- Books Name
- Mathmatics Book Based on NCERT
- Publication
- KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Integrals of some more types
- ∫ √(x2 - a2) dx
- ∫ √(a2 - x2) dx
- ∫ √(x2 + a2) dx
Proof:
[1] ∫ √(x2 - a2) dx
Let I = ∫ √(x2 - a2) dx
⇒I = ∫ 1. √(x2 - a2) dx
⇒I = ∫ √(x2 - a2) . 1dx
Let f(x) = √(x2 - a2) and g(x) = 1
∫ f(x) g(x) dx = f(x) ∫ g(x) dx - ∫ [ f '(x) ∫ g(x) dx] dx
Thus ∫ √(x2 - a2) . 1dx = √(x2 - a2) . ∫ 1 dx - ∫ [d/dx(√(x2 - a2)) ∫1dx] dx
⇒ I = √(x2 - a2) . x - ∫ 1/(2(√(x2 - a2))) . 2x .x dx
⇒ I = x√(x2 - a2) - ∫ x2/√(x2 - a2) dx
⇒ I = x√(x2 - a2) - ∫ (x2 - a2 + a2)/√(x2 - a2) dx
⇒ I = x√(x2 - a2) - ∫ (x2 - a2)/√(x2 - a2) dx - ∫ a2/√(x2 - a2) dx
⇒ I = x√(x2 - a2) - ∫ √(x2 - a2) dx - ∫ a2/√(x2 - a2) dx
⇒ I = x √(x2 - a2) - I - ∫ a2/√(x2 - a2) dx
⇒ 2I = x √(x2 - a2) - a2 ∫ 1/√(x2 - a2) dx
⇒ 2I = x √(x2 - a2) - a2 log|x + √(x2 - a2)| + C
⇒ I = x/2 . √(x2 - a2) - a2/2 . log|x + √(x2 - a2)| + C
Note: The integral of √(x2 - a2) can also be evaluated by substituting x = a sec θ.
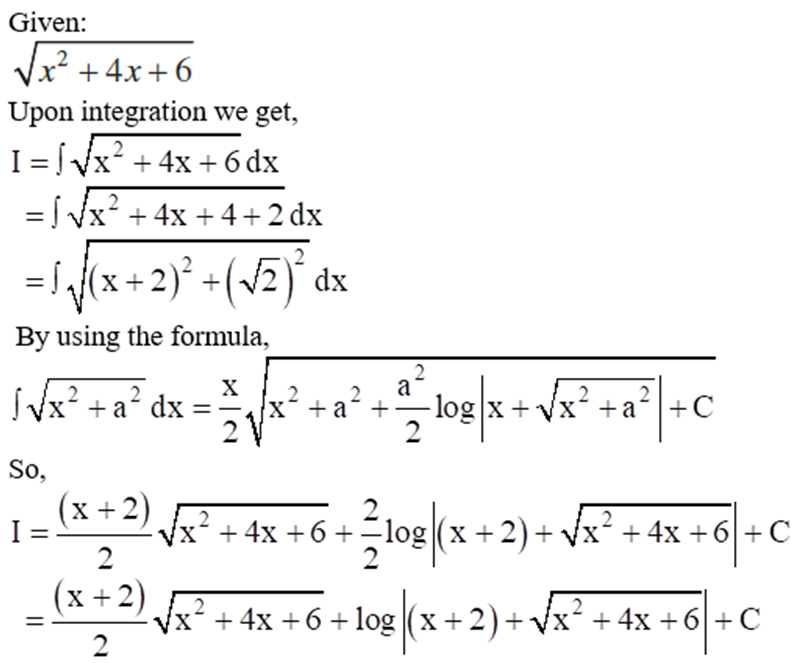
[2] ∫ √(x2 + a2) dx
Let I = ∫ √(x2 + a2) . 1dx
Let f(x) = √(x2 + a2) and g(x) =1
∫ f(x) g(x) dx = f(x) ∫ g(x) dx - ∫ [ f '(x) ∫ g(x) dx] dx
I = √(x2 + a2) ∫ 1 dx - ∫ [d/dx (√(x2 + a2)) ∫ 1dx] dx
⇒ I = √(x2 + a2) . x - ∫ 1/(2√(x2 + a2)). 2x . x dx
⇒ I = x √(x2 + a2) - ∫ x2/√(x2 + a2) dx
⇒ I = x √(x2 + a2) - ∫ (x2 + a2 - a2)/√(x2 + a2) dx
⇒ I = x√(x2 + a2) - ∫ (x2 - a2)/√(x2 + a2) dx + ∫ a2/√(x2 + a2) dx
⇒ I = x√(x2 + a2) - ∫ √(x2 + a2) dx + ∫ a2/√(x2 + a2) dx
⇒ I = x √(x2 + a2) - I + ∫ a2/√(x2 + a2) dx
⇒ 2I = x √(x2 + a2) + ∫ a2 /√(x2 + a2) dx
⇒ 2I = x √(x2 + a2) + a2 ∫ 1 /√(x2 + a2) dx
⇒ 2I = x √(x2 - a2) + a2 log|x + √(x2 + a2)| + C
⇒ I = x/2 . √(x2 + a2) + a2/2 . log|x + √(x2 + a2)| + C
Note: The integral of √(x2 + a2) can also be evaluated by substituting x = a tan θ.
[3] Let I= ∫ √(a2 - x2) dx
= ∫ √(a2 - x2) . 1 dx
= ∫ √(a2 - x2) . 1dx
Let f(x) = √(a2 - x2) and g(x) = 1
∫ f(x) g(x) dx = f(x) ∫ g(x) dx - ∫ [ f '(x) ∫ g(x) dx] dx
= √(a2 - x2) ∫ 1dx - ∫ [d/dx (√(a2 - x2)) ∫ 1dx] dx
⇒ I = √(a2 - x2) . x - ∫ 1/2(√(a2 - x2)) . (-2x) . x dx
⇒ I = x√(a2 - x2) - ∫ -x2/√(a2 - x2) dx
⇒ I = x√(a2 - x2) - ∫ ((a2-x2)-a2)/√(a2 - x2) dx
⇒ I = x√(a2 - x2) - ∫ (a2-x2)/√(a2 - x2) dx + ∫ a2/√(a2 - x2) dx
⇒ I = x√(a2 - x2) - ∫ √(a2 - x2) dx + ∫ a2/√(a2 - x2) dx
⇒ I = x√(a2 - x2) - I + ∫ a2/√(a2 - x2) dx
⇒ 2I = x√(a2 - x2) + a2 ∫ 1/√(a2 - x2) dx
⇒ 2I = x√(a2 - x2) + a2 sin-1 (x/a) + C
⇒ I = x/2 √(a2 - x2)+ a2/2 sin-1 (x/a) + C
Note: The integral of √(a2 - x2) can also be evaluated by substituting x = a sin θ.

 KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
