- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Chemistry Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Chemistry
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Introduction :
Compounds containing the carboxyl group are distinctly acidic and are called carboxylic acids.There general formula is CnH2nO2.
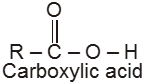
Carboxylic acid derivatives are compounds with functional groups that can be converted to carboxylic acids by a simple acidic or basic hydrolysis. The most important acid derivatives are esters, amides, nitriles, acid halides and anhydrides.
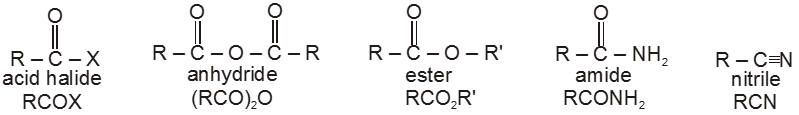
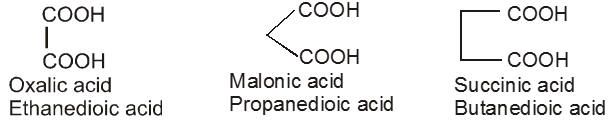
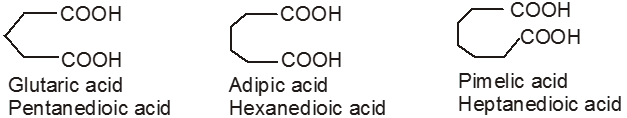
Dicarboxylic acids :
If the compound containing two carboxyl groups, these are known as dicarboxylic acid.
For example :
Physical properties of acids and acid derivatives :
(1) Boiling point : The boiling point of carboxylic acids are higher than that of alcohols, ketones or aldehydes of similar molecular weight.
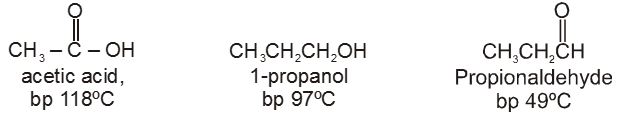
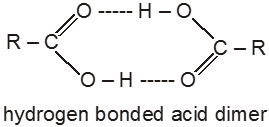
The high boiling points of carboxylic acids is the result of formation of a stable hydrogen-bonded dimer.
(2) Melting points :
Melting point of carboxylic acids : There is no regular pattern in melting point of carboxylic acid (up to 10 carbon atoms) having even number of C atoms are higher than neighbouring members having odd number of C atoms because carboxylic acid and methyl group in even members lie in opposite side of zig-zag carbon chain hence they fit better into crystal lattice resulting in higher melting points.Vice-versa is observed in case of carboxylic acid having odd no. of carbon atoms.

Amides have surprisingly high boiling points and melting points compared with other compounds of similar molecular weight. Primary and secondary amides participate in strong hydrogen bonding.
(3) Solubility:
Carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonds with water and the lower molecular - weight carboxylic acids (upto 4 carbon atoms) are miscible with water.
Acid derivatives (esters, acid chlorides, anhydrides, nitriles and amides) are soluble in common organic solvents such as alcohols, ethers, chlorinated alkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons. Acid chlorides and anhydrides cannot be used in nucleophilic solvents such as H2O and alcohols, because they react with these solvents.
(4) Aliphatic carboxylic acids upto nine carbon atoms are colourless liquids at room temperature, higher acids are wax like solids due to their low volatility.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
