We have learnt that production gives rise to income, income results in expenditure, which in turn, generates income again.
The National Income of a country can be measured in three different ways:
- Value Added Method
- Income Method
- Expenditure Method
It must be noted that all three methods give the same value of national income because they are used to measure the same physical output at three different phases.
VALUE-ADDED METHOD
This method is used to measure national income in different phases of production in the circular flow. Every individual enterprise adds a certain value to the product when it purchases from some other firm as intermediate goods. When value-added by each and every firm is summed up, we get the value of national income.
- Value Added: Value added is the difference between the value of goods as they leave a stage of production and the cost of the goods as they entered that stage.
Value Added = Value of output - Intermediate consumption
For Example: Suppose a sweet shop owner buys milk worth ₹100 from the milkman. After processing the milk into sweets, he sells it for ₹250.
So, here the milk is intermediate consumption as it was used for making sweets. The sweets which are sold off are output and termed as the value of output.
The difference between this value of output and intermediate consumption is termed as ‘value-added’. Value added by each producing enterprise is known as the Gross Value Added (GVA mp).
Sum total of all GVAmp of all producing enterprises within the domestic territory of a country during one year is equal to GDPmp.
∴ ΣGVAmp = GDPmp
- If the value of intermediate consumption is given, then imports are not included separately as imports are already included in the value of intermediate consumption.
However, if domestic purchases are given, then imports will also be included.
For Example:
Case 1:
- Intermediate Consumption = ₹500
- Imports = ₹200
Here imports would not be included and the value of intermediate consumption is ₹500.
Case 2:
- Purchase of Raw Material from domestic firm=.₹700
- Imports =₹300
Here, the value of intermediate consumption = Purchase of Raw material from domestic firm + Imports =700+300
Intermediate consumption =₹1000
- Value of Output: Value of output refers to the market value of all goods and services produced during a period of one year.
How to calculate the value of output:
- When the entire output is used is sold in an accounting year then the value of output is equal to sales.
- When the entire output is not sold in an accounting year then the value of output is calculated as follows:
Value of output = Sales + change in stock
[Change in stock= Closing stock - Opening stock]
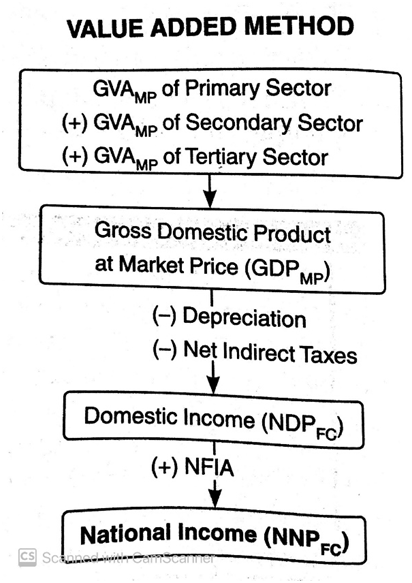
Steps to Calculate National Income by Value Added Method
Step 1- Identify and classify the production units:
The first step is to identify all the producing units into the primary, secondary and tertiary sector.
Step 2- Estimate Gross Domestic Product at Market Price:
Now gross value added to market price (GVAmp) of each sector calculated and the sum total of GVAmp of all sectors gives GDPmp i.e GDPmp= ΣGVA (of all sectors).
Step 3- Calculate Domestic Income (NDPFC)
Now, to calculate NDPFC from GDPmp, we need to subtract both depreciation as well as net indirect taxes i.e NDPFC = GDPmp – Depreciation – Net Indirect Taxes.
Step 4– Calculate National Income (NNPFC)
For calculating NNPFC from NDPFC, NFIA is to be added NNPFC= NDPFC +NFIA

Precautions of Value-Added Method
Intermediate goods are not to be included in National Income - If intermediate goods would be included in National Income it would lead to double-counting, as these are already included in final goods.
Sale and Purchase of Second Hand Goods are not included- Since these goods are already included in the year of manufacture, these are not included again. However, any brokerage or commission earned or paid is to be included while calculation.
Production of services for self-consumption (Domestic Services) are not included: Domestic services like services of Housewife, kitchen gardening etc. are not included in national income as these services never entered market place and it's difficult to find their market value.
Production of goods for self-consumption will be included - It is not included in national income as they contribute to current output. Their value is to be estimated or imputed, as they are not sold in the market.
Change in the stock of goods will be included - Net increase in the stock of inventories will be included in national income as part of capital formation.
The problem of Double Counting:
Double Counting refers to the counting of output more than once while passing through various stages of production.
While calculating national income, the only value of final goods is to be included. The problem of double counting arises when the value of intermediate goods are also included along.
How to avoid Double Counting:
Final Output Method – As per this method, the value of only the final output should be added to determine national income. For example, the value of sweets of Rs 250 sold to final customers should be taken in national income.
Value- Added Method – The value-added in every stage of production is included under this method for calculation of National Income.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
