- Books Name
- Physics Book Part l and ll
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Physics
Chapter 14: Semiconductors Electronics
Intrinsic Semiconductor
CLASSIFICATION OF METALS, CONDUCTORS AND SEMICONDUCTORS
Metals:
They possess very low resistivity (or high conductivity).
![]()
Semiconductors:
They have resistivity or conductivity intermediate to metals and insulators.
![]()
Insulators:
They have high resistivity (or low conductivity).
![]()
The values of ρ and σ have given above are indicative of the magnitude and could well go outside the ranges as well.
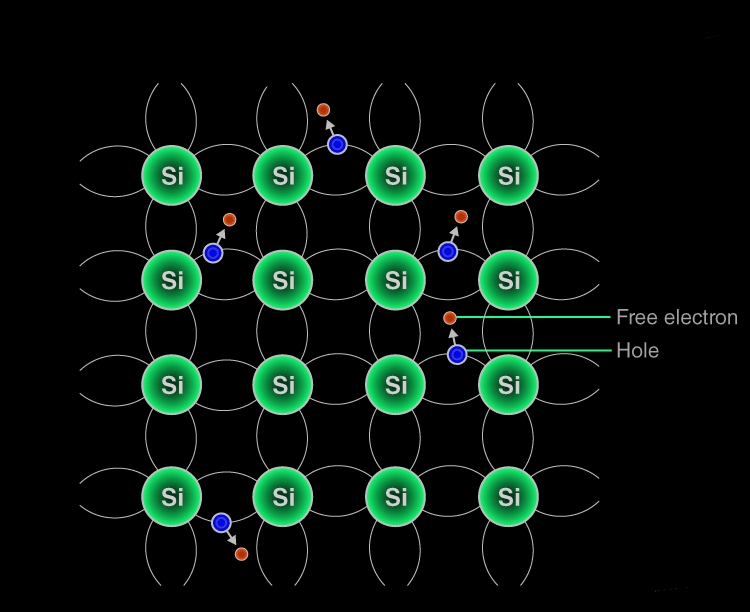
Intrinsic Semiconductors
Semiconductors that are chemically pure, in other words, free from impurities are termed as intrinsic semiconductors. The number of holes and electrons is therefore determined by the properties of the material itself instead of the impurities. In intrinsic semiconductors, the number of excited electrons is equal to the number of holes; n = p.
Working Mechanism of Intrinsic Semiconductors
Electronic Configuration of Silicon and Germanium
Silicon 1s2 2s22p6 3s2 3p2
Germanium 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p2
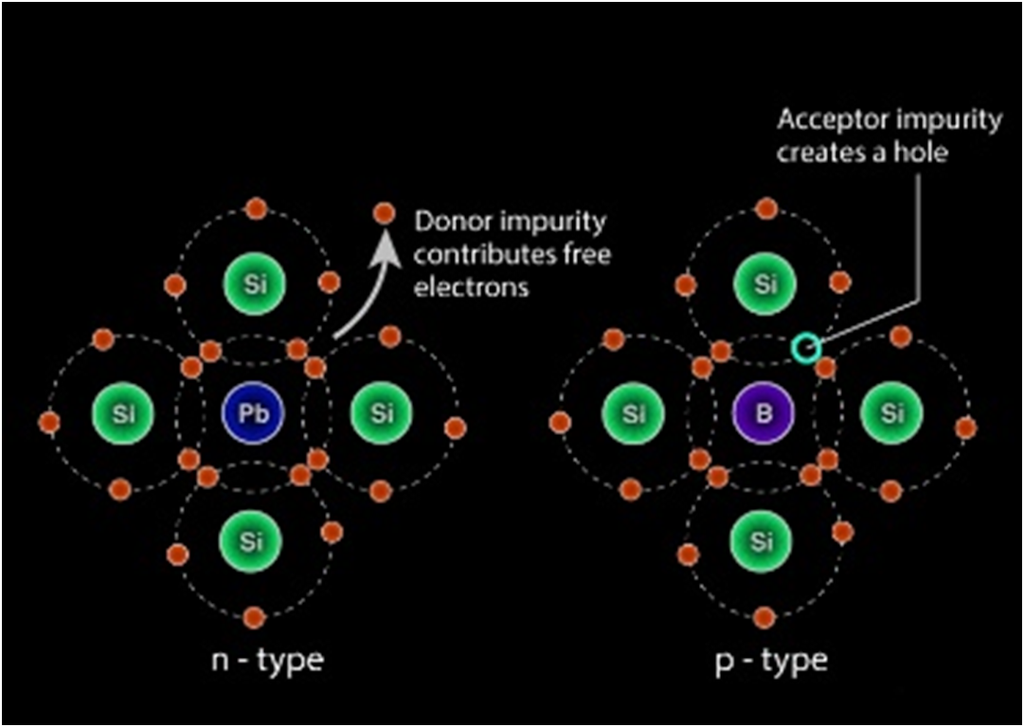
EXTRINSIC SEMICONDUCTOR
n-type semiconductors
When a tetravalent atom such as Si or Ge is doped with a pentavalent atom, it occupies the position of an atom in the crystal lattice of the Si atom. The four of the electrons of the pentavalent atom bonds with the four neighboring silicon atoms and the fifth one remains weakly bound to the parent atom. As a result of this, the ionization energy required to set the fifth electron free is very less and the electrons become free to move in the lattice of the semiconductor. Such semiconductors are termed as n-type semiconductors.

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
