- Books Name
- Psychology Book Class-12
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Psychology
Assessment of Intelligence
- 1905 - Alfred Binet and Theodore Simon - first attempt to formally measure intelligence (Binet-Simon Scale)
- Mental Age (MA) is a measure of a person's intellectual development relative to people of her/his age group.
- Chronological Age (CA) is the biological age from birth.
- Retardation was defined as being two mental age years below the chronological age.
- IQ = MA/CA x 100 (by William Stern in 1912)
Intelligence Quotient (IQ) refers to mental age divided by chronological age multiplied by 100. The number 100 is used as a multiplier to avoid the decimal point.
MA = CA, IQ = 100
MA > CA, IQ > 100
MA < CA, IQ < 100
- For example, a 10-year-old child with a mental age of 12 would have an IQ of 120 (12/10 x 100), whereas the same child with an MA of 7 would have an IQ of 70 (7/10 x 100).
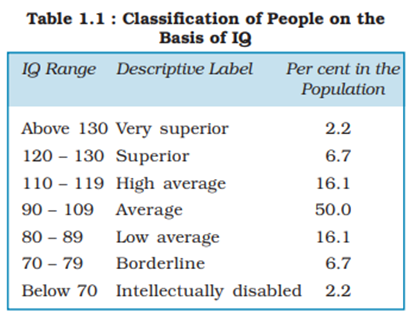
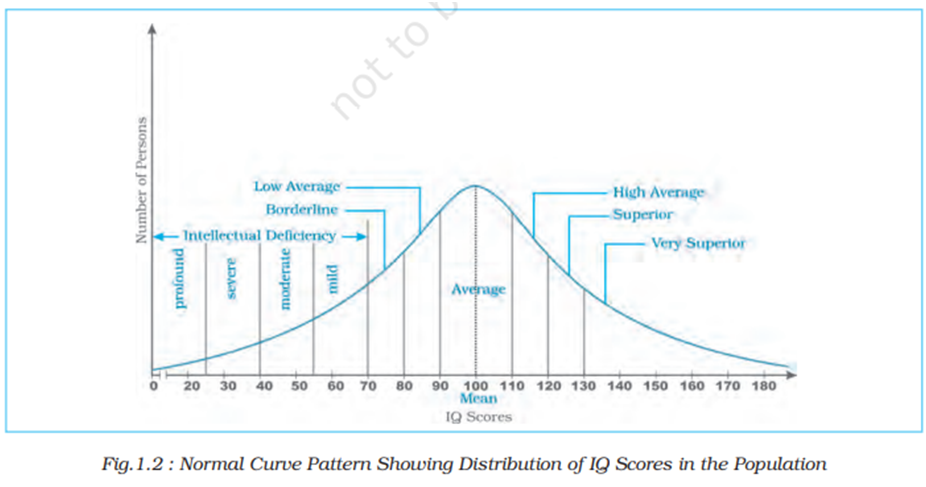
- The scores of most people tend to fall in the middle range of the distribution. Only a few people have either very high or very low scores.
- The frequency distribution for the IQ scores tends to approximate a bell-shaped curve, called the normal curve. This type of distribution is symmetrical around the central value, called the mean.
- Mean IQ score in a population is 100.
- People with IQ scores in the range of 90–110 have normal intelligence.
- Those with IQ below 70 are suspected to have ‘intellectual disability’, while persons with IQ above 130 are considered to have exceptional talents.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
