- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Chemistry Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Chemistry
Ethers
Preparation of ether :
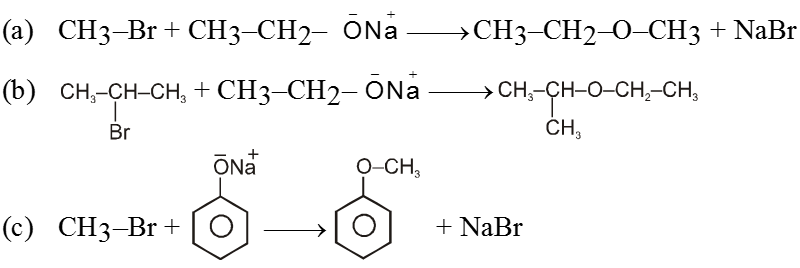
(i) From Wiliamsons synthesis method :
![]()
Ex.
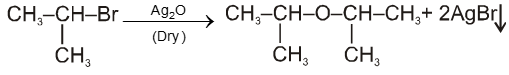
(ii) By using dry Ag2O :
![]()
Ex.
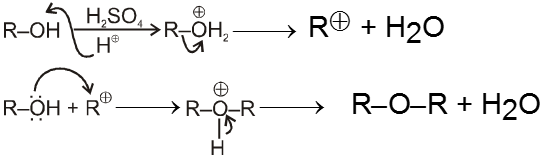
(iii) From alcohols :
![]()
(Trace)
- By intermolecular dehydration of alcohols ethers can be prepared in presence of trace amount of H2SO4.
Mechanism :
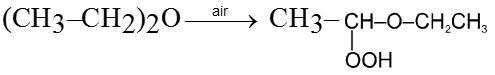
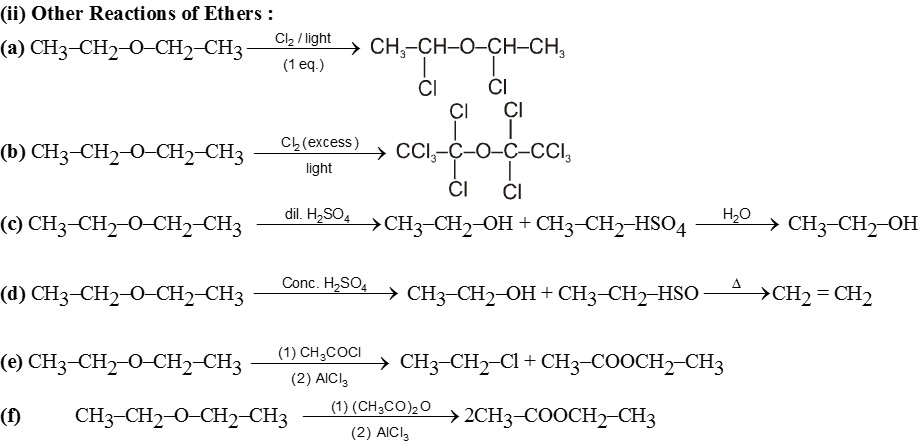
Purification of ethers :
On standing in contact with air they form unstable peroxide (R2O ® O) which is explosive in nature. Peroxide is formed at the carbon atom next to the etherial oxygen.
- The presence of peroxide in ether can be identified on shaking it with freshly prepared ferrous sulphate solution followed by addition of potassium thiocyanate. This result into red colour of ferric thiocyanate. During the reaction peroxide oxidises Fe2+ to Fe3+ which reacts with thiocyanate ion to give red colour of ferric thiocyanate.
![]()
(Red colour)
- Ethers are purified from peroxide before use. The peroxide from ether can be removed by treating ether with KI solution where peroxide is reduced to ether and iodide ion is oxidised to I2 molecule.
- Peroxide formation can be checked by adding few ammount of Cu2O in ether
- Ether is lewis base hence forms co-ordinate bond with lewis acid
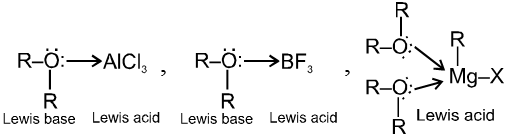
Chemical properties of ethers :
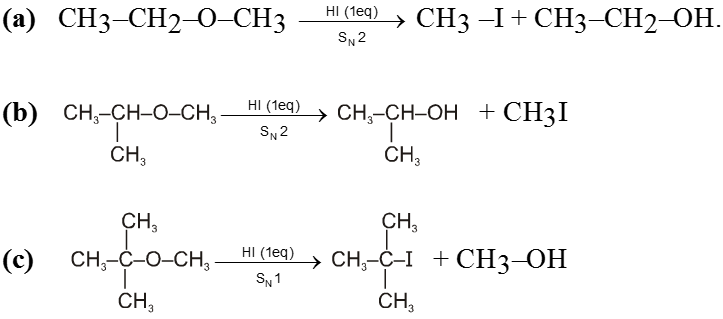
(i) Reaction with HI :
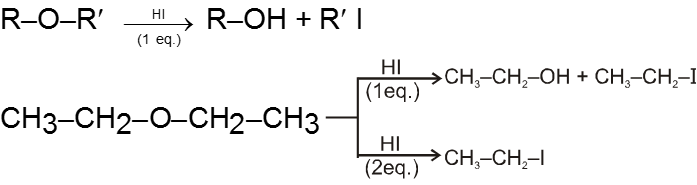
- Those protic acids whose conjugate base is a good nucleophile leads to cleavage of ethers. HI is such a very prominent acid of this kind.
- In most cases of unsymmetrical ethers 1 eq. of HI leads to give a mixture of four products in which it is not possible to predict the major product. However if 2 eq. of HI is used then two iodides are obtained.
Ex.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
