Functions of Money:
We can conclude these four functions under the following two categories:
1 - Primary function
2 - Secondary function
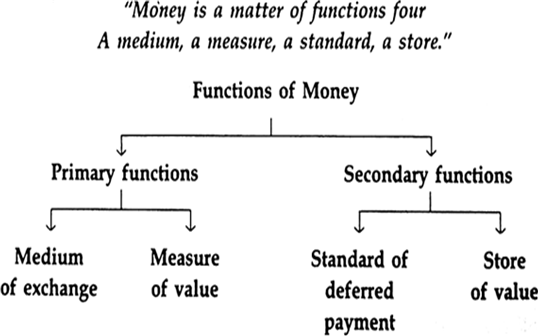
Primary function or Main function:
The primary function includes the most important functions of money, which it must perform in an economic system irrespective of time and place. The following two functions are included under this category.
(i) Medium of exchange
- Money when used as a medium of exchange helps to eliminate the basic limitation of barter trade, that is, the lack of double coincidence of wants.
- Individuals can exchange their goods and services for money and then can use this money to buy other goods and services according to their needs and convenience.
- Thus, the process of exchange shall have two parts: a sale and a purchase.
- The ease at which money is converted into other goods and services is called “liquidity of money”.
(ii) Measure of value /unit of account
- Another important function of money is that it serves as a common measure of value or a unit of account.
- Under barter economy, there was no common measure of value in which the values of different goods could be measured and compared with each other. Money has also solved this difficulty.
- As Geoffrey Crowther puts it, “Money acts as a standard measure of value to which all other things can be compared.” Money measures the value of economic goods.
- Money works as a common denominator into which the values of all goods and services are expressed.
- When we express the values of a commodity in terms of money, it is called price and by knowing prices of the various commodities, it is easy to calculate exchange ratios between them.
Secondary Functions:
(i) Standard of deferred payments
- Credit has become the life and blood of a modern capitalist economy.
- In millions of transactions, instant payments are not made.
- The debtors make a promise that they will make payments on some future date. In those situations, money acts as a standard of deferred payments.
- It has become possible because money has general acceptability, its value is stable, it is durable and homogeneous.
(ii) Store of value
- Wealth can be conveniently stored in the form of money. Money can be stored without loss in value.
- Savings are secured and can be used whenever there is a need.
- In this way, money acts as a bridge between the present and the future.
- Money means goods and services. Thus, money serves as a store of value.
- It is also known as asset function of money.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
