water is salty.
- Marine Mammals like whales migrate to long distances in order to cope up with the temperature changes.
Oceans
- Most organisms have streamlined bodies and gills
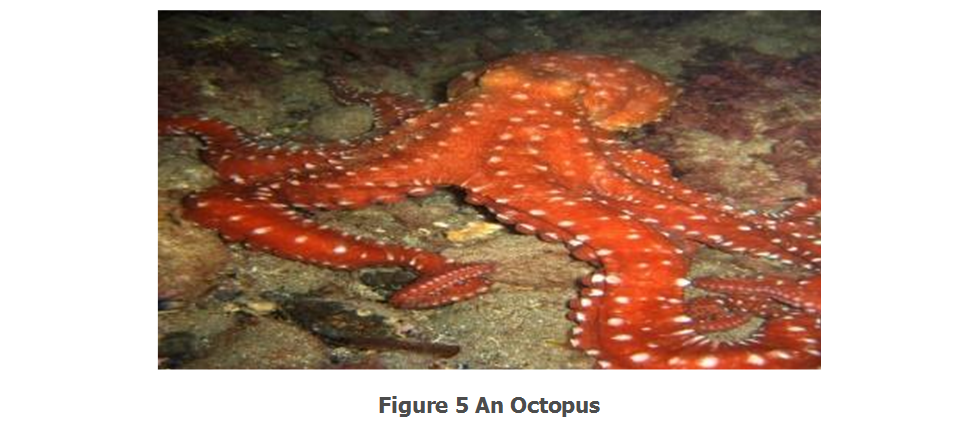
- Octopuses do not have streamlined bodies so they stay deep in ocean, but when moving they make a streamline motion.
- Whales have blowholes instead of gills This enables them to breathe easily when they swim near the surface of water.

Freshwater Habitat:
- Rivers, lakes, ponds etc comprise the freshwater habitats.
- Three percent of world’s water is accounted as freshwater but still a wide variety of species are found here.
- Snails, worms, mollusks etc are found in this habitat
Ponds and Lakes:
- Plants: Water plants can be completely submerged in water (like Hydrilla) or floating on the surface of water(like Water Lily, Lotus, Water Hyacinth). Roots are much reduced in size, since their main function is to hold the plant in place. Stems of aquatic plants are long, hollow and light so that these can bend in along with water movement. e.g Water Lily. The stems grow up to surface of water, while the leaves and flowers float on surface of water.
- Totally submerged plants have narrow and ribbon like leaves (e.g tape grass). These can bend in flowing water.
- Stems have air spaces to enable the plant to float. Floating plants are large and flat. They have waxy upper surfaces that makes them waterproof. They have stomata on the upper surfaces which are exposed to air.
- Frogs are adapted to live both on land and water, they have strong back and legs and webbed feet which allows them to swim in water.
Coastal Habitat:
- Habitats where the land meets the sea.
- Beaches, special type of trees called mangroves are found in this habitat
- Coastal plants like seaweed attach to the rocks firmly so that they are not swayed by the waves,
Acclimatisation: Due to certain changes in the surroundings, organisms adapt through them by making small changes in the body over short periods of time.
For e.g: The changes which take place in the body when we travel from plains to mountains. The adjustment which the body makes is called Acclimatisation
Terrestrial Habitat:
a) Deserts:
The following adaptations of various organisms are enlisted below:
- Snakes and rats dig burrows to escape intense heat as they dont have long legs such as a camel. These animals come out only during the night, when it is cooler
- In desert plants leaves are reduced to spines and lose little water through transpiration
- The stems of desert plants have a waxy coating on them and in most of them photosynthesis is carried out by the stem
- Their roots go deep into the soil so as to absorb water.
- The leaves in desert plants are absent to prevent loss of water due to transpiration.
- Some of the animals are camels, kangaroo rats etc

When organisms live on land, this place of living is known as terrestrial habitat.
- Forests, deserts, orchards, tea gardens and mountains are examples of terrestrial habitat.
- Air is the medium in terrestrial habitats.
Mountain

b) Mountain Regions:
- The trees are cone shaped with slope like branches, also needle-like leaves are present so that rain and snow slide off them easily.
- Animals have thick fur which provides protection from cold. e.g. Snow Leopard
- Presence of strong hooves help the mountain goat to run on the rocky slopes.
- Eg are Pines, mountain goats, yaks, sheep etc. Yaks have long hair to keep them warm.
- The mountain is a special terrestrial habitat where temperature is very low and most of the areas are covered with snow.
- The plants like grasses, mosses and lichens and animals like snow bear, fox, water fowl, musk deer and wolf are found commonly in this habitat
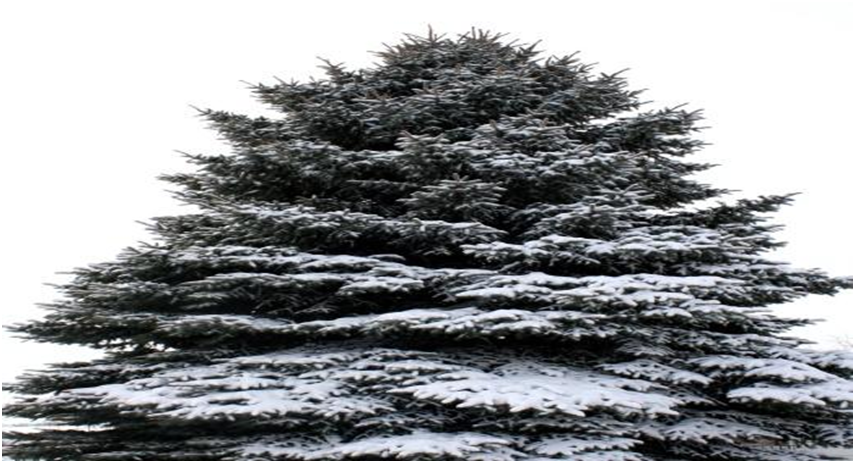

A tree found in mountain region
c) Grasslands:
- The light brown colour of the lion helps it to hide in dry grasslands and the presence of long claws help to capture the prey.
- Deer has strong teeth to eat plant stems also its long ears help to listen to predator movement. They have eyes on its sides of the head which help them to look in all directions to lookout for danger.
- Some of the animals living in these habitats are elephants, giraffes, lions.
d) Rainforest:
- This habitat receives a lot of rain and hence its rich in animal life.
- Mammals, Amphibians, Reptiles all sorts of animals are found here.
- The climate is hot and humid and animals have to learn to adapt to survive.
e) Polar Habitat:
- These habitats are very cold and windy.
- The animals are mostly carnivores and have thick fur to survive in cold.
- Some blend in ice and some may hibernate in the coldest months.
- Examples of animals are polar bears, reindeers, penguins etc.
Characteristics of organisms
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Characteristics of Organisms

Life is a process seen only in living objects in the form of growth, movement, feeding or eating, sensitivity, respiration, excretion and reproduction. All living things on this earth possess certain basic characteristics.
Life Span: Each animal lives for a certain period. This period is referred to as life span.
These include the following:
- Growth
- Movement
- Feeding
- Responsiveness
- Excretion
- Respiration
- Cellular structure
- Reproduction
- Adaptation
Growth:
Growth is defined as the permanent irreversible increase in the size and total weight of the living object.
- Animals grow for a certain period.
- In the case of trees, growth takes place throughout life.
- Growth in plants and animals is influenced by several factors like food, climate, lifestyle, etc.
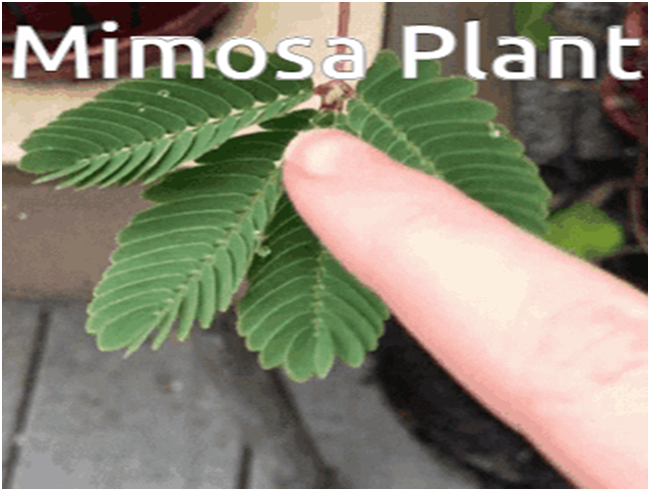
Movement:
Change in the position from one place to another is called movement.
- Locomotion: The movement involving a change of place in animals is called locomotion.
- Animals use wings (bird), fins (fish), limbs (cow, horse, buffalo, man) for locomotion.
- Plants generally show movements of various parts, e.g., flower buds open, roots grow away from light, when we touch the leaves of mimosa (touch me not), they shrivel up.
Cellular Structure :
- Cells constitute plants and animal bodies.
- Cells are organised in various ways in different organisms.
- They help in carrying out various functions like nutrition, respiration, etc.
- They are called the structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
Nutrition:
The process of taking food by organisms is generally referred to as nutrition or nourishment. Food and water are essential for life. Food provides energy that helps in the growth of the body and its repair.
- Autotrophs: They are the living forms which can synthesize their own food by photosynthesis, e.g., green plants.
- Heterotrophs: They are living organisms which cannot manufacture their own food, e.g., all animals.
- Saprophytes: The living organisms which obtain their nutrition from the dead plants and animals are called saprophytes.
- Parasites: The plants and animals that feed on the other living bodies are called parasites.
Respiration :
- Respiration is a process in which oxygen taken by an organism combines with reserved food, undergoes oxidation and releases energy.
- Breathing: Taking in air and releasing it in animals is referred to as breathing.
- We inhale oxygen (O2) and exhale carbon dioxide (CO2).
Excretion :
- The removal of excretory waste from the body of a living being is called excretion.
- The process of removal of wastes in plants is referred to as secretion.
- Latex, resin and gum are wastes for the plant but useful for us.
Response to Stimuli :
- Living beings respond to changes in their surroundings.
- Stimuli: The factors like food, water, light, touch, gravitational force, etc., are stimuli (stimulus) to which plants and animals respond.

Reproduction:
- The process of a living being to produce of its own kind is called reproduction.
- Life produces life.
- Plants reproduce through seeds. Some plants also reproduce through vegetative parts.
Conclusion:
- Adaptation: The change in specific features and habits which enable a plant or an animal to live in a particular habitat is called adaptation.
- Aquatic habitat: When organisms live in water, their place of living is known as aquatic habitat.
- Biotic component: Living things of a habitat form its biotic component.
- Excretion: The removal of nitrogenous waste substances from the body of a living being is called excretion.
- Growth: Increase in size and total weight of the living organism is called growth.
- Habitat: The place where an organism survives, flourishes and reproduces is called its habitat.
- Living things: These are the things which need water, air and nutrients for their survival.
- Reproduction: The process of a living being to produce of its own kind is called reproduction.
- Respiration: Respiration is a process in which air taken by an organism combines with the reserved food, undergoes oxidation and releases energy.
- Stimulus: The factors like food, water, light, touch, gravitational force, etc., are stimuli to which plants and animals respond

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
