1. Integers
- Books Name
- Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Chapter - 6
Integers
Introduction to integers
Introduction
The numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 are Natural numbers and so on. When zero is added in to the collection of natural numbers, we get the new numbers called as whole numbers, that is, 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and so on.
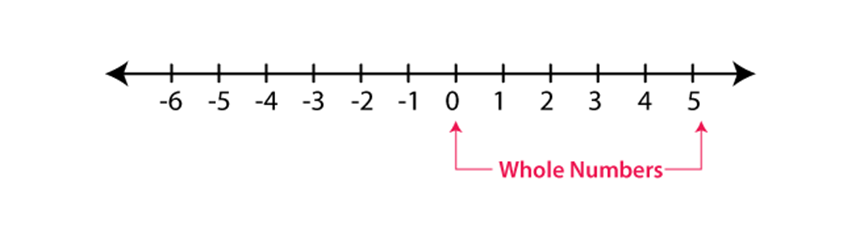
There are negative numbers also that exist. When the whole numbers and the negative numbers are arranged together, the resultant of numbers will look as shown ….-4,-3,-2,-1, 0, 1,2,3,4 and so on. This resultant numbers are called as an Integer.
Numbers that are more than zero - 1, 2, 3... Are called positive integers and numbers that are below zero – 1, – 2, – 3 ... are called negative integers.

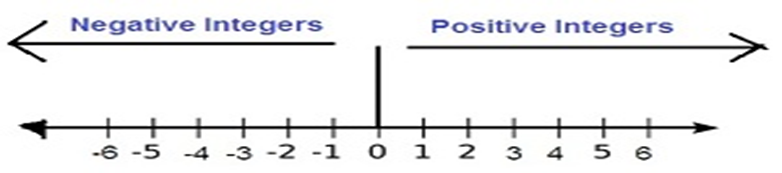
Representing integers on a number line
The integers are represented on the number line as follows:
The numbers that are the left of number zero are negative integers while numbers to the right of number zero are positive integers.

Comparing integers
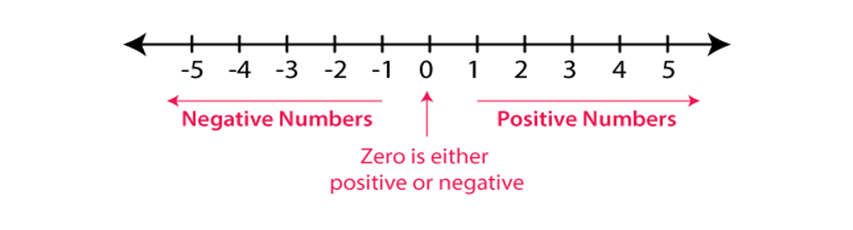
If we are at the zero mark on the number line, then either we can go negative integers left towards or positive integers right towards.
When moving left towards zero on the number line, the value of positive integer’s decreases and negative are increasing. When we move right direction from zero on the number line, the value of negative integers decreases.
Two integers that are middle from zero and on opposite sides of zero are called opposite numbers. The total of an integer and its opposite is zero altogether.
9 > 5 (since 9 is to the right of 5)
4 > 0 (since 4 is to the right of 0)
-7 < -2 (since -7 is to the left of -2)
-6 < 7 (since -6 is to the left of 7)
|
1. A positive number is greater than always than the negative number. |
|
2. When two positive integers are compared, then the integer with more number of digits is always greater than the integer with less number of digits. (ii) If two positive integers have the exactly same number of digits, then compare the left-most digit of two numbers till reaches across unequal digits.
|
|
3. When compared with two negative integers, the greatest number with a negative sign is the smaller of two negative integers. |
|
4. Negative numbers are less than zero always. |
|
5. Positive numbers are greater than zero always. |
Ordering integers
Order of integers: When we go to the right the integer’s value will increase. Therefore number 5 is greater than integer 3, integer 3 is greater than 2 and number 0 is greater than -2, -2 is greater than integer 2 and so on.
We can say that the number, – 4 < – 3, – 3 < – 1, – 2 < 0, 0 < 2, 2 < 3, 3 < 4 so on.
The number line tells us that which integers are lie between two integers and which integer is the greater integer. The number line shows how much steps should be taken to move forward or backward in order to go from one integer to another.
Addition of integers
Addition of Integers
Adding integers without using number line
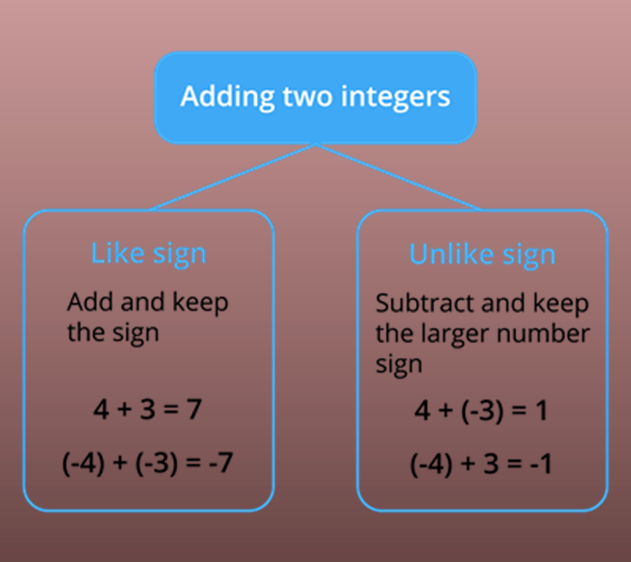
When the integers to be added with the same sign, add the numbers and assign the same sign to the sum
Sum of positive integers is a positive integer
Sum of negative integers is a negative integer
Additive Inverse
When two integers are added to each other, and their sum is zero, it means these two integers are called additive inverse of each other.
For example, -2 is the additive inverse of 2
Addition of integers on a number line,
Addition of Integers
The sums of any two positive numbers are also known as the addition of two positive integers. For e.g. 4+3= 7.
The sum of any two negative integers exactly same as positive integer addition except that the difference that answer will come with a negative sign. For e.g. (–4) + (–3) = (4+3) = –7
Whenever we have two integers, one positive and one negative integer, the integer must get subtracted, and the answer will use the sign of the integer whichever is bigger than second integer.
|
Ignore the signs of the numbers when you want to choose a bigger integer. |
For e.g.
(3) + (-1) = 3-1 = 1. 3> 1. Hence the answer is positive.
(2) + (-4) = 2-4 = -2. 4>2. Hence the answer is negative.
Numbers such as 1 and – 1, 5 and – 5, when added always give their sum as zero. They are known as the additive inverse of each other.
We can perform Operations of addition and subtraction by using a number line.
We move forward to the right, whenever we want to add a positive number we move backward to the left, whenever we want to add a negative number
Whenever we want to subtract a positive number, we move backward to the left.
We move forward to the right, whenever a negative number is subtracted,
Addition of Integers on a Number Line
Addition of Two Positive Integers
Example
Add integer 3 and integer 4 on the number line.
Solution
To add numbers 3 and 4, first, we move 3 steps forward to the right of zero then again move 4 steps forward to the right from point 3.
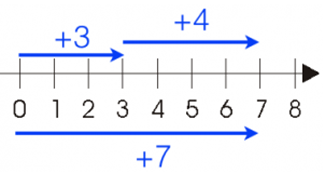
We then reached to the point 7, therefore numbers (+3) + (+4) = number +7
This tells that the sum of any two positive integers is always get positive number
Addition of Two Negative Integers
Example
Add numbers (-2) and (-5) using a number line.
Solution
To add numbers (-2) and (-5), first move 2 steps backward to the left of zero then again move 5 steps backward to the left of (-2).
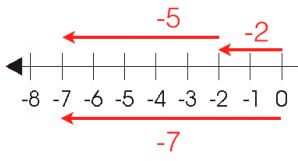
Then we will be reached to the point (-7), therefore integer (-2) + (-5) = -number 7.
This tells us that the sum of any two negative integers is always get the negative number
Addition of One Negative and One Positive Integer
A. when a positive number is greater than the negative number
To add number (+6) and number (-2),
first move forward 6 steps to the right from zero
Then move 2 steps backward to the left of point 6.
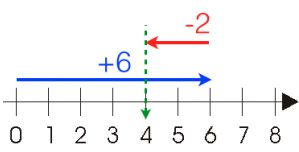
Then we get the point 4, hence number (+6) + (-2) = number +4
b. When a negative integer is greater than the positive integer
2. To add Number (-5) and number (+4),
first move 5 steps backward to the left of zero
Then move 4 steps forward to the right from point (-5).
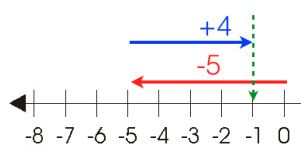
Then we get the point -1, hence number (-5) + (+4) = number (-1)
C. Additive Inverse
If we add numbers like (-2) and 2 then we get the result as zero. So these are called the Additive inverse of each other.
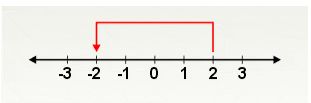
First move backward 2 steps to the left of zero
Then move forward two steps to the right of (-2).
Then finally reached to zero.
Therefore, when positive number and negative number of the same integer are added then the answer will be the zero.
Subtraction of integers,
Subtraction of Two Positive Integers
Example
Subtract number 2 from number 5.
Solution
To subtract number 2 from number 5,
first, move 5 steps forward to the right from zero then
Move 2 steps backward to the left
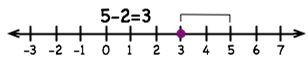
Then we are at the point 3, so the number 5 – (+2) = 5 – 2 = 3
Subtracting an integer from another is somewhat similar as performing addition of integer’s additive inverse.
Additive inverse for an integer X, is –X.
Example: Subtract number 4 from -3
4 – (-3) = 4 + 3 = 7 (the additive inverse of number -3 is 3.)
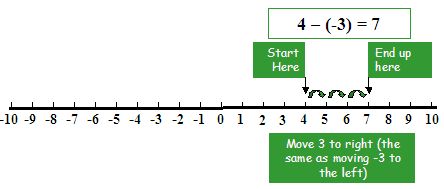
|
The sum of all positive and negative numbers always keeps the sign of a larger number |
Subtraction of integers on a number line
|
Subtraction of a number means to add its opposite numbers. |
Subtracting integers on number line
Positive integer is Subtracting from a positive integer, e.g. 9 – 3 then 9 – 3 = 6
Negative integer is Subtracting from a positive integer, e.g. 8 – (-6) then 8 – (-6) = 14
A positive integer is Subtracting from a negative integer, e.g. -7 – 6 then (-7) – 6 = -13
Subtracting a negative integer from a negative integer, say e.g. -5 – (-7)-5 – (-7) = 2
Subtraction of One Negative number and One Positive number
To subtract a positive integer from any other integer.
Example
Subtract number 3 from number (-4)
Solution
To subtract number (-4) from number (3),
first, we have to move backward 4 steps to the left of zero
Then move 3 steps forward more to the left.
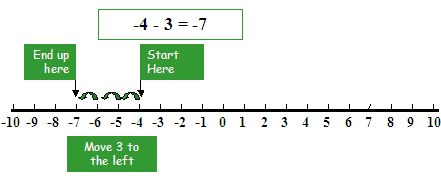
Then reached to point (-7), therefore point (-4) – (+3) = point (-4) + (-3) = number -7.
To subtract a negative number from any other number
Example Subtract number (-3) from number (4)
Solution
To subtract number (-3) from number (4), first move 4 steps forward to the right of zero then move 3 steps forward more to the right.
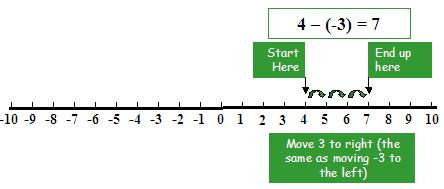
When we get point (7),
Number (4) – (-3) = number (4) + (+3) = number +7
Subtraction of One Negative number and One Positive number
To subtract a positive number from any other number.
Example
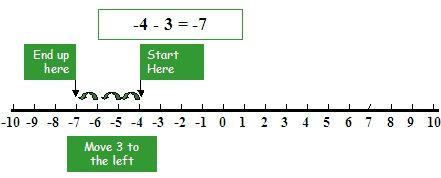
Subtract number 3 from number (-4)
Solution
To subtract number (-4) from number (3),
first, move 4 steps backward to the left of zero
Then move 3 steps backward more to the left.
As we get point (-7),
Therefore number (-4) – (+3) = number (-4) + (-3) = number -7.
Subtracting integers on number line
1. from a positive integer Subtracting a positive integer then 5 – 2
5– 2 = 3
2. From a positive integer, Subtracting a negative integer e.g. 6 – (-5)
6– (-5) = 11
3. From a negative integer, subtracting a positive integer then -5 – 9
(-5) – 9 = -14
4. From a negative integer, Subtracting a negative integer then -6 – (-8)
-6 – (-8) = 2
5. We move to the backward in left, whenever we want to subtract a positive integer,
6. Whenever a negative integer is subtracted, we move forward to the right the reason behind is that we are having a bigger integer. E.g. 6- (-4) = 6+4 = 10.
7. Add the additive inverse of the integer that is being subtracted, whenever we want to subtract a number from another number to the other number.
E.g. In the case of 7 - (-3), the additive inverse of -3 can be used. The additive inverse of -3 is 3.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 ReginaTagebücher
ReginaTagebücher
