- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Joints
Joints: The point where two bones meet. Allow movement to take place. Bones are held together by ligaments.
(a) Movable Joints: It allows movement between bones and have cartilage
between them. Type of movable joints are:
(i) Hinge Joints: It allow movement only in one plane backwards and
forwards. Example: elbow joints, knee joints and joint between
phalanges of fingers and toes.
(ii) Ball and Socket Joints: It permit a circular movement. Example: the
shoulder.
(iii) Gliding Joints: It allow bones to slide a little. Example: bones inside
wrists and feet.
(iv) Pivotal Joints: Joint where the neck joins the head. It allows head to
move backward and forward and turn to right and left.
(b) Immovable or Fixed Joints: The bones cannot move at these joints. Example:
bones in skull, joint between upper jaw and rest of skull.
Types of Joints and their Location in Human Body
- A Pivot joint is a joint that rotates. Examples of pivot joints in the body in the neck that allows the head to rotate and the ones between the radius and ulna that allow forearm rotation.
- When bones can move along one axis, it indicates the presence of Hinge joint. e.g. Elbows and Knees.
- In the Ball and Socket joint, a partial spherical structure is present inside a socket allowing movement in all directions. e.g. hips and arms
- As the name suggests Fixed joint allows no movement to occur. e.g Skull
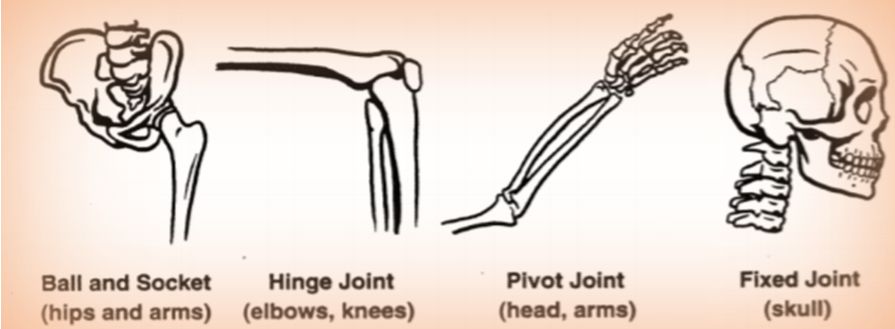
Figure 2: Types of Joints
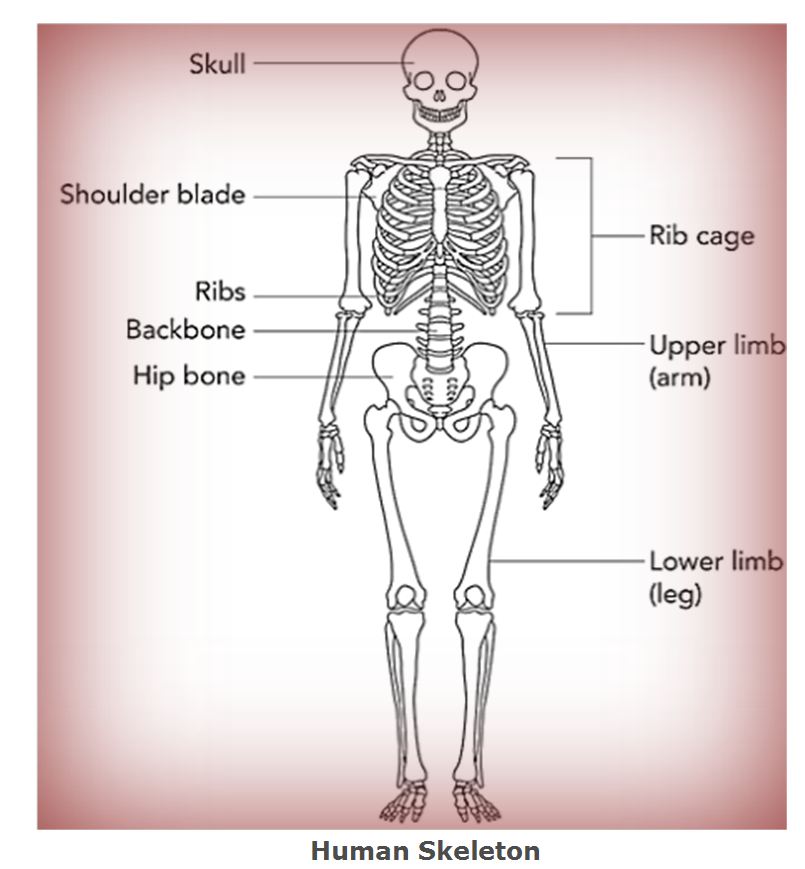
Skeletal System
- Bones in our body form the framework that supports the whole body. This framework is called the skeleton.
- Our skeleton is made up of a number of bones and cartilages.
- There are about 650 muscles attached to the various bones in our body.
- The bones are hard and rigid.
- Cartilages are comparatively soft and elastic.
Functions of skeleton
- Skeleton system gives support to the body.
- It protects the inner organs.
- Together with muscles, it gives the body its shape.
- Red blood cells and some white blood cells are produced in the marrow of the bone.
Important Points to remember in a Human Skeleton:
- Bones provide support, protection, movement and perform several other functions.
- The bones in the skull (Cranium, Mandible, Maxilla) give protection to the brain.
- The long bones such as humerus, radius, ulna, tibia, fibula support the weight of body
- The carpals are located in wrist and tarsals are located in ankles. They are examples of short bones.
- The bones protecting the spine are called as the vertebral column. Cervical area (top 7 vertebrae), Thoracic (next 12), Lumbar (bottom 5 vertebrae), Sacrum (5 fused or stuck together bones) and Coccyx (the tiny bit at the bottom of the spine).
- The sternum and rib cage constitute the chest bones.
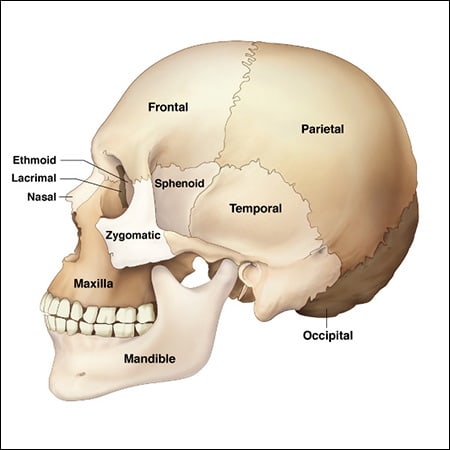
The skull: The skull has two main parts:
- Cranium: The bones of cranium are flat. They are held firmly like a zipper. It covers and protects the brain.
- Facial bones: The facial bones comprise the upper jaw, lower jaw and few other bones. The lower jaw is movable. The movement of lower jaw enables us to eat, talk and sing.
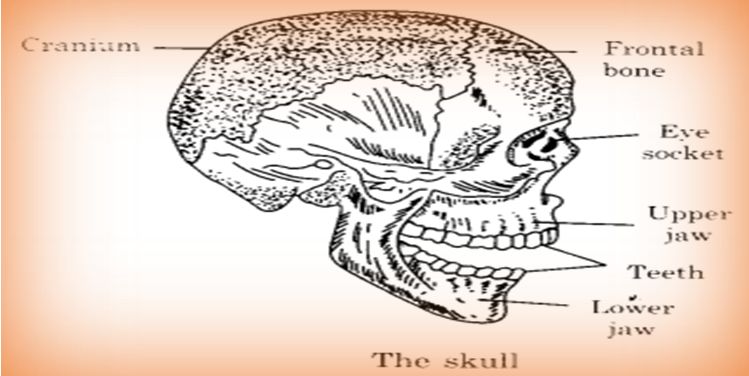
Eye sockets: The skull also includes a pair of eye sockets. These form a safe pocket for eyes.
Some More Points to Remember


 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
