Aggregate Demand & Related concepts
AGGREGATE DEMAND
Definition: Aggregate demand refers to the total demand for final goods and services in an economy during an accounting year.
Aggregate demand is aggregate expenditure on ex-ante (planned) consumption and ex-ante (planned) investment that all sectors of the economy are willing to incur at each income level.

 Components of Aggregate Demand:
Components of Aggregate Demand:
Private (or Household) consumption demand
The total expenditure incurred by all the households of the country on their personal consumption is known as private consumption expenditure.
Consumption demand depends mainly on disposable income and propensity to consume.
Private investment demand
Private investment demand refers to the demand for capital goods by private investors.
It is addition to the existing stock of real capital assets such as machines, tools, factory – building etc.
Investments demand depends upon marginal efficiency of capital (Marginal efficiency of investment) and interest rate.
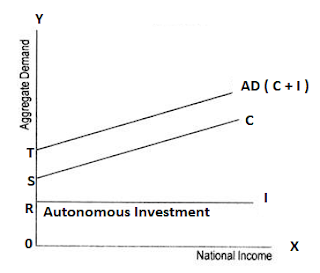
Investment is of two types, Autonomous Investment and Induced investment, but in Keynes theory investment is assumed to be Autonomous.
The basic difference between Induced Investment and Autonomous Investment
Government Expenditure
Government demand for goods and services. Its curve is upward sloping rises up to Right.
In a modern economy, the government is an important buyer of goods and services.
It is income inelastic, i.e., it is not affected by change in income level. The volume of autonomous investment is the same at all levels of income.
Its curve is a straight line parallel to horizontal axis.
The government demand may be because of public needs for roads, schools, hospitals, power, etc, for the maintenance of law and order and for defence.
Demand for net export (X – M)
Net export represents foreign demand for goods and services produced by an economy.
When exports exceed imports, net exports is positive and when imports exceed, net exports is negative.
Exports and imports of a country are influenced by a number of factors such as foreign trade policy, exchange- rate, prices and quality of goods etc.
Thus, aggregate demand consists of these four types of demand.
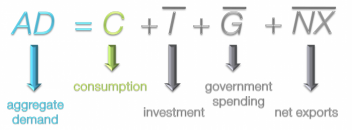
However, for the sake of simplicity Keynes included only two types of demand,
-> Consumption demand (C)
-> Investment demand (I)
Diagrammatic representation of AD
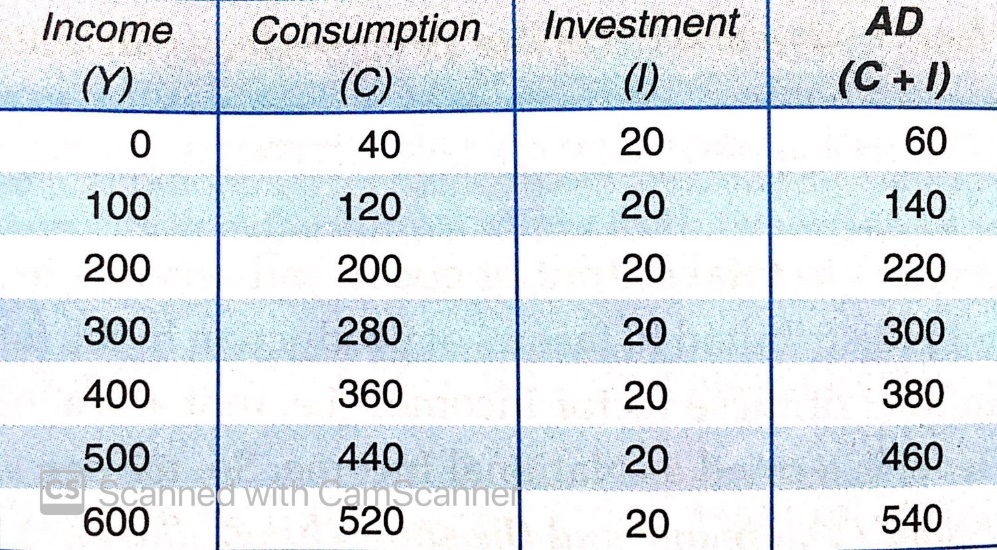
AGGREGATE DEMAND SCHEDULE

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
