- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
METHODS OF SEPARATION
(i) Hand picking :
The method of handpicking can be used for separating slightly larger sized impurities like the pieces of dirt, stone, and husk from wheat, rice or pulses. The quantity of such impurities is usually not very large. In such situations, we find that handpicking is a convenient method of separating substances.

Handpicking stones from grain
AIM : to separate impurities from grain by hand picking .
Materials required : A packet of grain.
Method : Spread the grain on a sheet of paper. This contains pieces of stones, husks and other grain particle. Now, remove with hand the pieces of stone, husks and other grains from it. This method of handpicking can be used for separating slightly larger sized impurities like the pieces of dirt, stone, and husk from wheat, rice or pulses. The quantity of such impurities is usually not very large. In such situations, we find that handpicking is a convenient method of separating substances.
(ii) Threshing :
The process that is used to separate grain from stalks is threshing. In this process, the stalks are beaten to free the grain seeds. Sometimes, threshing is done with the help of bullocks. Machines are also used to thresh larger quantities of grain.


(iii) Winnowing :
Winnowing is used to separate heavier and lighter components of a mixture by wind or by blowing air. This method is commonly used by farmers to separate lighter husk particles from heavier seeds of grain.
The husk particles are carried away by the wind. The seeds of grain get separated and form a heap near the platform for winnowing. The separated husk is used for many purpose such as fodder for cattle.
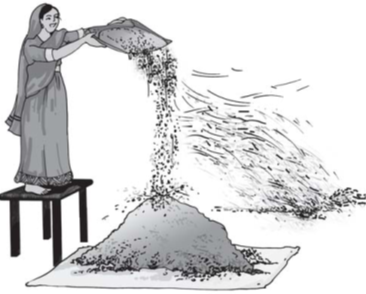
Winnowing
(iv) Sieving :
In a flour mill, impurities like husk and stones are removed from wheat before grinding it. Usually, a bagful of wheat is poured on slanting sieve. Sieving removes pieces of stones, stalk and husk that may still remain with wheat after threshing and winnowing.
Similar big sieves are used at construction sites to separate pebbles and stones from sand.


 Param Publication
Param Publication
