- Books Name
- Education Vision Political Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Political Science
EVOLUTION OF THE UN
Why International Organizations?

- UN is regarded as most important international organization.
- UN is great hope of humanity
- The United Nations was not created to take humanity to heaves but to save it from hell- Dag Hammarskjold
- International Organization helps sought out matter of war.
- Countries have conflicts and differences that does not mean they should go for war;
countries have UN as a platform to solve their issues - UN i.e., International organization is not a state or super state with authority over its members.
Importance of International Organization?
- There are some issues that can only be dealt when all countries are together.
- E.g.- Disease, Global Warming, Population control etc. aids, small pox etc.
- An international organization help to produce ideas that how to co-operate and provide a mechanism, rules and bureaucracy.
- International organizations are not the answers to everything but they are helpful to ensure world peace by solving problems peacefully.
- Joint efforts of all the nations are required to resolve certain global issues.
- An international organization is helpful to co operate the efforts of the nation of states.

Evolution of the UN
- After the first World War, world invested in international organizations to resolve conflicts. League of nations was born but it could not prevent war as a result Second World War (1939-45) took place and many people died.
- UN was formed as a successor to the League of Nations after the Second World War in 1945.
- Organisation was setup by signing of United Nations charter by 51 member/ countries.
- Objectives
-
- Peace and cooperation
- Minimizing war
- Social economic development
-
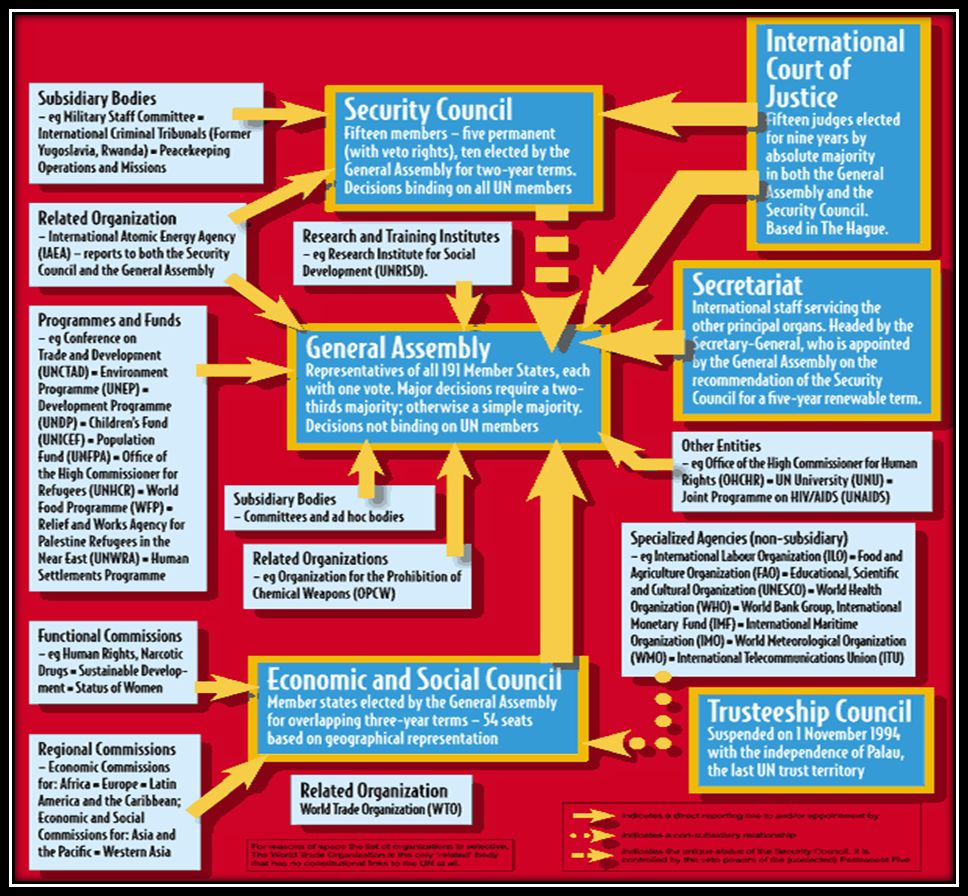
- By 2006 UN had 192 members. They are included in UN General Assembly with one vote (India is also a member)
- UN Security Council have five permanent members. All of them were made the permanent members because, they were powerful after the Second World War.
-
- US
- UK
- France
- China
- Russia
- They permanent members have veto power.

-
- The UN’s representative head is the Secretary-General.
- The present Secretary General is Antonio Guterres, he’s the 9th secretary general of the UN, he took over as a secretary general on 1st January 2017. He was the Prime Minister of Portugal from 1995 to 2002 and the UN High Commissioner of refugees from 2005 to 2015.
- The UN has many organizations like – WHO, UNDP, UNHRC, UNHCR, UNICEF, UNESCO and many others.
3. Reform of the UN after the Cold War
- Structural and Processes Reforms:
-
- Functioning of Security Council, the demand for increase in UN Security Council permanent as well as non-permanent members. So that realities of world politics are better reflected.
- Proposals to increase membership from Asia, Africa and South America
- US and other Western countries want improvements in the UN’s budgetary procedures and its administration.
-
- Jurisdictional Reforms
-
- Some countries wanted you want to play major role in peace and security missions, while others wanted its role to be confined to development and humanitarian work (health, education, environment, population control, human rights, gender and social justice)
-
- Changes that occurred after cold war
- Soviet Union had collapsed
- US was the new superpower
- China was fastest growing power and India was also growing
- Economics of Asia most developing
- Many new countries joined even after the disintegration of USSR
- New set of challenges were:
- Civil war
- Ethnic conflict
- Genocide
- Terrorism
- Climate change
- Environmental degradation

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
