- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Stem
• The stem is the aerial part on which buds, leaves, flowers and fruits are borne.
• It grows from the plumule of the embryo of a seed.
• It forms the main axis that connects the root system with the rest of the plant body.
• It grows away from the soil and towards sunlight.
• The stem may be branched or unbranched.
• The young stem is usually green and soft though it is hard and woody in some plants.
• Stem conduct water.
• Minerals dissolved in water also move up in the stem along with the water.
• The water and minerals go to leaves and other plant part attached to the stem through narrow tube inside the stem.
• The stem conducts water from roots to the leaves (and other parts) and food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
• The leaves grow on the stem at definite points called nodes.
• There may be one or more leaves at a node.
• The part of the stem between two successive nodes is the internode.
• The angle formed between the base of a leaf and the stem is termed as leaf axil.
Primary Function of Stem :
1. Support : It supports branches, leaves, flowers, fruits and buds.
2. Transportation : It helps in the transportation of water and minerals salts absorbed by the roots of the plant and helps in supply of food from the leaves to various parts of the plant.
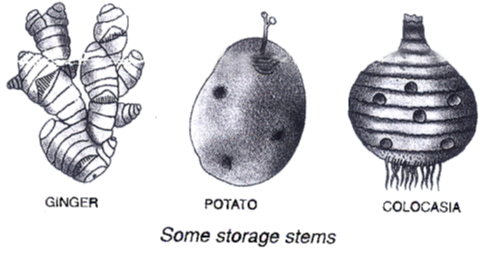
3. Food storage : The stem also functions as the storehouse of food material as in case of potato, garlic, ginger.
4. Climbing : In weak plants like the gourd, bitter gourd the stem gets modified to form tendrils which help the climbers in climbing.
5. Photosynthesis : The green stem can make food for the plant as in the case of cactus.
6. Perennation : Certain underground stems like potato, garlic and ginger help the plant to tide over unfavourable climatic conditions this is called perennation.
Secondary Function of Stem :
(i) Support : In plant such as bean, sweet potato and morning glory the stem spirals around a support as it is weak and slender. Climbers are also known as twinners.
(ii) Making food : In plants such as cacti which grow in dry climates, leaves are reduced to spines or scales to prevent loss of water. Such plants have a flattened or cylindrical green stem to manufacture food. It also stores food and water for the plant.
(iii) Storage of Food : In some plants the entire stem remains underground and only leaves and flowering shoots are seen above the ground. It is thickened to store excess food which helps plants to survive through long bad seasons. Examples are ginger, potato and onion. Potato, onion and ginger not considered as root. These have node and internodes and scaly leaves.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
 Param Publication
Param Publication
