- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Our body is capable of performing a wide variety of simple and complex functions. It is able to do so because of the internal structure that facilitates its movement.
Locomotion: Movement of organisms from place to place.
Human Body and Its Movements
Locomotion
There are two kinds of movements:
- The organisms move their body parts without changing their position.
- Animals move from one place to another. This kind of movement is called locomotion.
The human skeleton is the internal framework which is responsible for giving support, shape and protection to our bodies. It contains 206 bones, each playing a distinct yet important task. The skeleton can be classified into two parts called as the axial and the appendicular. The axial skeleton comprises of the central part of the skull, spine, and ribs and the appendicular skeleton consists of the arms and legs.
Locomotion in human body:
(i) Human skeleton: It forms a framework that gives shape and support to the body.
It consists of 206 bones. It protects internal organs.
(a) Skull: It protect the brain. It is rigid box made up of plates of bone firmly
joined together.
(b) Rib cage: It is flexible case of ribs. Each rib curves round the side of the chest
from the backbone and is joined in front to a plate of bone called sternum. Ribs are connected to one another by the muscles. Two lower most pairs of ribs are called ‘floating ribs’.
(c) Backbone: It is also called the spine or vertebral column. It is a chain of small bones called vertebrae. It protects the spinal cord, which carries messages between the brain and body. It also supports the skull, ribs and limbs.
(d) Limbs: It is made up of long bones with joints that allows them to move. They are mainly for support.
Bones of hands and legs: Bones of arms, thighs, etc., are long. They give strength to our body. Bones of fingers and toes are short. They help us in holding things. The hands and legs are constructed in same pattern as described below
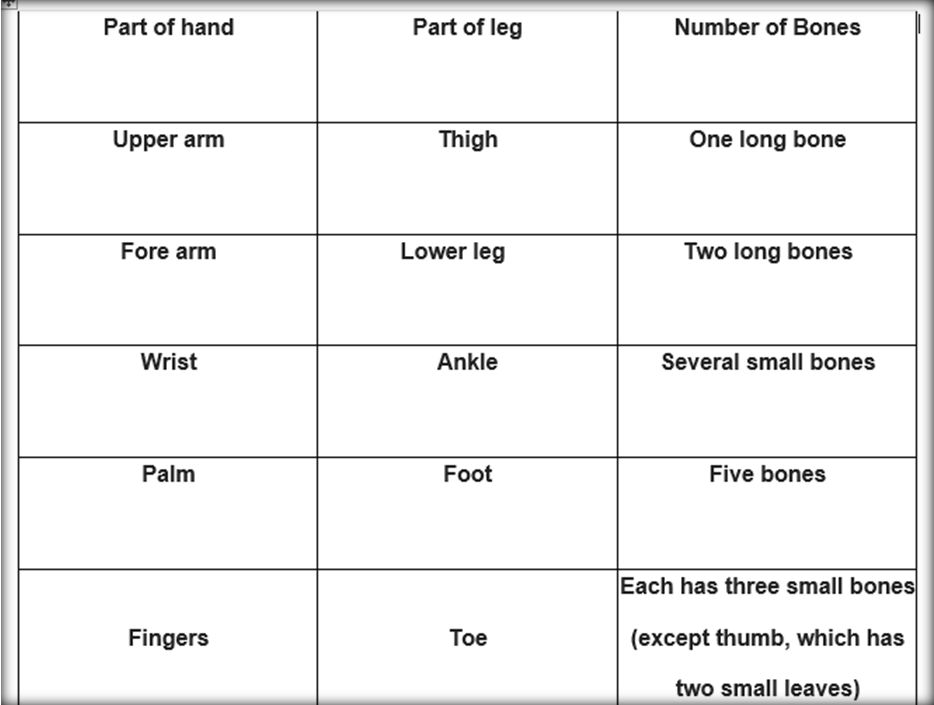
(i) Arms: Fore-arms is made up of two bones and hands have several small
bones. Shoulder bones have a pair of collar bones in front and a pair of
shoulder blades.
(ii) Legs: Lower leg is made up of two bones and feet have several small
bones. Hip bones or gridles bear weight of body and are attached to
thigh bones.
· Locomotion in other animals:
(i) Fish: Locomotion achieved by lateral contractions of the muscular body with a
final thrust by the tail. Fish swim by forming loops alternately on two sides of the body.
(ii) Birds: When the large flight muscles contract, they pull the wings down.
(iii) Snails: The muscular foot helps in locomotion.
(iv) Earthworms: Move by stretching out body in front and keeping the hind end fixed to the ground.
· The bones are moved by alternate contractions and relaxations of two sets of muscles.
· The bone joints are of various kinds depending on the nature of joints and direction of movement they allow.
· Strong muscles and light bones work together to help the birds fly. They fly by flapping their wings.
· Snakes slither on the ground by looping sideways. A large number of bones and associated muscles push the body forward.
· The body and legs of cockroaches have hard coverings forming an outer skeleton. The muscles of the breast connected with three pairs of legs and two pairs of wings help the cockroach to walk and fly.
Terms -
Limbs: The arms or legs of an animal.
Bones: These are the hard white structures below our skin that protect our internal organs. Bones are incapable of bending.
Joints: These are defined as the points at which two bones are fitted together. These are the points at which we can rotate and bend our bodies.


 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
