Treatments of different items in National Income
- National Income includes income earned by a normal resident of a country as a reward for their productive services in the current year.
The following items are not included while calculating national income:
Transfer Income and payments like Pension, Scholarship, gifts, etc.
Compulsory Transfer Payments like interest tax, capital gain tax, etc.
Sale and purchase of financial assets.
Windfall gains like lotteries, gambling, etc.
Non - market transactions like kitchen gardening, etc.
Intermediate consumption expenditure like the purchase of raw material by a firm, vegetables purchased by a dairy shop, etc.
Sale or purchase of second- hand goods like sale/purchase of an old house, etc.
Capital loss like the destruction of a building by earthquake or flood etc.
Capital gains like profit due to increase in the price of land, building, shares, etc.
National debt interest or interest paid by households to commercial banks.
Following items are included while calculation of National Income:
Brokerage/Commission on sale/purchase of second- hand goods.
Services provided by the owners of production units like imputed rent of owner’s occupied house interest on own capital etc.
Capital Formation (Investment) like the purchase of machinery by a firm, construction of flyover, bridges, etc.
Payment of bonus, contribution to provident fund by employer etc.
Payment of bus fare by households, examination fees paid by students, payment of telephone bills, etc.
Profit earned by an Indian company from its branches abroad, wages received by Indian employee working abroad, etc.
Free services, (Dispensary, education) by government, government expenditure on street lighting.
Interest on the loan paid by commercial banks.
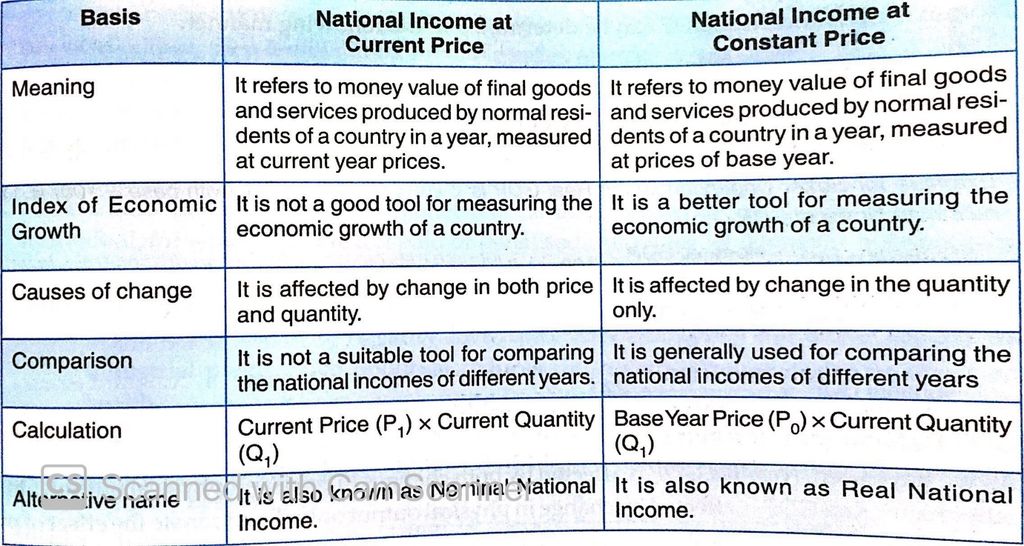
National Income at Current price and Constant price:
National Income at Current Price: It is the money value of final goods and services produced by normal residents of a country in a year, measured at prices of the current year.
It is also known as ‘Nominal National Income ’. For example – measuring India’s National Income of 2018-19 at prices of 2018-19 or measuring India’s National Income of 2017-18 at prices of 2017-18.
It does not show the true picture of the economic growth of a country as any increase in national income may be due to rise in price level without any change in physical output.
National Income at Constant Price: It is the money value of final goods and services produced by normal residents of a country in a year, measured at price of base - year. Base year is a normal year which is free from price fluctuations). Presently 2011-12 is taken as base year in India.
It is also known as ‘Real National Income’. It shows the true picture of the economic growth of a country as any increase in real national income is due to the increase in output only.
Numerical Example -
National Income at current price and at constant price.
- It can be seen that national income at current price is Rs22000 and at base price is Rs17000. The difference of Rs 5000 is not real. It does not give a true picture of economic growth as the increase is merely due to rise in prices.
Conversion of National income at current price into constant price.
- Conversion of national income at current into constant price can be done using price index, price index is an index number which shows the change in price level between two different time periods.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
