- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Chemistry Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Chemistry
Vitamins
Definition : Vitamins may be defined as a group of biomolecules which are required in small amounts for normal metabolic process and for the life, growth and health of human beings and animals.
Sources of Vitamins : Human body can synthesize vitamin eg. some members of vitamin B complex synthesized by micro organisms present in the intestinal tract. Most of the vitamins can not be synthesize by our body. Therefore, they must be supplied in the food. Plants can synthesize almost all vitamins. Vitamin D may either be supplied in the food or may be produced in the skin by the irradiation of ergosterol (a sterol present in our body) with ultraviolet light.
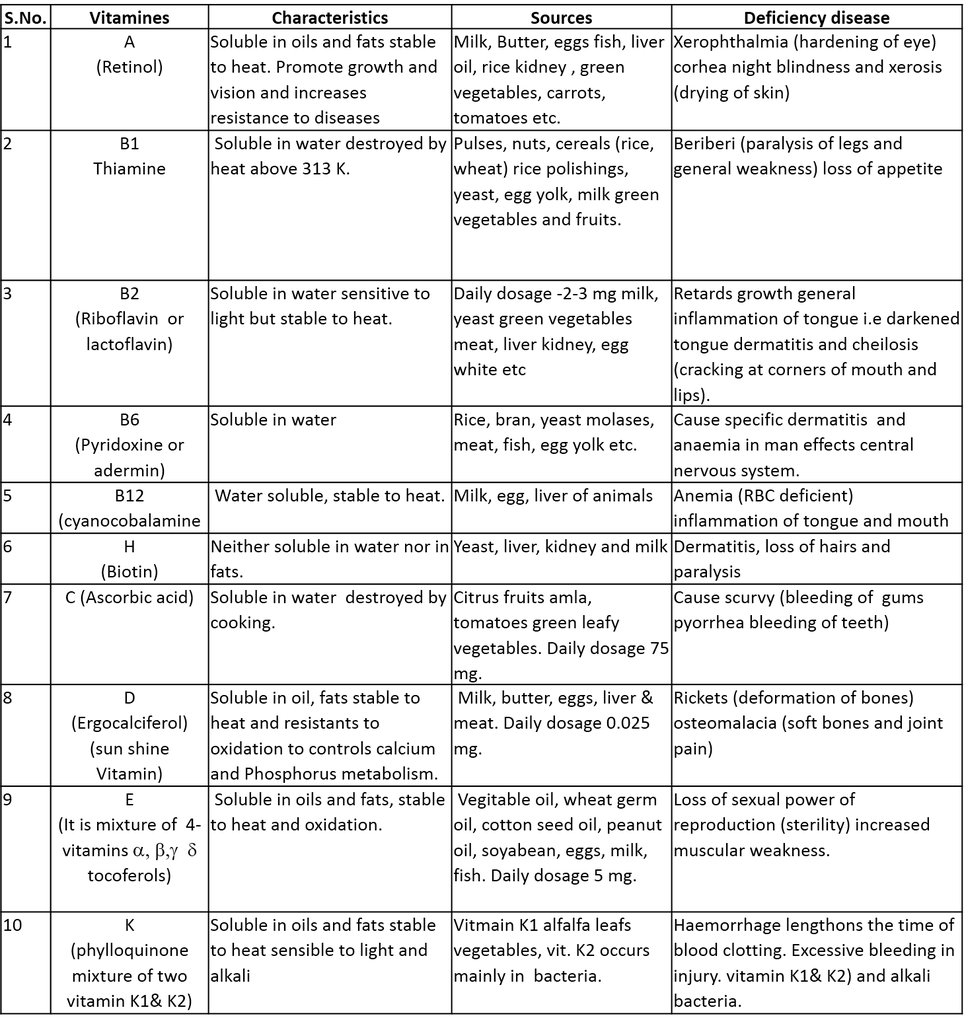
Classification of Vitamins : There is very little common to the various vitamins, therefore there are usually desiganated by alphabet letters A, B, C, D, E and K. Some of these are classified as sub groups eg. B1, B2, B3, B4, B6, B12 D1, D2 etc. About 25 vitamins are known to date. Vitamins are broadly classified into two catagories.
(i) Water soluble vitamins : Vitamin B-complex and vitamin C are water soluble vitamins and must be supplied regularly in diet.
(ii) Fat soluble vitamins : These are oily substances and soluble in fats These are A,D,E and K. They are stored in liver and adipose (fat storing) tissues.
(iii) Biotin (Vitamin H) : It is neither soluble in water nor in fats. Lack of particular vitamin causes a specific deficinecy disease. Some important vitamins their characteristics, sources and deficiency diseases are summarised in the following table.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
