- Books Name
- Mathmatics Book Based on NCERT
- Publication
- KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Order and Degree of a differential equation
What is ODE and PDE?
Ordinary differential equations or (ODE) are equations where the derivatives are taken with respect to only one variable. That is, there is only one independent variable. Partial differential equations or (PDE) are equations that depend on partial derivatives of several variables.
Order of differential equation
The highest order of the derivative present in the dependent variable with respect to the independent variable in the given differential equation is called order of DE.
Degree of differential equation
Degree of the differential equation is the exponent of the highest derivative of the differential equation
Example:
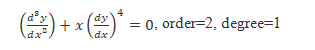
Example:
![]()
order=2, degree=not defined because it is not a polynomial function.
Example:
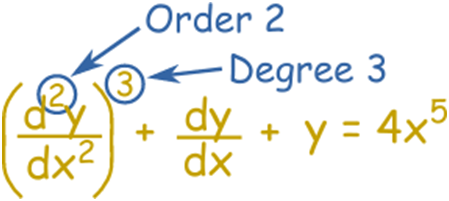
order=2 ,degree=3
Example :
![]()
Here, the exponent of the highest order derivative is one and the given differential equation is a polynomial equation in derivatives. Hence, the degree of this equation is 1.
Example :
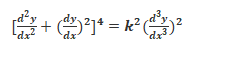
The order of this equation is 3 and the degree is 2 as the highest derivative is of order 3 and the exponent raised to the highest derivative is 2.
Order and degree (if defined) of a differential equation are always positive integers.

 KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
