- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
Taylor’s Contribution to Scientific Management
- Science not Rule of Thumb:
- It states that there was only one best method to maximize efficiency.
- This method can be developed through scientific study and analysis of each element of a job and should substitute ‘Rule of Thumb’.
- This standard method should be followed throughout the organization. Involved investigation of traditional methods through work-study, and develop one best method to maximize efficiency
- Adopt the best practices to save human energy, wastage of time and materials
- Example - Sending information by e-mail instead of a post is more effective
- Harmony, Not Discord:
- There should be absolute understanding and harmony between workers and management.
- Both should realize that each one is important
- Management should share the gains of the company with the workers.
- In return, workers should work hard with discipline and loyalty
- Prosperity for the employer cannot exist for a long time unless it is accompanied by prosperity for the employees and vice versa’
- Cooperation, Not Individualism:
- Extension of principle of ‘Harmony not discord.
- Competition should be replaced by cooperation.
- Management should award workers for giving valuable suggestions and involves in decision making
- Workers should avoid making unreasonable demands and strikes
- The employer takes care of the needs of employees, which would prevail as in the case of Japanese companies.
- Development of Each and Every Person to His or Her Greatest Efficiency and Prosperity:
- Industrial efficiency depends upon the efficiency of workers. Workers' efficiency depends upon proper training and their selection
- Employees with the required qualification and experience should be selected.
- Provide training to the selected employees to make them fit and confident in doing their duties.
- Assign work that suits her/his physical, mental and intellectual ability
- Efficient employees would produce more and earn more. This will ensure the greatest efficiency and prosperity for both company and workers
Studies of Taylor
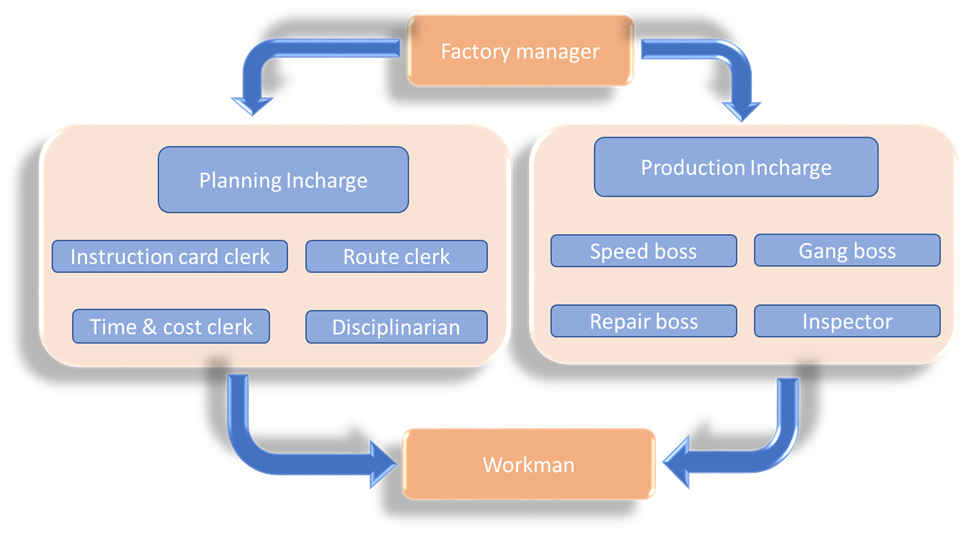
Functional Foremanship:-Separation of planning and execution functions which is extended to the lowest level of the shop floor
- Extension of the principle of division of work.
- Each worker will have to take orders from the eight foremen
- Under the factory manager, there was planning in charge and production in charge.
Planning in charge: In the planning officer, four foremen exist according to Taylor.
- Route clerk: specify the route of production
- Card and instruction clerk: issue various instructions to workers to carry on the job
- Time and cost clerk: fix the time for starting and completing of job and prepares a cost sheet.
- Disciplinarian: maintains discipline among the employee.
Production in charge: In the production officer four specialist bosses are existing.
- Gang boss: makes arrangements for machinery, material, tools etc. for the job
- Speed boss: checks the speed of work and investigates the cause for delays and removes them.
- Repair boss: maintains the machinery and other equipment and makes proper repairs.
- Inspector: checks the quality of work.
Standardization of Work
Standardization refers to the process of setting standards for every business activity. The company establishes a standard such as product dimensions, size, quality and then the company produces products based on that standard
Process of setting standards for every business activity; it can be standardization of process, raw material, time, product, machinery, methods, or working conditions.
The objectives
- Establish standards of quality in materials.
- Establish standards of performance of men and machines.
- To reduce a given line or product to fixed types, sizes and characteristics.
Simplification of Work
- Aims at removing unnecessary varieties, sizes and dimensions
- Simplification aims at eliminating unnecessary diversity of products.
- It results in savings of costs on labor, machines and tools.
- It implies reduced inventories, fuller utilization of equipment and increasing turnover.
Method Study
- Meaning: -find out one best way of doing the job out of various methods
- Objectives The objective of the whole exercise is to minimize the cost of production and maximize the quality and satisfaction
- Benefits: - Minimize the cost of production and maximize the quality of the customer
- Instrument used: process charts and operations research etc
Motion study
- Meaning:-Motion study refers to the study of movements like lifting, putting objects, sitting and changing positions etc., which are undertaken while doing a typical job. Unnecessary movements are sought to be eliminated so that it takes less time to complete the job efficiently.
- Purpose:- Possible to find out motions that are productive and which are unproductive
- Benefits:- Unnecessary movements are can be removed so to complete the job efficiently
- Instruments used:- stopwatches and various symbols and colors
Time Study
Meaning:-Analysis the time taken by each worker to finish a standard
Objective:-Determine number of workers to be employed Determine cost of labor Frame suitable incentive schemes
Benefits: - improving the efficiency of workers by creating time awareness
Example - standard time 1 hour @ 3 boxes, total working hour 7 hour
Instruments used: - stopwatches
Fatigue study
- There should be proper rest intervals between two work spans.
- A person will feel tired physically and mentally if she/he does not rest while working.
- Help workers regain stamina and work again with the same capacity.
- There can be many causes for fatigue like long working hours, doing unsuitable work, having cordial relations with the boss or bad working conditions, etc.
Differential Piece Wage System
- Efficient workers are paid at a higher rate for their entire output and a less efficient worker is to be paid less when the production falls below the standard.
Example
- Standard output per day = 20 units
- Wage rate for efficient workers = Rs 50 for standard output/more than standard
Wage rate for inefficient workers.

 ABCD CLASSES
ABCD CLASSES
