Introduction
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
INTRODUCTION
There are many instances when we notice a substance being separated from a mixture of materials. Tea leaves are separated from the liquid with a strainer, while preparing tea. Grain is separated from stalks, while harvesting. Milk or curd is churned to separate the butter.
Before we use a substance, we need to separate harmful or non-useful substances that may be mixed with it. Sometimes, we separate even useful components if we need to use them separately.
The substances to be separated may be particles of different sizes or these may be solids, liquids or even gases.

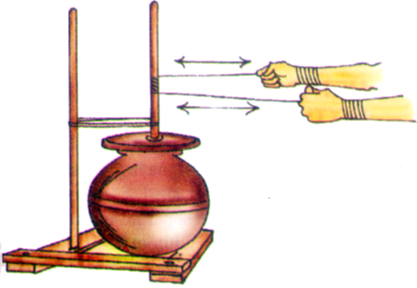
Separating tea leaves with a strainer Butter is taken out by churning milk or curds
Method of Separation Part-1
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
METHODS OF SEPARATION
(i) Hand picking :
The method of handpicking can be used for separating slightly larger sized impurities like the pieces of dirt, stone, and husk from wheat, rice or pulses. The quantity of such impurities is usually not very large. In such situations, we find that handpicking is a convenient method of separating substances.

Handpicking stones from grain
AIM : to separate impurities from grain by hand picking .
Materials required : A packet of grain.
Method : Spread the grain on a sheet of paper. This contains pieces of stones, husks and other grain particle. Now, remove with hand the pieces of stone, husks and other grains from it. This method of handpicking can be used for separating slightly larger sized impurities like the pieces of dirt, stone, and husk from wheat, rice or pulses. The quantity of such impurities is usually not very large. In such situations, we find that handpicking is a convenient method of separating substances.
(ii) Threshing :
The process that is used to separate grain from stalks is threshing. In this process, the stalks are beaten to free the grain seeds. Sometimes, threshing is done with the help of bullocks. Machines are also used to thresh larger quantities of grain.


(iii) Winnowing :
Winnowing is used to separate heavier and lighter components of a mixture by wind or by blowing air. This method is commonly used by farmers to separate lighter husk particles from heavier seeds of grain.
The husk particles are carried away by the wind. The seeds of grain get separated and form a heap near the platform for winnowing. The separated husk is used for many purpose such as fodder for cattle.
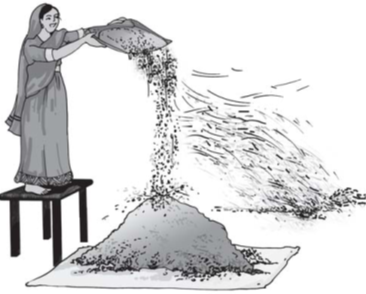
Winnowing
(iv) Sieving :
In a flour mill, impurities like husk and stones are removed from wheat before grinding it. Usually, a bagful of wheat is poured on slanting sieve. Sieving removes pieces of stones, stalk and husk that may still remain with wheat after threshing and winnowing.
Similar big sieves are used at construction sites to separate pebbles and stones from sand.

METHODS OF SEPARATION (PART:- 2)
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Activity–2
AIM : Some common materials that are to be separated and their purpose to separate.
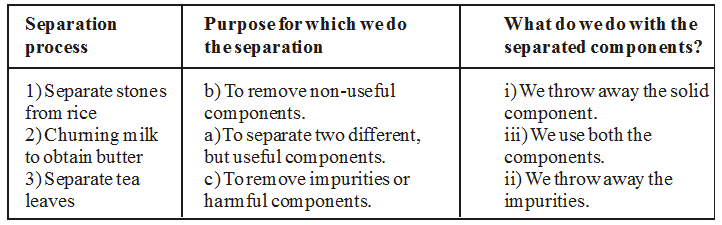
In Column 1 of Table, are given a few processes of separation. The purpose of separation and the way separated components are used is mentioned in Column 2 and 3 respectively. However, the information given in Columns 2 and 3 is jumbled up. So we have to match the separation process with purpose and the separated components.
Now the table in which separation process, purpose of separation and separated components are matched is given below :
(v) Sedimentation, Decantation and Filtration :
Sometimes, it may not be possible to separate components of a mixture by winnowing and handpicking. For example, there may be lighter impurities like dust or soil particles in rice or pulses.
Rice or pulses are usually washed before cooking. When you add water to these, the impurities like dust and soil particles get separated. These impurities go into water, which becomes a little muddy.
When the heavier component in a mixture settles after water is added to it, the process is called sedimentation. When the water (along with the dust) is removed, the process is called decantation.
The same principle is used for separating a mixture of two liquids that do not mix with each other. For example, oil and water from their mixture can be separated by this process. If a mixture of such liquids is allowed to stand for some time, they form two separate layers. The component that forms the top layer can then be separated by decantation.
A mixture of insoluble solid and liquid can be separated by the process of filtration.
If water is muddy, impurities can be separated by a filter that has even smaller pores. A filter paper is one such filter that has very fine pores

Separating two components of a mixture by sedimentation and decantation
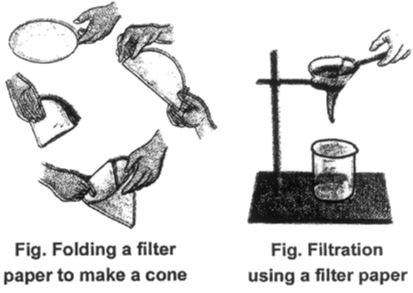
The figure shows the steps involved in using a filter paper. A filter paper folded in the form of a cone is fixed onto a funnel. The mixture is then poured on the filter paper. Solid particles in the mixture do not pass through it and remain on the filter.
Fruit and vegetable juices are usually filtered before drinking to separate the seeds and solid particles of pulp.
Methods of separation
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Activity–3
AIM : To show sedimentation, decantation and filtering process.
Materials required : (i) Water (ii) soil (iii) piece of cloth (iv) filter paper
Method : Mix some soil to water in a glass. Let it stand for half an hour. Observe the water carefully and note the observations. Now, slightly tilt the glass without disturbing the water. Let the water from the top flow into another glass. Now filter the water through a piece of cloth. In a piece of cloth, small holes or pores remain in between the woven threads. These pores in a cloth can be used as a filter. If the water is still muddy, impurities can be separated by a filter that has even smaller pores. A filter paper is one such filter that has very fine pores in it. Solid particles in the mixture do not pass through it and remain on the filter.
(vi) Evaporation :
The process of conversion of water into its vapour below its boiling point is called evaporation. The process of evaporation takes place continuously wherever water is present.
Sea water contains many salts mixed in it. One of these salts is the common salt. When sea water is allowed to stand in shallow pits, water gets heated by sunlight and slowly turns into water vapour, through evaporation. In a few days , the water evaporates completely leaving behind the solid salts. Common salt is then obtained from this mixture of salts by further purification.
Activity–4
AIM : Evaporation of water containing salt.
Materials required : (i) beaker (ii) water (iii) stand (iv) burner
Method : Allow the water to boil as shown. If we continue heating, water disappear completely.

Heating a beaker containing salt water
Now, add two spoons of salt to water in another beaker and stir it well. Heat the beaker containing the salt water. Let the water boil away. In this activity, we used the process of evaporation, to separate a mixture of water and salt. The process of conversion of water into its vapour is called evaporation. The process of evaporation takes place continuously wherever water is present. In this activity water is boiled out as vapours and salt is remained in the beaker.
SEPARATION OF SALT FROM SEA WATER
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
SEPARATION OF SALT FROM SEA WATER
Sea water contains many salts mixed in it. One of these salts is the common salt. When sea water is allowed to stand in shallow pits, water gets heated by sunlight and slowly turns into water vapour, through evaporation. In a few days, the water evaporates completely leaving behind the solid salts. Common salt is then obtained from this mixture of salts by further purification.

Obtaining salt from sea water
USE OF MORE THAN ONE METHOD OF SEPARATION :
Often, one method is not sufficient to separate the different substances present in a mixture. In such a situation, we need to use more than one of these methods.
For example :
It we take a mixture of sand and salt. Handpicking would not be a practical method for separating these. In order to separate them we keep this mixture in a beaker and add some water to it and leave it aside for some time. We will see the sand settling down at the bottom. The sand can be separated by decantation or filtration.
Now, we need to separate salt and water from the decanted liquid. For this we transfer this liquid to a kettle and close its lid. The kettle is heated for some time. We notice steam coming out from the spout of the kettle.
Then we hold a metal plate with some ice on it just above the spout of the kettle. Let all the water in the kettle boil off.
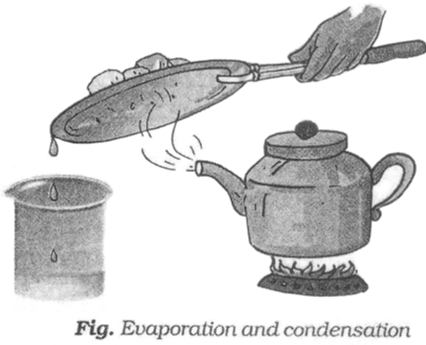
When the steam comes in the contact with the metal plate cooled with ice, it condenses and forms liquid water. The process of conversion of water vapour into its liquid form is called condensation.
After all the water has evaporated, salt is left behind in the kettle.
We have thus, separated salt, sand and water using processes of decantation, filtration, evaporation and condensation.
CAN WATER DISSOLVE ANY AMOUNT OF A SUBSTANCE
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
CAN WATER DISSOLVE ANY AMOUNT OF A SUBSTANCE
Many substances dissolve in water and form a solution.The solution made in water are called aqueous solutions.
Activity : Pour half a cup of water in the beaker. Add one teaspoonful of salt and stir it well, until the salt dissolve completely. Again add a teaspoonful of salt and stir well. Go on adding salt, one teaspoonful at a time and stir.
After adding a few spoons of salt, we find that some salt remains undissolved and settles at the bottom of the beaker. This means that no more salt can be dissolved in the amount of water we have taken. The solution is now said to be saturated.
Now, add a small quantity of salt to this saturated solution and heat it.
We find that now salt dissolves in it. Such solution which contains more amount of substances dissolved in it than required to form a saturated solution is called super saturated solution. Let this hot solution cool. We notice that salt appear to settle at the bottom of the beaker again.
A solution that contains less amount of solute than required to form a saturated solution is called an unsaturated solution.
KEY WORDS
1. Churning (or centrifugation) : It is the process of separation of the lighter particles of a suspended solid from a liquid. For example, to obtain butter from the curd or milk.
2. Condensation : The process of conversion of water vapour into its liquid form is called condensation.
3. Crystallisation : The process of crystallisation is used for obtaining pure crystalline substance from impure sample.
4. Decantation : It is the transfer of clean liquid from one vessel to the other without disturbing the settled (sedimented) particles.
5. Evaporation : It is the process of removing water (or moisture) from a mixture either by heating on flame or direct sunlight. For eample, salt from sea water is obtained by this method.
6. Filtration : Filtration is used to separate solid particles from liquid by passing the mixture through a filter paper.
7. Handpicking : This method is used for separating small particles of dirt, stone, husk, etc., from the grains of wheat, rice, pulses, etc.
8. Loading : It is the process of faster sedimentation by suspending alum to a liquid.
9. Sedimentation : It is the process of settling of heavy solid particles in a mixture at the bottom of the vessel.
10. Sieving
(i) Sieving is used when two components of a mixture have different particle sizes.
(ii) Sieving allows the fine particles to pass through the holes of she sieve, while the bigger particles remain on the sieve. For example, sieving of wheat flour, sieving of sand at construction sites.
11. Saturated solution : A solution in which no more soluble substance can be dissolved at room temperature is called saturated solution.
12. Solution : When a soluble substance is dissolved completely in a liquid (say sugar in water), a homogeneous mixture is formed. It is known as a solution.
13. Threshing : The process that is used to separate grain from stalks is threshing.
14. Winnowing : Winnowing can be used to separate lighter and heavier components of mixture. For example, to separate husk from grain with the help of air.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
