- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Chemistry Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Chemistry
COMPOUNDS OF XENON
Xenon–FLUORINE compounds :
All fluorides of xenon are white solids. They are volatile, readily subliming at room temperature (298 K)
![]()
They can be stored indefinitely in nickel or monel metal containers.
Xenon difluoride
Xe + F2 (2 : 1 mixture) ![]() XeF2 .
XeF2 .
It is soluble in water, giving solution 0.15 M at 0ºC. The solution which have pungent smell due to XeF2 are powerful oxidizing agents.
XeF2(aq) + 2H+ + 2e– ® Xe + 2HF(aq) ; Eº = + 2.64 V
XeF2 + H2 ®2 HF + Xe
Hydrolysis is slow in water due to dissolution of XeF2 in HF formed, but is rapid in basic solution.
2Xe F2 + 2H2O ®2 Xe + 4HF + O2
XeF2 + 2OH– ® Xe + ![]() O2 + 2F– + H2O
O2 + 2F– + H2O
It acts as fluoride ion donor XeF2 (Lewis base) + PF5 (Lewis acid) [XeF]+ [PF6]–
Xenon tetrafluoride
Xe + 2F2 (1 : 5 mixture) 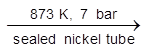 XeF4
XeF4
XeF4 reacts violently with water, giving dangerously explosive XeO3.
6XeF4 + 12H2O ® 4Xe + 2 XeO3 + 24 HF + 3O2
XeF4 can act as F– acceptor as well as F– donors and thus form anionic species in reactions such as :
XeF4 + NaF ® Na+ XeF5–
XeF4 + SbF5 ® [XeF3]+ [SbF6]–
Xenon hexafluoride
Xe + 3F2 (1 : 20 mixture) ![]() XeF6
XeF6
XeF4 + O2 F2 ® XeF6 + O2
XeF6 reacts violently with water but slow hydrolysis with atmospheric moisture giving XeO3.
XeF6 + 6 H2O ® XeO3 + 6HF (complete hydrolysis)
With small quantities of water, partial hydrolysis takes place.
XeF6 + H2O ® XeOF4 (colourless liquid) + 2HF
XeF6 + 2 H2O ® XeO2F2 + 4HF
XeF6 reacts with fluoride ion donors to form fluoroanions.
XeF6 + MF® M+ [XeF7]– (M = Na, K, Rb or Cs)
Xenon–oxygen compounds :
Hydrolysis of XeF4 and XeF6 with water gives XeO3.
6 XeF4 + 12 H2O ® 4 Xe + 2 XeO3 + 24 HF + 3 O2
XeF6 + 3 H2O ® XeO3 + 6 HF
Partial hydrolysis of XeF6 gives oxyfluorides, XeOF4 and XeO2F2 .
XeF6 + H2O ®XeOF4 + 2 HF
XeF6 + 2 H2O ® XeO2F2 + 4 HF
XeO3 is a colourless explosive solid and has a pyramidal molecular structure. XeOF4 is a colourless volatile liquid and has a square pyramidal molecular structure.
Uses :
Helium is a non–inflammable and light gas. Hence, it is used in filling balloons for meteorological observations. It is also used in gas–cooled nuclear reactors. Liquid helium (b.p.4.2 K) finds use as cryogenic agent for carrying out various experiments at low temperatures. It is used to produce and sustain powerful superconducting magnets which form an essential part of modern NMR spectrometers and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) systems for clinical diagnosis. It is used as a diluent for oxygen in modern diving apparatus because of its very low solubility in blood.
Neon is used in discharge tubes and fluorescent bulbs for advertisement display purposes. Neon bulbs are used in botanical gardens and in green houses.
Argon is used mainly to provide an inert atmosphere in high temperature metallurgical processes (arc welding of metals or alloys) and for filling electric bulbs. It is also used in the laboratory for handlsing substances that are air–sensitive.
Xenon and Krypton are used in light bulbs designed for special purposes

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
