- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Chemistry Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Chemistry
Preparation methods of Aldehydes and Ketones
By oxidation of alcohols :
Primary alcohols ![]() Aldehydes
Aldehydes
Secondary alcohols ![]() Ketones
Ketones
By dehydrogenation of alcohols :
Dehydrogenation means removal of hydrogen and reagent used is heated copper.
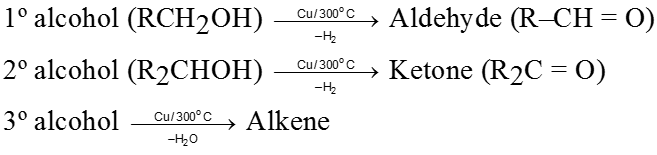
Ozonolysis of alkene :
It is used to get carbonyl compounds from alkene. The reaction is
Note :
(i) During the cleavage of ozonide Zn is used to check further oxidation of aldehyde into acid.
(ii) By this method we can locate double bond in olefin or exact structrue of hydrocarbon can be determined by knowing ozonolysis product i.e. by placing double bond at the place of two carbonyl oxygen atoms of two carbonyl compounds.
(iii) Among the three molecules of carbonyl compounds.
(a) If one molecule contains two carbonyl groups, then hydrocarbon will be alkadiene.
(b) If all the three molecules contain two carbonyl group then hydrocarbon will be cycloalkatriene.
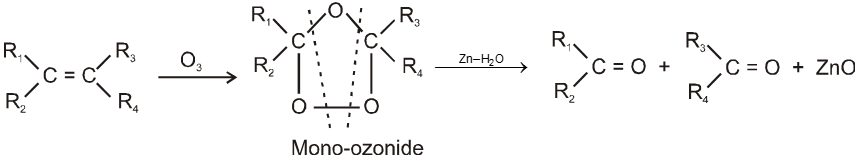
Wacker process :
Alkenes can directly be oxidised to corresponding aldehydes or ketones by treating them with a solution of PdCl2 containing a catalytic amount of CuCl2 in presence of air or O2 . Except ethene any higher alkene will give ketone.
Note : During the reaction PdCl2 is reduced to Pd and CuCl2 is reduced to Cu(I)
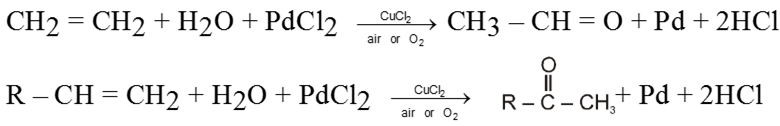
Hydration of alkynes :
![]()
Other alkynes give ketones in this reaction.
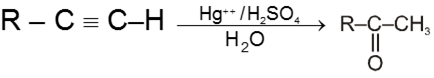
Hydroboration of alkyne :
It is used to get aldehyde from terminal alkyne. Here reagent is (i) diborane (B2H6) (ii) H2O2,OH–
![]()
In this reaction Borane (BH3) is act as electrophile.
Dry distillation of calcium salt of acid :
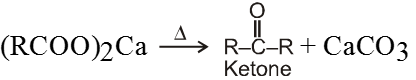
Ex.
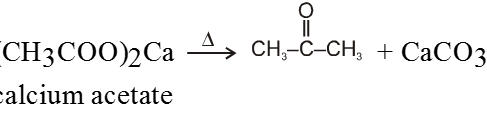
On dry distillation of calcium salt of acetic acid with calcium salt of formic acid we get a mixture of aldehyde, ketone and formaldehyde.
On passing vapours of fatty acids over Mangnous oxide at 300ºC :
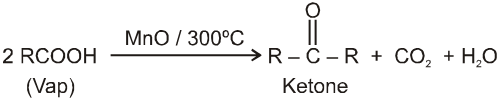
On passing mixture of vapours of fatty acid with formic acid we get a mixture of aldehyde, ketone and formaldehyde.
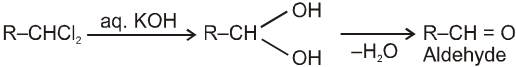
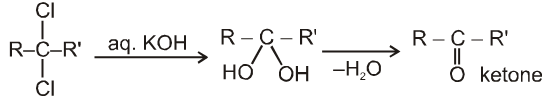
On aqueous alkali hydrolysis of gem-dihalides :
Terminal gemdihalides will give aldehyde while non-terminal will give ketone as follows

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
