- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
CAPITAL STRUCTURE
Financial risk?
- The risk of default on the payment of debt.
- Higher use of debt increases the financial risk of a business
Capital Structure
- Refers to the mix of debt and equity
Optimum Capital Structure
- Proportion of debt and equity that results in an increase in the value of shareholders (higher E.P.S)
Factors affecting the Choice of Capital Structure:
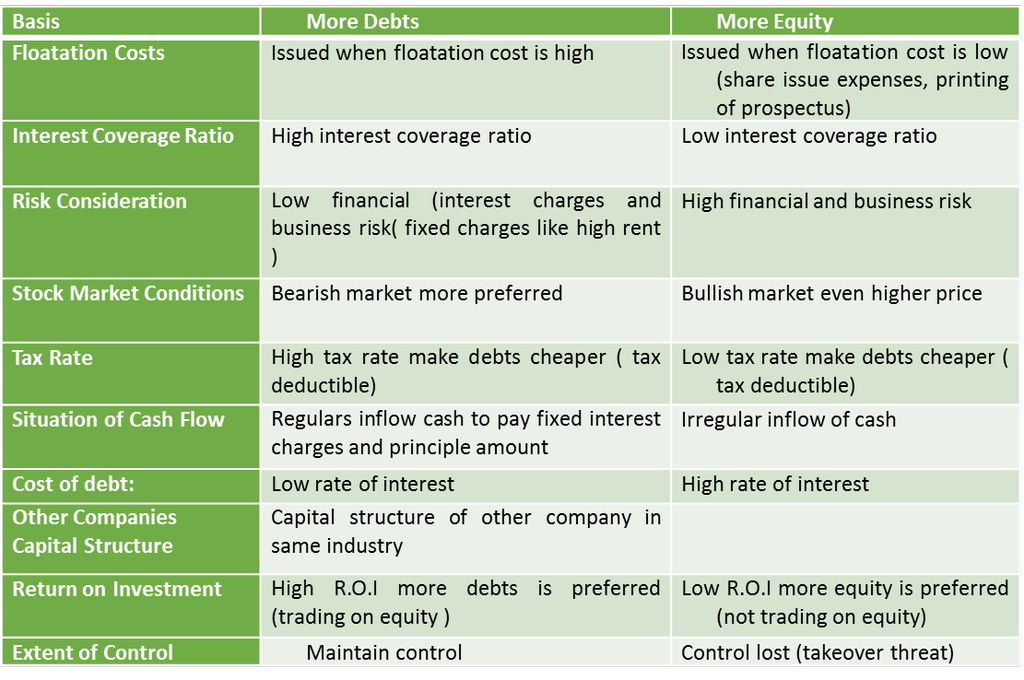
- Cash Flow Position: Cash flows must not only cover fixed cash payment obligations but there must be sufficient safeguards also. It must be kept in mind that a company has cash payment obligations for normal business operations.
- Interest Coverage Ratio: refers to the number of times earnings before interest and taxes of a company cover the interest obligation. The higher the ratio, the lower is the risk of the company failing to meet its interest payment obligations.
- Formula for calculating ICR = EBIT/interest.
- Return on Investment: If the ROI of the company is higher, it can choose to use trading on equity to increase its EPS, i.e., its ability to use debt is greater.
- Cost of debt: A firm’s ability to borrow at a lower rate increases its capacity to employ higher debt. Thus, more debt can be used if the debt can be raised at a lower rate.
- Tax Rate: Since interest is a deductible expense, the cost of debt is affected by the tax rate makes debt relatively cheaper.
- Floatation Costs: Public issue of shares and debentures requires large expenditure. Getting a loan from a financial institution may not cost so much.
- Risk Consideration: Debt increases the financial risk to meet fixed interest payments and repayment obligations. If a firm’s business risk is lower, its capacity to use debt is higher and vice-versa.
- Flexibility: If a firm uses its debt potential to the full, it loses the flexibility to issue further debt. To maintain flexibility, it must maintain some borrowing power to take care of unforeseen circumstances.
- Control: A company that wants to retain control can use debts( up to a certain extent) . A public issue of equity may reduce the management holding in the company and may cause a takeover threat
- Regulatory Framework: Every company operates within a regulatory framework provided by the law e.g., public issues of shares and debentures have to be made under SEBI guidelines.
- Stock Market Conditions: If the stock markets are bullish, equity shares are more easily sold even at a higher price. During a bearish phase, a company may find rising equity capital more difficult and it may opt for debt.
- Capital Structure of other Companies: A useful guideline in capital structure planning is the debt-equity ratios of other companies in the same industry
SUMMARY:

 ABCD CLASSES
ABCD CLASSES
