- Books Name
- Mathmatics Book Based on NCERT
- Publication
- KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions:
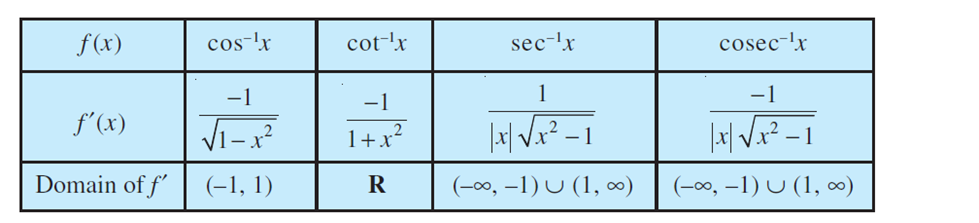
Inverse of sin x = arcsin(x) or
Let us now find the derivative of Inverse trigonometric function
Example: Find the derivative of a function ![]()
Solution: Given
![]()
Differentiating the above equation w.r.t. x, we have:
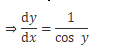
Putting the value of y form (i), we get
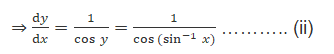
From equation (ii), we can see that the value of cos y cannot be equal to 0, as the function would become undefined ![]()
i. e.![]()
From (i) we have ![]()
![]()
Using property of trigonometric function,
![]()
![]()
Now putting the value of (iii) in (ii), we have ![]()
Therefore, the Derivative of Inverse sine function is ![]()
Example:Find the derivative of a function
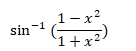
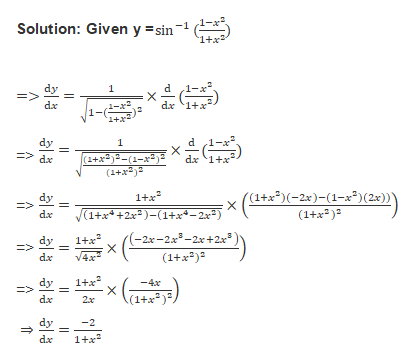
Problem: y = cot-1(1/x2)
Solution:
As we are solving the above three problem in the same way this problem will solve
By using chain rule,
y’ = (cot-1(1 / x2))’
= { – 1 / (1 + (1 / x2))2 } . (1 / x2)’
= { – 1 / (1 + (1 / x4)) . (-2x-3)
= 2x4 / (x4 + 1)x3
Example: Solve f(x) = tan-1(x) Using first Principle.
Solution:
For solving and finding tan-1x, we have to remember some formulae, listed below.
- limh->0 {f(x + h) – f(x)} / h
- tan-1(θ/θ) = 1
- tan-1x – tan-1y = tan-1[(x – y) / (1 + xy)]
f(x) = tan-1x
f(x + h) = tan-1(x + h)
Apply 1st formula
limh->0 {tan-1(x + h) – tan-1x } / h
Now Apply 3rd formula
limh->0 tan-1[(x – h – x) / (1 + (x + h)x] / h
limh->0 tan-1[(h / (1 + x2 + xh ] / h . [(1 + x2 + xh) / (1 + x2 + xh)]
limh->0 tan-1 {h / 1 + x2 + xh} / {h / 1 + x2 + xh} . limh->0 1 / 1 + x2 + xh
Now we made the solution like so that we apply the 2nd formula
= 1 . 1 / (1 + x2 + x . 0)
= 1 / (1 + x2)

 KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
