- Books Name
- Physics Book Part l and ll
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Physics
Prism
A prism is a transparent medium bounded by the three plane faces. Out of the three faces, one is grounded and the other two are polished. The polished faces are called refracting faces. The angle between the refracting faces is called angle of prism, or the refracting angle. The third face is called base of the prism.
Refraction of light through a prism
Fig. shows the cross section of a triangular prism ABC, placed in air. Let ?A? be the refracting angle of the prism. A ray of light PQ incident on the refracting face AB, gets refracted along QR and emerges along RS. The angle of incidence and refraction at the two faces are i1, r1 , r2 and i2 respectively. The angle between the incident ray PQ and the emergent ray RS is called angle of deviation, d. In the ∆QER, the exterior angle FER = angle EQR + angle ERQ
d = (i1 - r1) + (i2 - r2)
d = (i1 + i2) - (r1 + r2) ????.(1)
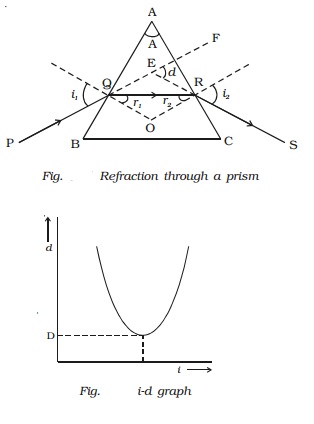
In the quadrilateral AQOR, the angles at Q and R are right angles
Angle Q + Angle R = 1800
A + Angle R = 1800 ????.(2)
Also, from the ∆QOR
r1+ r2 = A ??????..(4)
Substituting in (1),
d = i1 + i2 - A
or A + d = i1 + i2 ...(5)
For a given prism and for a light of given wavelength, the angle of deviation depends upon the angle of incidence.
As the angle of incidence i gradually increases, the angle of deviation d decreases, reaches a minimum value D and then
increases. D is called the angle of minimum deviation. It will be seen from the graph (Fig. ) that there is only one angle of
incidence for which the deviation is a minimum.
At minimum deviation position the incident ray and emergent ray are symmetric with respect to the base of the prism. (i.e)the refracted ray QR is parallel to the base of the prism.
At the minimum deviation
i1 = i2 = i and r1 = r2 = r
from equation (4) 2r = A or r = A/2
and from equation (5) 2i = A + D or i = ( A+D )/2
The refractive index is ? = sin i/sin r
? = [sin((A+D) / 2)] / sin(A/2)
- Dispersion of light
Dispersion is the splitting of white light into its constituent colours. This band of colours of light is called its spectrum.
In the visible region of spectrum, the spectral lines are seen in the order from violet to red. The colours are given by the word VIBGYOR (Violet,Indigo, Blue, Green,Yellow, Orange and Red) (Fig. )
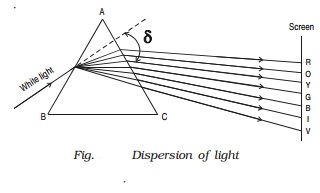
The origin of colour after passing through a prism was a matter of much debate in physics. Does the prism itself create colour in some
way or does it only separate the colours already present in white light?
Optical Instruments
- Optical instruments are instruments using reflecting and refracting properties of mirrors, lenses and prisms.
- A number of optical devices and instruments have been designed utilising reflecting and refracting properties of mirrors, lenses and prisms.
- Periscope, kaleidoscope, binoculars, telescopes; microscopes are some examples of optical devices and instruments.
- Some of optical instruments which consists of lenses and prisms are:-
1.Binoculars
2.Telescope
3.Microscope
4.Eye

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
