1. Elements of a Communication System
- Books Name
- Physics Book Part l and ll
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Physics
Chapter 15: Communication System
Elements of a Communication System
Communication Systems
The communication system is a system which describes the information exchange between two points. The process of transmission and reception of information is called communication.
Types Of Communication Systems
Depending on Signal specification or technology, the communication system is classified as follows
- Analog
Analog technology communicates data as electronic signals of varying frequency or amplitude. Broadcast and telephone transmission are common examples of Analog technology.
- Digital
In digital technology, the data are generated and processed in two states: High (represented as 1) and Low (represented as 0). Digital technology stores and transmits data in the form of 1s and 0s.
BASIC TERMINOLOGY USED IN ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
The definitions of the terms used in the communication system are discussed below.
Information
Message or information is the entity that is to be transmitted. It can be in the form of audio, video, temperature, picture, pressure, etc.
Signal
The single-valued function of time that carries the information. The information is converted into an electrical form for transmission.
Transducer
A device or an arrangement that converts one form of energy to the other. Example: Microphone – converts audio signals into electrical signals. Photodetector – converts light signals into electrical signals.
Amplifier
The electronic circuit or device that increases the amplitude or the strength of the transmitted signal is called an amplifier.
Modulator
As the original message signal cannot be transmitted over a large distance because of their low frequency and amplitude, they are superimposed with high frequency and amplitude wave called carrier wave.
Transmitter
It is the arrangement that processes the message signal into a suitable form for transmission and subsequently reception.
Channel
A channel refers to a physical medium such as wire, cables, space through which the signal is passed from the transmitter to the receiver.
Noise
Noise is one of the channel imperfection or impairment in the received signal at the destination. There are external and internal sources that cause noise.
BANDWIDTH OF SIGNALS
Bandwidth refers to the frequency range over which an equipment operates or the portion of the spectrum occupied by the signal. Different types of signals (music, picture or computer data) require different bandwidth.
- Speech signal requires a bandwidth of 2800 Hz (3100 Hz – 300 Hz) for telephonic conversation.
- Video signals for transmission of pictures require about 4.2 MHz of bandwidth.
- A TV signal contains both voice and picture and is usually allocated 6 MHz of bandwidth for transmission.
Bandwidth of Transmission Medium
Different types of transmission media offer different bandwidths.
- The commonly used transmission media are wire, free space and fiber optic cable.
- Coaxial cable offers a bandwidth of approximately 750 MHz. Such cables are normally operated below 18 GHz.
2. Electromagnetic Waves
- Books Name
- Physics Book Part l and ll
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Physics
Electromagnetic Waves
Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves
Various propagation modes for em waves are shown in the figure given below
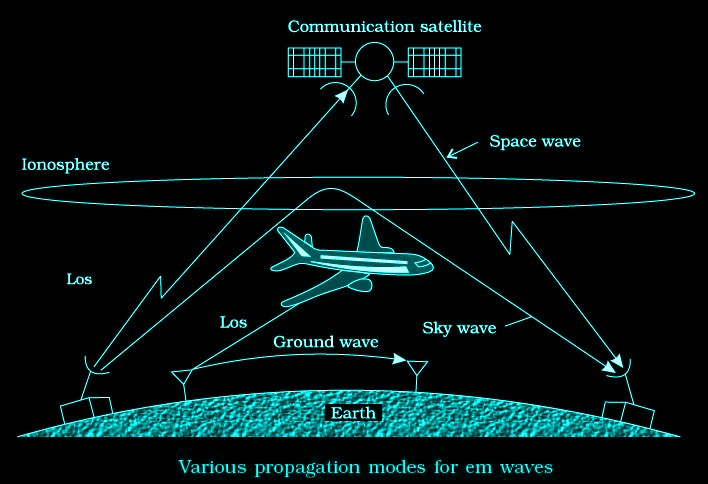
Ground wave propagation
Radio waves traveling through atmosphere and moving along the surface of the earth are termed as ground waves. Ground wave propagation is suitable for low frequencies (500 kHz to 1500kHz) or for radio broadcast at long wavelength i.e., upto 1 MHz.
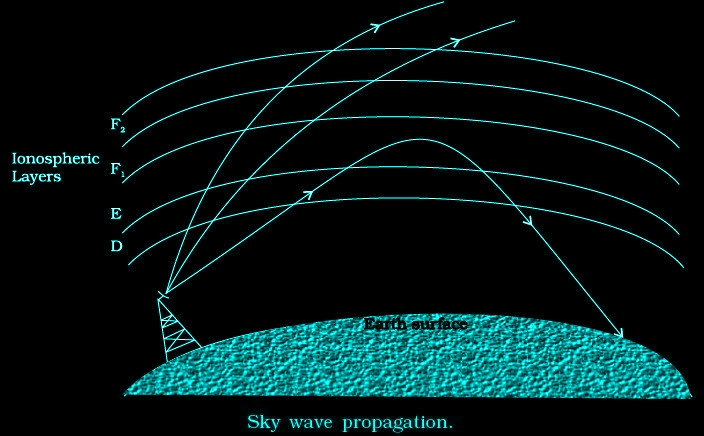
Sky wave propagation
The frequency range from a few MHz up to 30 to 40 MHz, long distance communication can be achieved by ionospheric reflection.
MODULATION AND ITS NECESSITY
Transmission of information by communication systems over large distances is quite a feat of human ingenuity. We can talk, video chat and text anyone on this planet! The communication system uses a very clever technique called Modulation .
Types of Modulation
1.Amplitude Modulation
2.Frequency Modulation
3.Phase Modulation
AMPLITUDE MODULATION
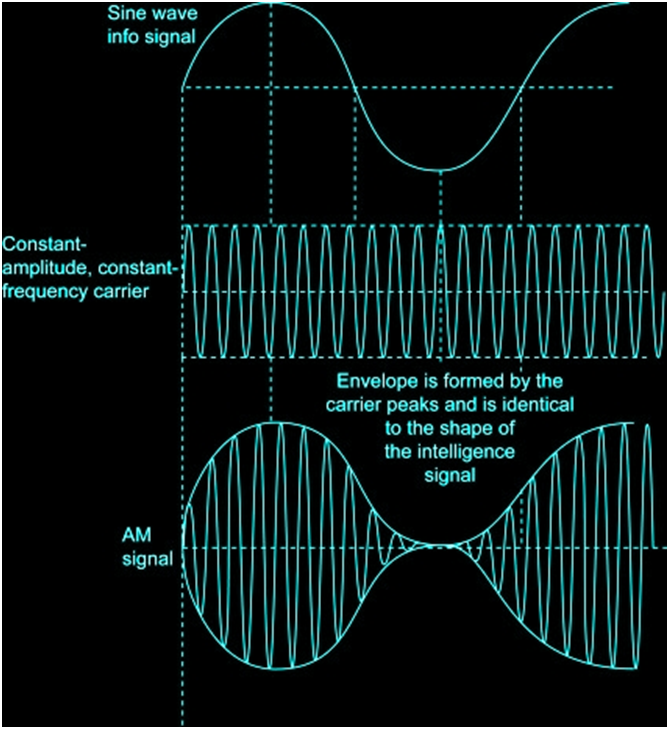
In AM, the voltage or power level of the information signal changes the amplitude of the carrier in proportion. With no modulation, the AM carrier is transmitted by itself.
PRODUCTION OF AMPLITUDE MODULATED WAVE

DETECTION OF AMPLITUDE MODULATED WAVE
The transmitted message gets attenuated in propagating through the Channel. The receiving antenna is therefore to be followed by an amplifier And a detector. In addition, to facilitate further processing, the carrier Frequency is usually changed to a lower frequency by what is called an
Intermediate frequency (IF) stage preceding the detection.

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
