Major Policies of 1991 Reforms
THE NEW ECONOMIC POLICY
The New Economic Policy (NEP) was announced in July 1991. It consisted of a wide range of economic reforms. The main aim of the policy was to create a more competitive environment in the economy and remove the barriers to entry and growth of firms. The New Economic Policy can be broadly classified into two kinds of measures:
1. Stabilisation Measures: They refer to short-term measures which aim at:
- Correcting weaknesses of the balance of payments by maintaining sufficient foreign exchange reserves; and
- Controlling inflation by keeping the rising prices under control.
2. Structural Reform Measures: They refer to long-term measures, which aim at:
- Improving the efficiency of the economy; and
- Increasing international competitiveness by removing the rigidities in various segments of the Indian economy.
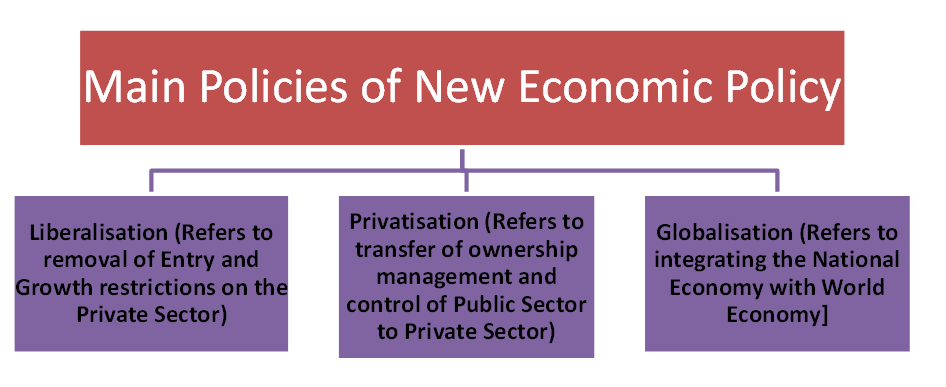
Main Policies of New Economic Policy
The government initiated a variety of policies, which fall under three heads:
- Liberalization
- Privatization
- Globalization
Liberalization, Privatisation and Globalisation or 'LPG' are the supporting pillars, on which the structure of the new economic policy of our Government has been erected and implemented since 1991.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
