Meaning of Employment
Meaning: Employment is an activity, which enables a person to earn means of living. It refers to an arrangement, by which a person earns income or means of livelihood. Employment can be in form of:
- Self-employment
- Wage employment.
Self-Employment
Meaning: An arrangement, in which a worker uses his own resources to make a living, is known as self-employment.
- Workers who own and operate an enterprise to earn their livelihood are known as self-employed.
- About 52% of workforce in India belongs to this category.
- Self-employment is a major source of livelihood for both men and women.
- In the case of self-employment, a person makes use of his own land, labor, capital and entrepreneurship, to make a living.
- For example, shopkeepers, traders, businesspersons, etc.
Wage Employment
Meaning: An arrangement in which a worker sells his labor and earns wages in return, is known as wage employment.
- Under wage employment, the worker is known as an employee (or hired worker) and the buyer of labor is termed as an employer.
- Workers do not have any other resources (land, capital and entrepreneurship), except their own labor.
- They offer their labor services to others and in return get wages.
- For example, a doctor running his own clinic is an example of self-employment. However, if the doctor is employed by a hospital, then it will be wage employment.
- Wage employment is of two types:
- Regular Workers;
- Casual Workers.
Regular Workers
Meaning: When a worker is engaged by someone or by an enterprise and is paid wages on a regular basis, then such a worker is known as a regular salaried employee.
- Workers are hired on a permanent basis and get social security benefits (like pension, provident fund, etc.).
- Regular workers account for just 18% of India's workforce.
- For example, Professors, Teachers, Civil engineers working in the construction company, etc.
Casual Workers
Meaning: Workers who are casually engaged and, in return, get remuneration for up work done, are termed as casual workers.
- Casual workers are not hired on a permanent basis. It means they do not have: (i) Regular income; (ii) Protection or regulation from the government; (iii) Job security; and (iv) Social benefits.
- Casual workers account for 30% of India's workforce.
Distribution of Employment
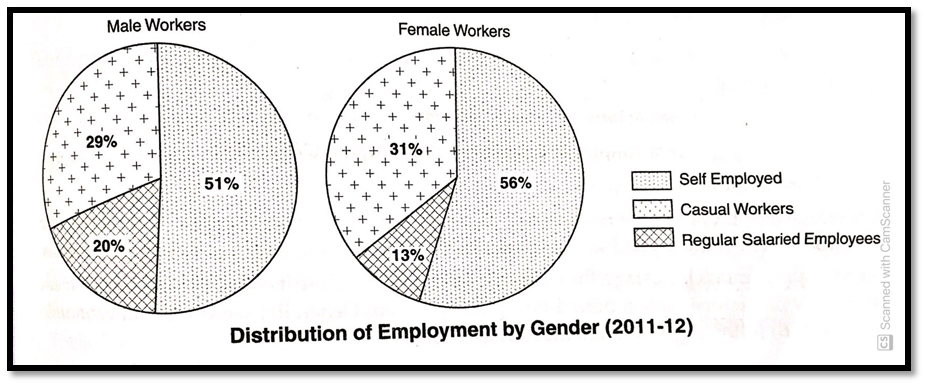
From the Pie diagrams, the following points are noticed:
- Self-employment is a major source of livelihood for both men (51%) and women (5601
- Casual workers account for the second major source for both men (29%) and women (310
- In the case of regular salaried employment, men are found in greater proportion (20%), whereas women form only 13%. The reason for this could be skill requirements as regular salaried jobs require skills and a higher level of literacy.
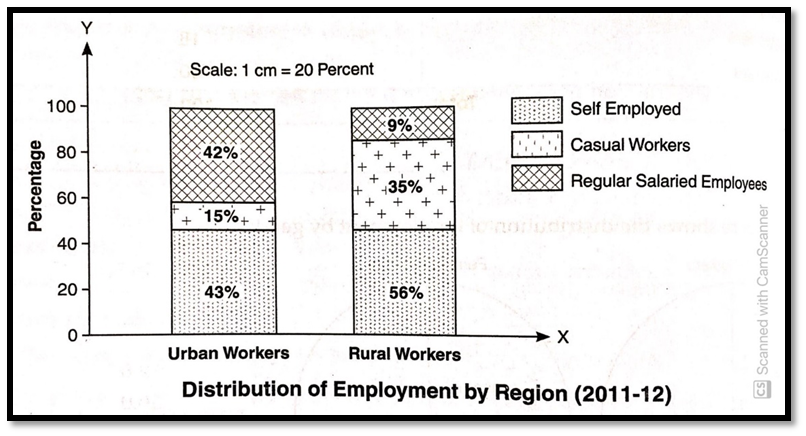
Distribution of Employment by Region.
- Self-Employment: It is a major source of livelihood in both urban areas (43%) and rural from (56%). However, in the case of rural areas, self-employed workers are greater as a majority of rural people are engaged in farming on their own plots of land.
- Casual Workers: In the case of rural areas, casual workers account for the second major source of employment with 35% of the workforce. Casual workers in urban areas account for 15%.
- Regular Salaried Employees: In urban areas, it is the second major source with 42% of work force. Urban people have a variety of employment opportunities because of their educational attainments and skills. In urban areas, the nature of work is different and enterprises require workers on a regular basis. However, only 9% of rural people are engaged as regular salaried employees due to illiteracy and lack of skills.
Distribution of Employment in Different sectors
In the course of the economic development of a country, labor flows from agriculture and other related activities to industry and services. In this process, workers migrate from rural to urban areas. Eventually, at a much later stage, the industrial sector begins to lose its share of total employment as the service sector enters a period of rapid expansion. Generally, we divide all economic activities into the following 8 different industrial divisions:
Distribution of Rural-Urban Employment in different sectors.
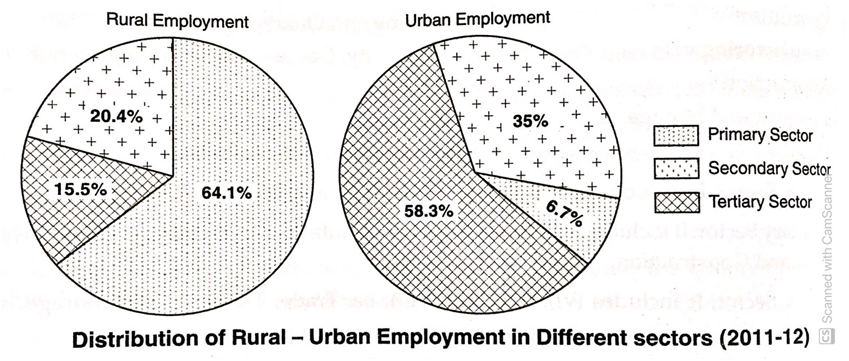
Employment in Rural Areas
- 64.1% of the workforce in rural areas are engaged in the primary sector. (Agriculture, mining, and quarrying).
- 20.4% of rural workers are working in the secondary sector. (Manufacturing industries, construction and other divisions).
- The service sector or Tertiary sector provides employment for 15.5% of rural workers.
Employment in Urban Areas
- In the case of urban areas, the primary sector has the least share with just 6.7%. Therefore, activities like agriculture or mining are not the major source of employment in urban areas.
- The secondary sector gives employment to about 35% of the urban workforce.
- People are mainly engaged in the service sector with 58.3% of urban workers.
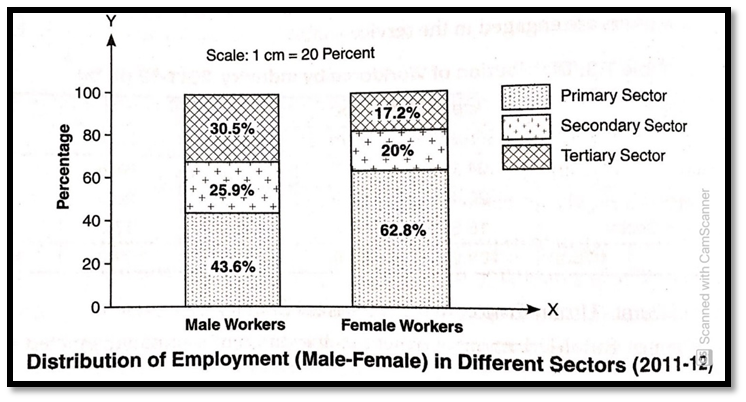
Distribution of Employment (Male-Female) in Different sectors

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
