- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Chemistry Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Chemistry
Types of Solids (Amorphous/Crystalline)

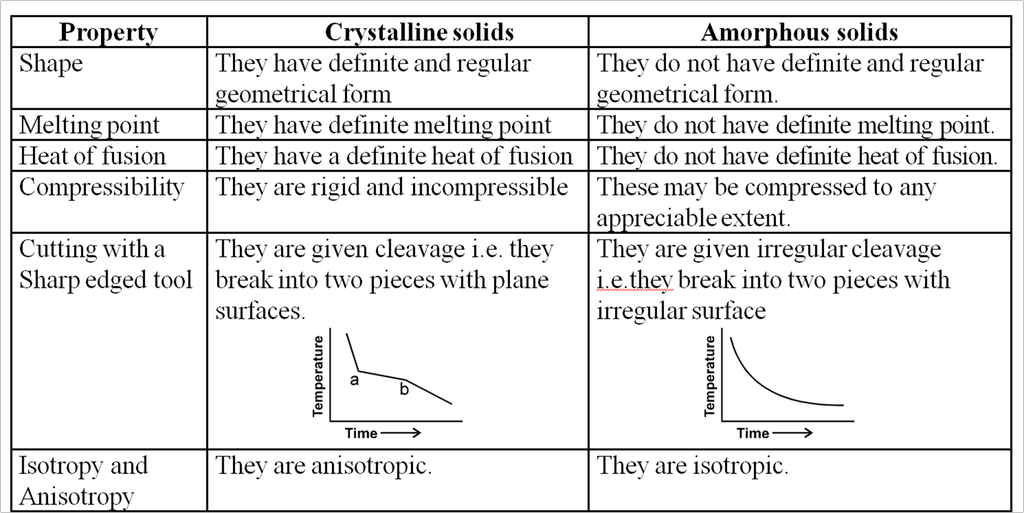
Crystalline solids :
(a) In this type of solids the atoms or molecule are arranged in a regular pattern in the three dimensional network.
(b) They have well defined geometrical pattern, sharp melting point, definite heat of fusion and anisotropic nature.
(c) Anisotropic means they exhibit different physical properties in all directions.
e.g. The electrical and thermal conductivities are different directions.
(d) They are generally incompressible.
(e) The general examples of crystalline solids are as Quartz, diamond etc.
Amorphous Solids :
(a) In this type of solids, the arrangement of building constituents is not regular.
(b) They are regarded as super cooled liquids with high viscosity in which the force of attraction holding the molecules together are so great, that the material becomes rigid but there is no regularity in structure.
(c) They do not have sharp melting points.
(d) They are isotropic as they exhibit same physical properties in all the directions.
(e) The general examples of this solids are as glass, Rubber, plastics etc.
Difference between crystalline and amorphous solids :

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
