- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
NUMERICAL
Example I: A company requires Rs 30, 00,000 to finance its operations. The expected rate of return is 15% and the tax rate is 30%. Financing options are:
- Equity shares @ Rs 10 per share OR
- Equity @ Rs 10 per share and debt @ 10% per annum.
The calculations of EBT (Earnings before Tax), EAT (Earnings after taxes), and EPS (Earning per
Share) under the above three alternatives can be given as:
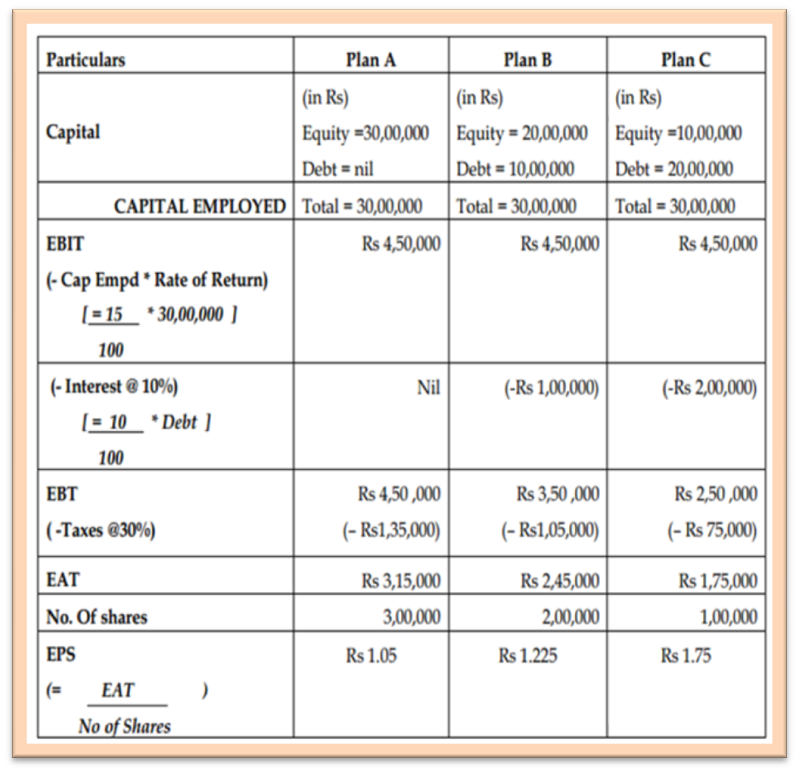
In the above example, we see that Plan C has a higher EPS as:
- Tax paid is least in Plan C as compared with tax paid in Plans A and B.
- The rate of return on investment (=15%) is more than the cost of debt (10%)
- The number of shareholders under Plan C = 1, 00,000 which is much lesser than that under plan A (3, 00,000) or B (2, 00,000).
Que. Sahil Industries needs to raise funds of Rs.30,00,000. Its expected earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) are Rs. 2,00,000. The company wishes to use more debt content as compared to equity to raise earnings per share (EPS) of equity shareholders. The debt is available at an interest of 10%. As finance Manager, advise whether the company should prefer more debt or more equity to have higher EPS. Give reasons to support your answer.
Ans. Sahil Industries should use less debt (preferably no debt) to have higher EPS because the current return on investment (ROI) is less than the cost of debt. The prevailing ROI is only 6.66% (=2,00,000/30,00,000 * 100) against the interest rate of 10%. When ROI is less than the interest rate on debt, then EPS falls with rising in use of debt. So, the company should prefer more equity to have higher EPS.
Que. Viyo Ltd.’ is a company manufacturing textiles. It has a share capital of ` 60 lakhs. The earnings per share in the previous year was ` 0.50. For diversification, the company required additional capital of ` 40 lakhs. The company raised funds by issuing 10% debentures for the same. During the current year, the company earned a profit of ` 8 lakhs on capital employed. It paid tax @40%.
(a) State whether the shareholders gained or lost, in respect of earning per share on diversification. Show your calculations clearly.
(b) Also, state any three factors that favor the issue of debentures by the company as part of its capital structure.
Answer:- Statement showing the calculation of earnings for shareholders
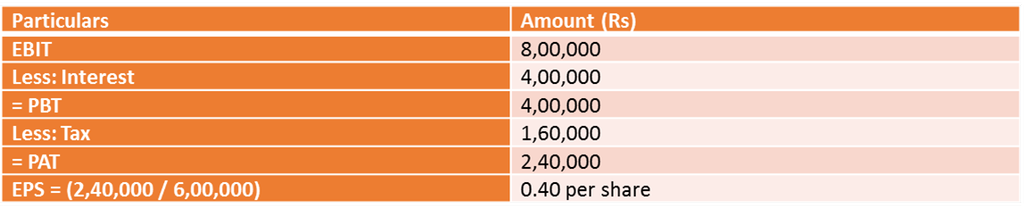
Thus the shareholders have lost wealth as earnings per share have decreased. Assuming the face value of a share is Rs 10.
Cost of Debt: As external sources of finance are always cheaper than internal sources of finance, debt helps in producing the overall cost.
- Tax Rate: Interest paid on debt is tax-deductible expenses. Due to this real cost of debt is much lower than the nominal one.
- Control: By rising debt, the control of shareholders is not diluted
Capital structure decision is essentially optimization of risk-return relationship
Ans.
i. Capital structure decision is related to the proportion of debt (risk) and equity (return).
ii. Debt is cheaper but is riskier for a business because payment of interest and the return of principal is obligatory for the business. Any default in meeting these commitments may force the business to go into liquidation. There is no such compulsion in the case of equity, which is, therefore, considered riskless for the business.
iii. Debt component in the total capital generates a higher return for equity shareholders as interest payable on debt is deductible from earning before tax payment.
iv. Thus, capital structure decision affects risk as well as return. So, it is true capital structure decision is essentially an optimization of the risk-return relationship.

 ABCD CLASSES
ABCD CLASSES
