- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Chemistry Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Chemistry
Chapter 12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes and Ketones
Introduction
Aldehydes & ketones have general formula CnH2nO and contains >C = O group. Thus aldehydes (R–CHO) and ketones (R–CO–R) are collectively called as carbonyl compounds. Aldehyde is always at terminal position while ketone is never at terminal position.
Structure and bonding in aldehydes and ketones
The carbonyl carbon atom is sp2 hybridized. The un hybridized p-orbital overlaps with a p-orbital of oxygen to form a pi bond. The double bond between carbon and oxygen is shorter, stronger, and polarized.
Orbital diagram for the formation of carbonyl group is as follows:
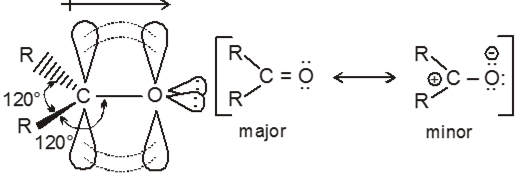
This polarity confirms that there is nucleophilic addition reaction takes place in carbonyl compound.
The double bond of the carbonyl group has a large dipole moment because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon.
Carbonyl carbon act as an electrophile (Lewis acid)
Carbonyl oxygen act as a nucleophile (Lewis base)

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
