Worker Population Ratio
PARTICIPATION OF PEOPLE IN EMPLOYMENT
Meaning: "Worker-Population ratio" is an indicator, which is used to analyze the employment situation du the country. The worker-Population ratio is calculated by dividing the total number of workers in India by the population in India and multiplying it by 100.
Important Points about Worker-Population Ratio
- The worker-Population ratio is very useful in determining the proportion of the population contributing to the production of goods and services of a country.
- Higher ratio indicates that a high proportion of its population is involved in economic activities.
- Medium or lower ratio indicates that less people are involved in economic activities.
- The worker-population ratio indicates the status of workers in society and their working conditions.
- By knowing the status with which a worker is placed in an enterprise, it may be possible to determine the quality of employment in a country.
- It also enables us to know the attachment, which a worker has with his job and the authority possessed by him over the enterprise and over other co-workers.
Facts and figures about worker-population ratio:
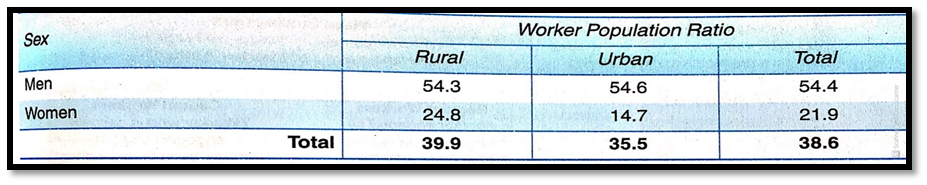
- For every 100 persons, 38.6% are workers in India.
- Higher Proportion of Rural People: In urban areas, the proportion is 35.5%, whereas in rural India, the ratio is about 39.9%.
- Employment Opportunities: Rural people have limited resources and participate more in the employment market. On the other hand, urban people have a variety of employment opportunities. They look for the appropriate job to suit their qualifications and skills.
- Education Level: In rural areas, many do not go to schools or colleges and even if some go, they discontinue in the middle to join the workforce. In urban areas, a considerable section is able to study in various educational institutions.
- Higher Proportion of Male Workers: As compared to females (21.9%), more males (54.4%) are found to be working. Men are able to earn high incomes and, therefore, families discourage female members from taking up jobs.
- More Women Workers in rural areas: The ratio of women workers in rural areas (24.8%) is more than the number of women workers in urban areas (14.7%). It happens because people in rural areas cannot stay at home due to their poor economic conditions.
- Underestimation of Women Workers: The number of women workers in our country is generally underestimated because many activities undertaken by them are not recognized as productive work. For example, many women are actively engaged in activities within the house and at family farms, but are neither paid for such work, nor are counted as a worker.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
