- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Attraction and repulsion between Magnets
Attraction And Repulsion
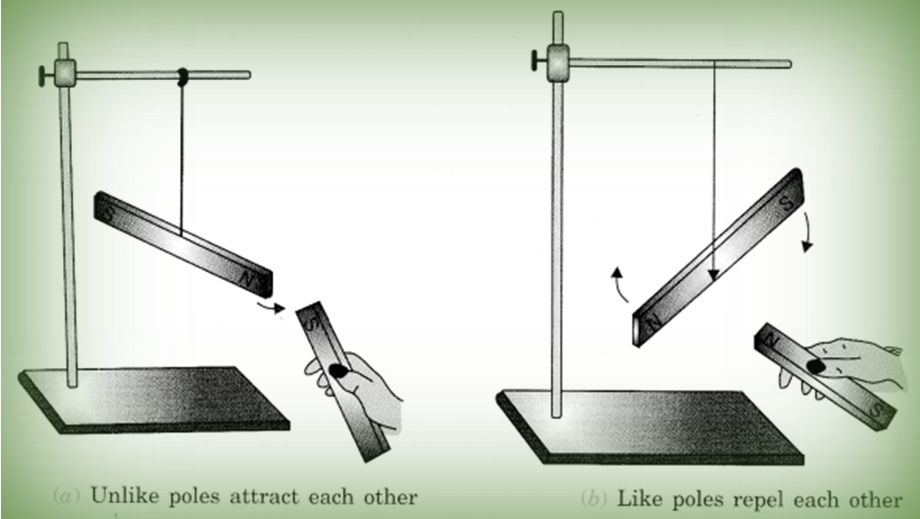
When two magnets are brought close to each other, they are either pulled towards each other, or pushed away from each other. When the magnets are pulled towards each other, they are said to attract each other. When they are pushed away from each other, they are said to repel each other. Whether the magnets attract or repel depends on which poles of the magnets are facing each other.

Attraction and Repulsion among Magnets
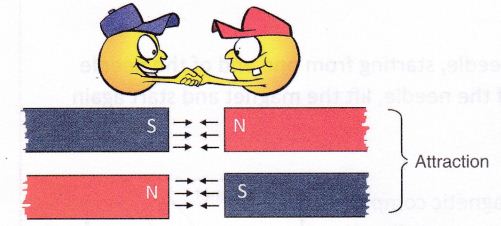
- Opposite or unlike poles i.e. North and the South Pole attract each and vice versa.
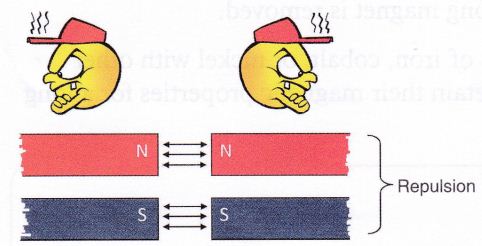
- Similar or like poles like north and north poles of two magnets repel each other. Same is the case with South poles of two magnets.
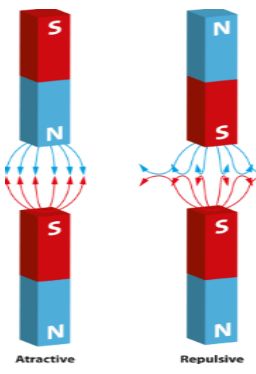
Attraction between opposite poles and repulsion between similar poles
When like poles of the magnets (N-N or S-S) are brought close to each other, they repel. This is called repulsion.
When unlike poles of the magnets (N-S or S-N) are brought close to each other, they attract. This is called attraction.
Notes of caution
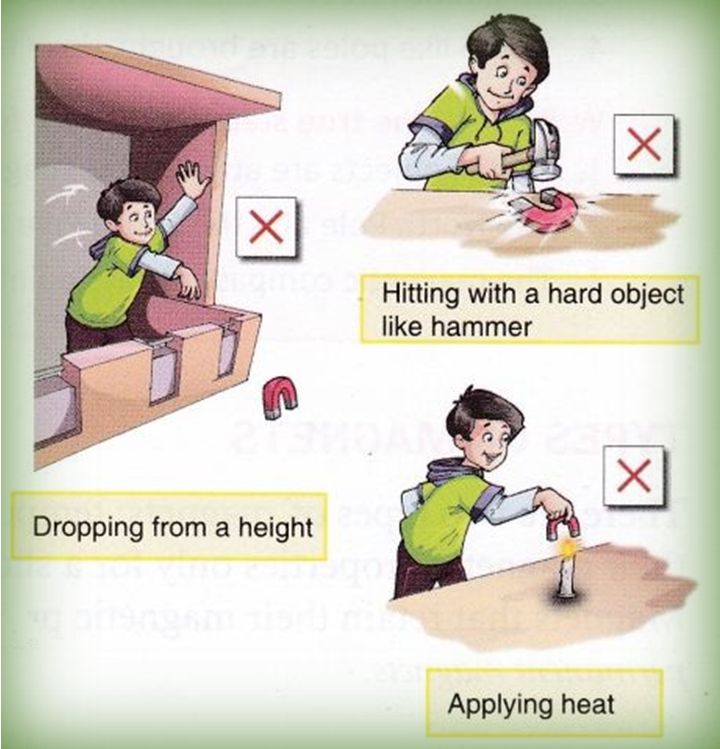
- When heated, hammered or dropped from a height, magnets tend to lose their properties.
- They become weak if they are not stored properly and hence:
- Bar magnets should be stored in pairs separated by a small block of wood and their unlike poles facing the same side with a soft iron across their ends.
- A piece of iron should be kept across the poles in case of a horseshoe magnet.
- should be kept away from computers, mobiles, televisions etc.
- Magnets should be handled with care and they should be stored properly.
Care Of Magnets
A magnet can lose its properties due to the following activities.
- Dropping from a height
- Hitting with a hammer
- Applying heat
- Improper storage can also cause loss of magnetic properties.
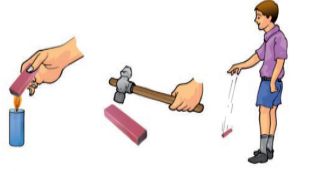
Bar magnets should be stored in pairs, with Dropping from a height unlike poles alongside each other. A horseshoe magnet should be stored with a piece of soft iron kept across its poles.
SUMMARY
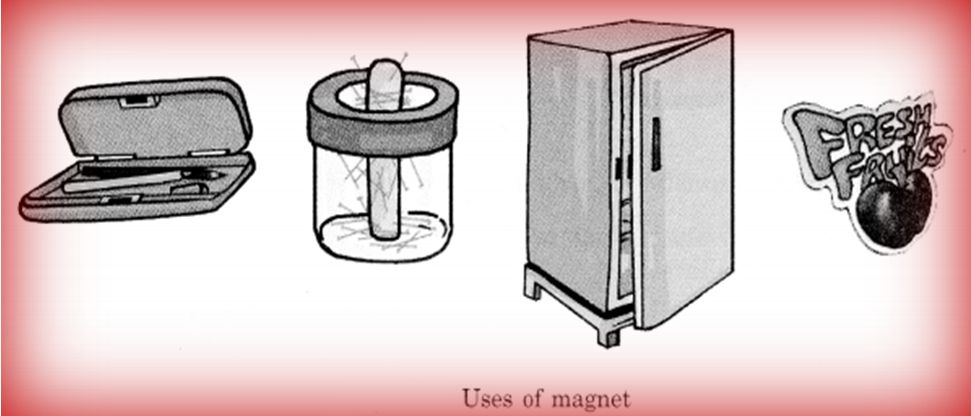
Uses of a Magnet: A magnet finds its use at a number of places. For example, refrigerator’s door, some pencil boxes, many toys, magnetic stickers, soap stand, pin stand, all make use of a magnet for their functioning.
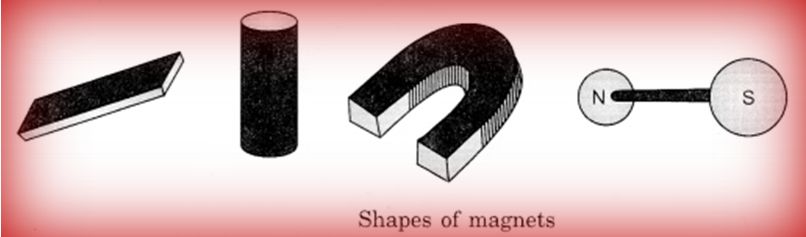
Shapes of Magnets: Magnets are made of different materials and in different shapes.
Effect of a magnet on materials: A magnet attracts certain materials, whereas some do not get attracted towards magnet.
Magnetic materials: The materials which get attracted towards the magnet are known as magnetic materials, e.g., iron, nickel, cobalt.
Non-magnetic materials: The materials which are not attracted towards the magnet are known as non-magnetic materials, e.g., leather, plastic, cloth, paper. Magnetic poles: Magnetic attraction is maximum near the ends of the magnet. These ends are called magnetic poles.
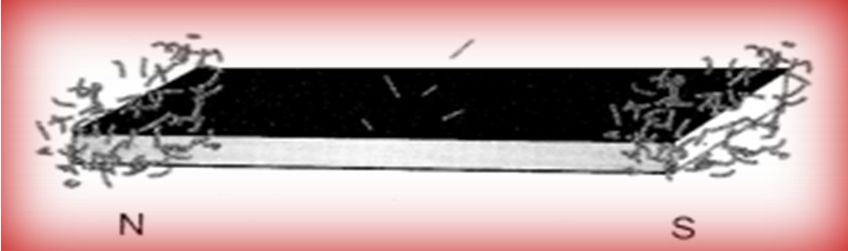
When suspended freely, magnet always aligns in north-south (N-S) direction.
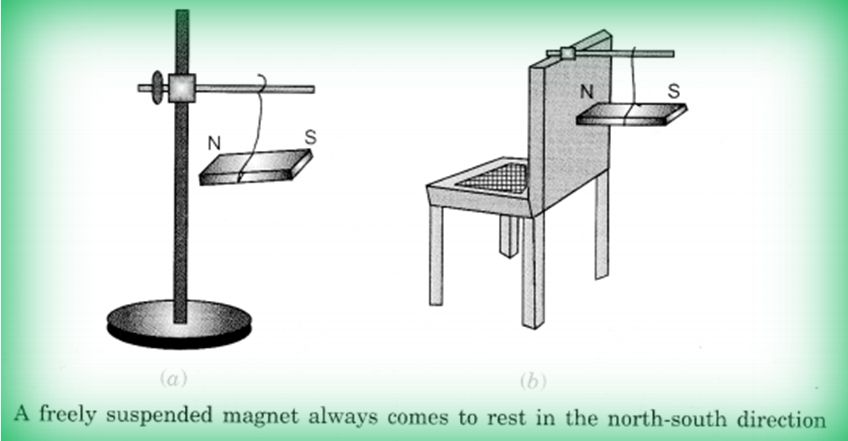
Lode stone: It was a stone used by sailors in olden days to identify directions when they were in sea.
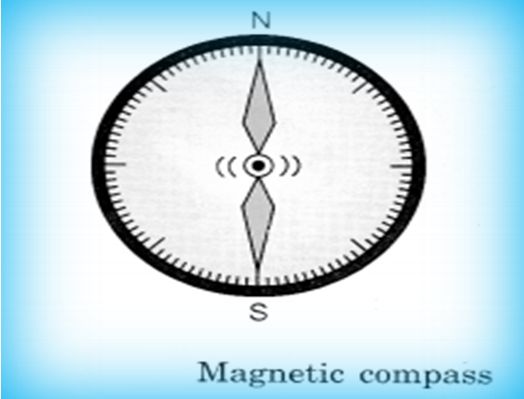
Compass: This is a small glass case containing a magnetised needle pivoted on a nail. The needle can rotate freely. Wherever it is kept, its needle always rests in north-south direction. Normally the north-pole of the needle is painted red or some other indication is given to identify north and south-poles. So using this needle, north and south can be identified.
Attraction between two poles: Opposite poles of two magnets attract each other. It is called attraction.
Repulsion between two poles: Similar poles of two magnets repel each other. It is called repulsion.
Magnetic effect can pass through screen: Magnetic influence can pass through screens of some substances like cloth, plastic, paper, glass, etc.
Magnets lose their properties if they are heated, hammered or dropped strongly and hardly.


To keep them safe, bar magnets should be kept in pairs with their unlike poles on the same side. They must be separated by a piece of wood while two pieces of soft iron should be placed across their ends. For horse-shoe magnet, we should keep a piece of iron across the poles.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
