- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Chemistry Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Chemistry
PHOSPHORUS
It occurs in nature in the form of stable phosphates. (Animal bones also contain calcium phosphate (58 %)). The important minerals are:
(i) Phosphorite, Ca3(PO4)2
(ii) Chloraptite, Ca3(PO4)2CaCl2
(iii) Fluoraptite, Ca3(PO4)2CaF2
(iv) Vivianite, Fe3(PO4)2·8H2O (v) Redonda phosphate, AlPO4
Phosphorus Allotropic Forms :
Phosphorus is found in many allotropic forms , the important one being white , red and black.
White phosphorus :
Preparation :
2Ca3(PO4)2 (f`rom bone-ash) + 10C + 6SiO2 ![]() 6CaSiO3 + 10CO + P4(s) (electric furnace method)
6CaSiO3 + 10CO + P4(s) (electric furnace method)
It is a translucent white waxy solid. It is poisonous , insoluble in water but soluble in carbon disulphide. Molecular formula is P4. Ignition temperature is around 30ºC.
When exposed to air it undergoes oxidation which gradually raises it temperature and ultimately catches fire when the temperature exceeds 30ºC. That is why it is kept in water. White phosphorus is less stable and therefore , more reactive than the other solid phases under normal conditions because of angular strain in the P4 molecule where the angles are only 600.
It glows in dark due to slow oxidation. This property is called phosphorescence (chemiluminescence).
P4 + 5O2 ® P4O10
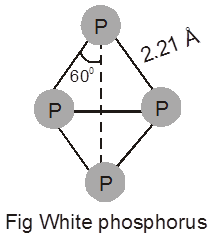
It consists of discrete tetrahedral P4 molecule as shown in Fig.
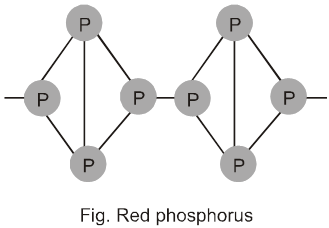
Red phosphorus is obtained by heating white phosphorus at 573 K in an inert atmosphere of CO2 or coal gas for several days. This red phosphorous may still contain some white phosphorus which is removed by boiling the mixture with NaOH when white phosphorus is converted in to PH3 gas but red phosphorus remains inert.
P4 + 3NaOH + 3H2O ® PH3(g) + 3NaH2PO2
When red phosphours is heated under high pressure, a series of phase of black phosphorus are formed. Red phosphorus possesses iron grey lustre. It is odourless , non – poisonous and insouble in water as well as in carbon disulphide. Chemically, red phosphorus is much less reactive than white phosphorus. It does not glow in the dark. Ignition temperature is 260ºC. It is polymeric, consisting of chains of P4 tetrahedra linked together in the manner as shown in Fig.
Black phosphorus has two forms a– black phosphorus and b – black phosphorus , a – Black phosphorus is formed when red phosphorus is heated in a sealed tube at 803 K. It can be sublimed in air and has opaque monoclinic or rhombohedral crystral. It does not oxidise in air.b – Black phosphorus is prepared by heating white phosphorus at 473 K under high pressure. It does not burn in air upto 673 K.
b - black phosphorus is a good conductor of electricity whereas a -Black phosphorus is non-conductor.
b - black phosphorus has layered structure like graphite. The distance between the two layers is found to be 3.68 Å.
Density : White phosphorus= 1.83 ; Red phosphorus = 2.20 ; Black phosphorus = 2.70 gm/cc ;
As polymerisation increases compactness increases and therefore, density increases.
Reactivity of the various allotropic forms of phosphorus towards other substances decreases in the order:
white > red > black, the last one being almost inert i.e. most stable.
Apart from their reactivity difference, all the forms are chemically similar.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
