- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Chemistry Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Chemistry
DIOXYGEN (O2)
It differs from the remaining elements of the VIth group because of the following properties.
(A) small size
(B) high electronegativity and
(C) non-availability of d-orbitals.
Preparation :
(i) By thermal decomposition of oxides of metals.
2 HgO ![]() 2 Hg + O2
2 Hg + O2
2 Ag2O ![]() 4 Ag + O2
4 Ag + O2
(ii) By thermal decomposition of oxygen rich compounds.
KClO3 ![]() 2 KCl + 3O2 (laboratory method)
2 KCl + 3O2 (laboratory method)
(iii) 2H2O2(aq.) ![]() 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
2H2O(l) + O2(g)
(iv) Industrial method :
(a) Electrolysis of water leads to the release of hydrogen at the cathode and oxygen at the anode.
(b) Oxygen is obtained by liquification of air and then its fractional distillation.
Physical properties :
Colourless , odourless and tasteless gas. It is paramagnetic and exhibits allotropy. Three isotopes of oxygen are ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() . Oxygen does not burn but is a strong supporter of combustion.
. Oxygen does not burn but is a strong supporter of combustion.
Chemical properties :
(i) Reaction with metals :
2Ca + O2 —® 2CaO
4Al + 3O2 —® 2Al2O3
(ii) Reaction with non-metals :
P4 + 5O2 —® P4O10
C + O2 —® CO2
(iii) Reaction with compounds :
2ZnS + 3O2 —® 2ZnO + 2SO2
CH4 + 2O2 —®CO2 + 2H2O
2SO2 + O2 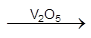 2SO3
2SO3
4HCl + O2 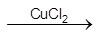 2Cl2 + 2H2O
2Cl2 + 2H2O
Note : It has been observed that its combination with other elements is often strongly exothermic which helps in sustaining the reaction. However, to initiate the reaction, some external heating is required as bond dissociation enthalpy of oxygen-oxygen double bond is high (493.4 kJ mol–1).
Use :
1. Oxygen mixed with helium or CO2 is used for artificial respiration.
2. Liquid oxygen (with combustion fuel hydrazine) is used as oxidising agent in rocket fuels.
3. Oxygen is used for production of oxy-hydrogen or oxy-acetylene flames employed for cutting and welding.
4. Pure dioxygen is used to convert pig iron into steel in the basic oxygen process which are kaldo and LD process.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
