- Books Name
- Mathmatics Book Based on NCERT
- Publication
- KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Rate of Change of Quantities :
![]() , we mean the rate of change of distance s with respect to the time t.
, we mean the rate of change of distance s with respect to the time t.
![]() the rate of change of y with respect to x.= f′ (x)
the rate of change of y with respect to x.= f′ (x)
![]() x=x0 (or f′ (x0 )) represents the rate of change
x=x0 (or f′ (x0 )) represents the rate of change
Further, if two variables x and y are varying with respect to another variable t, i.e., if x= f( t) and y =g (t), then by Chain Rule.
![]() ,if
,if ![]()
Thus, the rate of change of y with respect to x can be calculated using the rate of change of y and that of x both with respect to t.
Example :
Find the rate of change of the area of a circle per second with respect to its radius r when r = 5 cm
Answer:
The area A of a circle with radius r is given by A = π r 2 . Therefore, the rate of change of the area A with respect to its radius r is given by ![]()
When r = 5 cm. ![]()
Thus, the area of the circle is changing at the rate of 10π cm2 /s.
Example :
The volume of a cube is increasing at a rate of 9 cubic centimetres per second. How fast is the surface area increasing when the length of an edge is 10 centimetres ?
Solution:
Let x be the length of a side, V be the volume and S be the surface area of the cube. Then, V = x 3 and S = 6x 2 , where x is a function of time t. Now
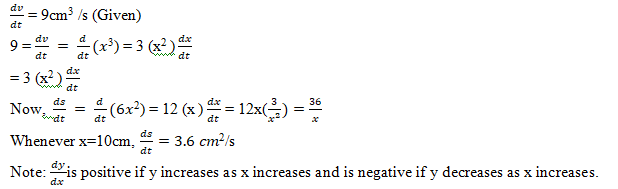
Example : The total cost C(x) in Rupees, associated with the production of x units of an item is given by C(x) = 0.005 x 3 – 0.02 x 2 + 30x + 5000
Find the marginal cost when 3 units are produced, where by marginal cost we mean the instantaneous rate of change of total cost at any level of output.
Solution: Since marginal cost is the rate of change of total cost with respect to the output, we have Marginal cost (MC) =![]() = 0.005(3x2) - 0.02(2x ) + 30
= 0.005(3x2) - 0.02(2x ) + 30
When x = 3, MC = 0.015(32)- 0.04(3) + 30 = 0.135 – 0.12 + 30 = 30.015.
Hence, the required marginal cost is ` 30.02 (nearly).

 KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
