Types of Foreign Exchange Rates:
Fixed exchange rate system (Pegged exchange rate system):
Meaning: A system in which exchange rate of a currency is fixed by the government.
- When domestic currency is tied to the value of foreign currency, it is known as
pegging. - To maintain stability in fixed exchange rate system, government buy foreign currency when exchange rate appreciates and sell foreign currency when exchange rate depreciate. This process is called Pegging operation, i.e., all efforts made by the central bank to keep the rate of exchange stable.
Note:
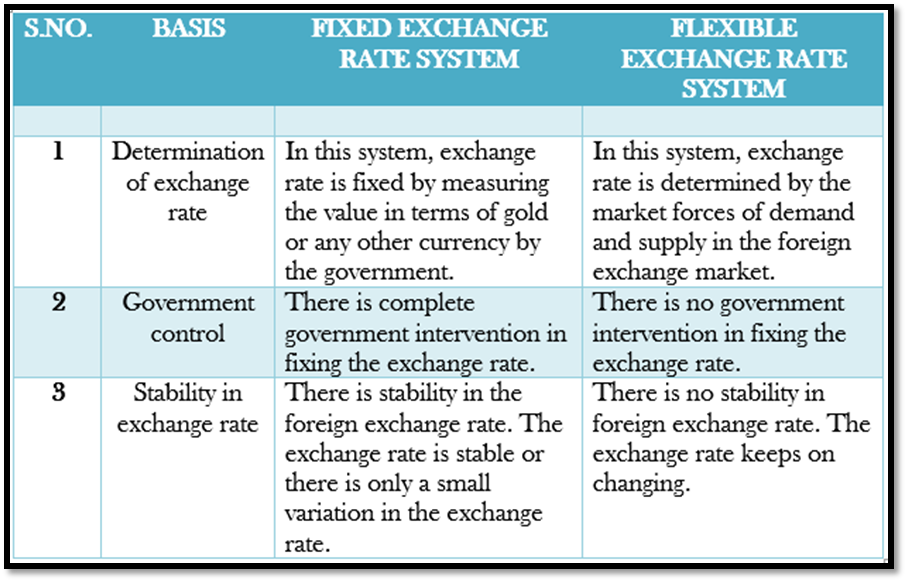
- Fixed exchange rate is not determined by the forces of demand and supply in the market. Such a rate of exchange has been associated with Gold Standard System during 1880-1914.
- According to this system, value of every currency is determined in terms of gold. Accordingly, ratio between gold values of the two countries were fixed as exchange rate between those currencies.
- For example, Value of one dollar = 100 gms of gold.
Value of a rupee = 5 gms of gold
Then, 1 dollar = 100/5 = Rs.20
Merits of fixed exchange rate system:
- Stability: It ensures stability, in the international money market/exchange market. Day to day fluctuations are avoided. It helps formulation of long term economic policies, particularly relating to exports and imports.
- Encourages international trade: Fixed exchange rate system implies low risk and low uncertainty of future payments. It encourages international trade.
- Co-ordination of macro policies: Fixed exchange rate helps co-ordination of macro policies across different countries of the world. Long-term economic policies can be drawn in the area of international trade and bilateral trade agreements.
Demerits of fixed exchange rate system:
- Huge international reserves: Fixed exchange rate system is often supported with huge international reserves of gold. This is because different currencies are directly or indirectly convertible into gold.
- Restricted movement of capital: Fixed exchange rate restricts the movement of capital across different parts of the world. Accordingly, international growth process suffers.
- Discourages venture capital: Venture capital in the international money market refers to investments in the purchase of foreign exchange in the international money market with a view to earn profits. Fixed exchange rate system discourages such investments. Fixed exchange rate discourages venture capital in the international money market.
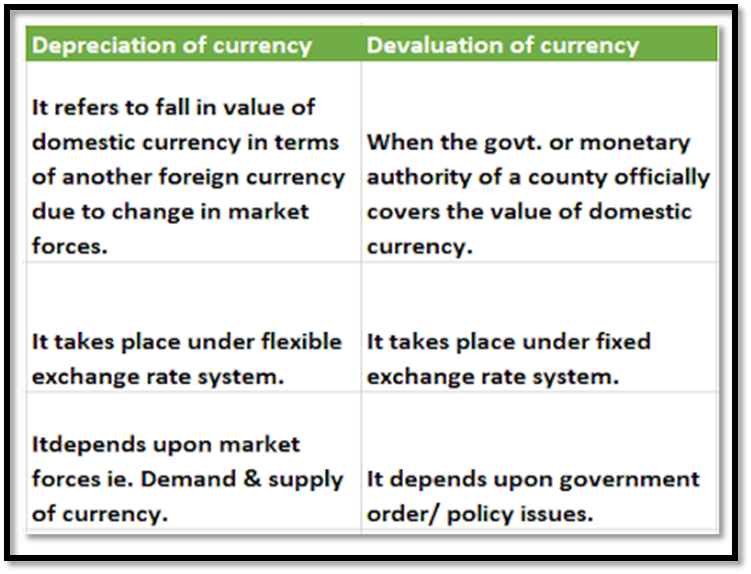
Devaluation of currency: Devaluation refers to decrease in the value of domestic
currency in terms of foreign currency by the government. It is a part of fixed
exchange rate.
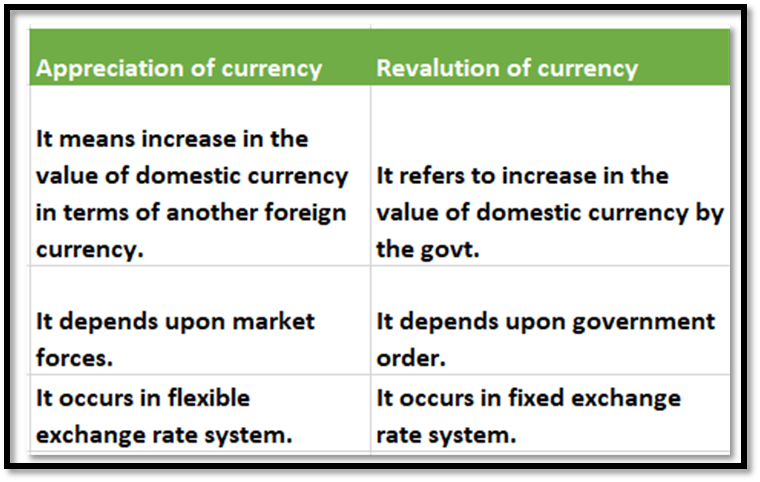
Revaluation of currency: Revaluation refers to increase in the value of domestic
currency by the central government. It is a part of fixed exchange rate.
Flexible exchange rate (floating exchange rate system):
Meaning: The system of exchange rate in which value of a currency is allowed to float freely as determined by the demand and supply foreign exchange.
- Under this system, the central banks, without intervention, allow the exchange rate to adjust to equate the supply and demand for foreign currency.
- The foreign exchange market is busy at all times by changes in the exchange rates.
Merits of flexible exchange rate system:
- No need for international reserves: Flexible exchange rate system is not to be supported with international reserves.
- International capital movements: Flexible exchange rate system enhances movement of capital across different countries of the world. This is due to the fact that member countries are no longer required to keep huge international reserves.
- Venture capital: Flexible exchange rate promotes venture capital in foreign exchange market. Trading in international currencies itself becomes an important economic activity.
Demerits of flexible exchange rate system:
- Instability: It causes instability in the international money market. Exchange rate tends to fluctuate like price of goods in the commodity market.
- International trade: Instability in foreign exchange market causes instability in the area of international trade. It becomes difficult to draw long period policies of exports and imports.
- Macro policies: While fixed exchange rate helps coordination of macro policies, flexible exchange rate makes it a difficult proposition. Day to day fluctuations in exchange rate makes bilateral trade agreements a difficult exercise.
Difference between Fixed exchange rate and Flexible exchange rate system:
Managed floating rate system:
- Managed floating exchange rate is a mixture of a flexible exchange rate (the float part) and a fixed exchange rate (the Managed part).
- In other words, it refers to a system in which foreign exchange is determined by free market forces (demand and supply forces), which can be influenced by the intervention of the central bank in foreign exchange market.
- Under this system, also called Dirty floating, central banks intervene to buy or sell foreign currencies in an attempt to stabilize exchange rate movements in case of extreme appreciation or depreciation.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
