- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Chemistry Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Chemistry
Enzymes and Hormones
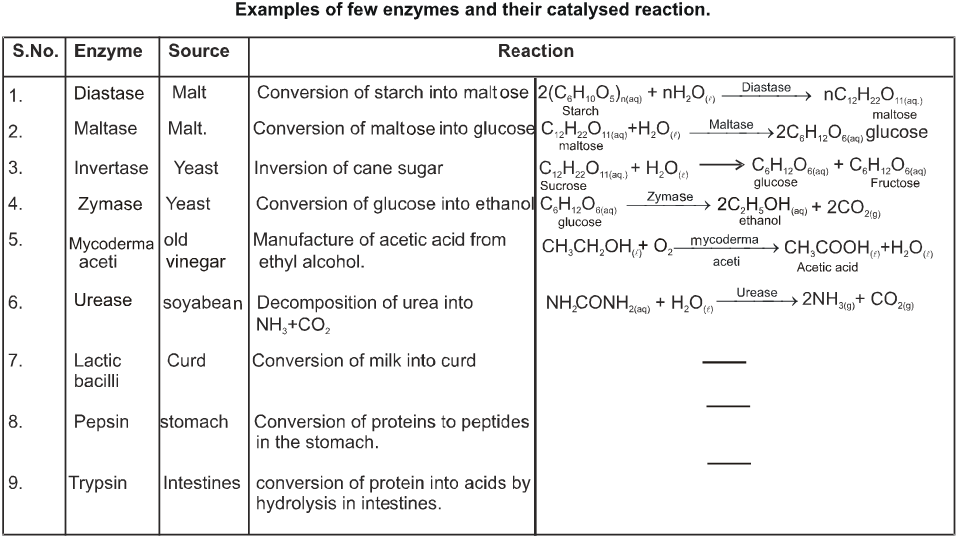
Enzymes :
Nitrogenous complex compounds with basic nature are called Enzymes. Enzymes are biological catalysts. All biological reactions are catalysed by enzyme. Enzyme lower the activation energy thereby increasing the rate of the reaction. For example activation energy for acid hydrolysis of sucrose is 6.22 KJ mol–1, while hydrolysis by SUCRASE enzyme the activation energy is 2.15 KJ mol–1.
Composition of enzymes :
Chemically all enzymes are globular proteins. However some enzymes are also associated with some non-protein component called the cofactor. For their activity. These cofactors are of two types : -
(a) Inorganic ions, such as Zn2+, Mg2+ , Mn2+ , Fe2+ , Cu2+ , Co2+ , Mo3+ , K+, Na+ etc
(b) organic molecules :- These are also of two types.
(i) Coenzymes : These are small organic molecules which are loosely held to protein and can be easily separated by dialysis. These are usually derived from vitamins such as thiamine, riboflavin, niacin etc.
(ii) Prosthetic group : These are also organic molecules which are tightly held to protein by covalent bonds but can be separated by only careful hydrolysis. Most of these are derived from vitamins such as biotin. Enzymes are vital for biological process without them the life process would be very slow. For example with out enzyme the meal would take 50 years to digest.
Characteristics of Enzymes :
(i) Specificity : Each enzyme catalyses only one chemical reaction.
(ii) Efficiency : Enzymes are very efficient catalyst. They increase the rate of reaction by 10 times.
(iii) Small quantity :- Only small amount of enzyme can be highly efficient because, they are regenerated after their catalytic activity
(iv) Optimum temp. and pH :- Enzymes catalyse reactions at pH of 7.4 and temperature range is 298-310 K (25ºC to 37ºC) (Exception pepsin work at pH 2–3)
Application of Enzymes :
(i) In the manufacture of BEER and WINE and vinegar by the fermentation of carbohydrates.
(ii) In the manufacture of sweet syrup from corn starch.
(iii) In the production of cheese by coagulation of milk.
(iv) Enzymes are helpfull mainly in the digestion process. Besides enzymes are used for controlling diseases such as
- Albinism diseases caused by the deficiency of the enzyme tryosinase
- streptokinase is used to dissolve blood clots in the treatment of heart disease.
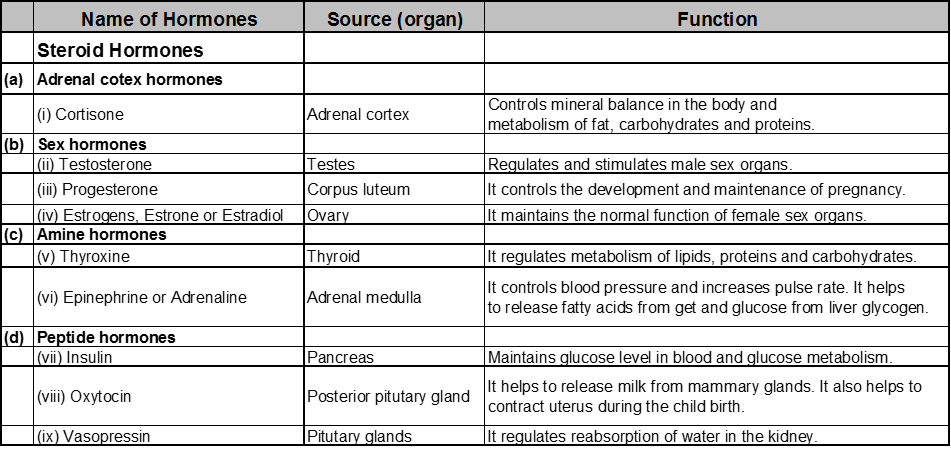
Hormones :
These are the chemicals which are secreted by ductless glands and transported to different parts of the body by the blood stream where they control different physiological action of the body. The word hormone is derived from Greek language, which means to gear up or to excite. Hormones control cell and tissue growth, heart beat, blood pressure, secretion of digestive enzymes, kidney function, the reproductive system and lactation, etc. In mammals, the secretion of the hormones is controlled by anterior lobe of the pitutary gland located at the base of brain. These hormones are then carried to other gland such as adrenal cortex and sex glands to stimulate the production of other hormones.
Classification of hormones: On the basis of structure and composition, hormones are classified into following types:
(i) Steroid hormones:
These hormones are composed to steroid nucleus having following structure:
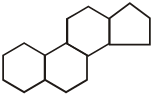
These are mostly secreted by Testes and adrenal cortex of males and hence, called as adrenal cortex hormones or sex hormones. Examples of these hormones are androgens Testosterones and dihydro testosterone. These hormones are stimulant of male sex characteristics. In females, sex hormones are estrogens. These hormones are produced in ovaries.
(ii) Polypeptides hormones :
These hormones are polypeptide (protein). These hormones are secreted by posterior lobe of the pitutary gland. eg. oxytocin, vasopressin.
(iii) Amine hormones :
These are water soluble hormones containing amino groups. These are derived from amino acids.
e.g thyroxine and adrenaline.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
