Introduction and Importance of Consumer protection
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
CONCEPT & MEANING
Protecting consumers from unfair trade practices, adopted by the producers and sellers of goods and services is termed consumer protection. It not only includes educating consumers about their rights and responsibilities but also helps in getting their grievances redressed.

IMPORTANCE OF CONSUMER PROTECTION
From the Consumer’s point of view
- Innocent consumer
- Widespread ignorance About rights and relief’s available to it and it
- It has become necessary to educate them to achieve consumer awareness.
- Consumers Are Unorganized
- Consumers need to be organized in the form of consumer organizations to take care of their interests
- In India, consumer organizations are working to protect and promote the interests of consumers.
- Exploitation Of Consumers
- Consumers are exploited by unfair trade false and misleading advertising, hoarding, black marketing, etc.
- Consumers need protection against such malpractices of the sellers
Business Point of View:
- Social responsibility
- A business has social responsibilities towards various interest groups. Consumers form an important group among the many stakeholders of business and like other stakeholders; their interest has to be well taken care of.
- Moral Justification:
- It is the moral duty of any business to take care of consumer‘s interests and avoid any form of their exploitation.
- A business must avoid unscrupulous, exploitative and unfair trade practices like defective and unsafe products, adulteration, false and misleading advertising, hoarding, black marketing, etc.
- Intervention of Government:
- Businesses involved in any exploitative trade practices would invite the government
- Can damage the image of the company.
- Long-term Interest of Business:
- It is in the long-term interest of business to satisfy their customers.
- This leads to repeat sales and provides good feedback to prospective customers and thus, helps in increasing the customer base of business.
- It leads to long-term profit maximization through customer satisfaction
- Entrepreneur uses Society’s Resources:
- Business organizations use resources that belong to society.
- They, thus, have a responsibility to supply such products and render such services which are in the public interest and would not impair public confidence in them.
legal protection to consumers
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
LEGAL PROTECTION FOR CONSUMERS:
The Consumer Protection Act, 1986:
Meaning:-Was formed in 1986 to protect and promote the consumers’ interest through speedy and inexpensive redressal of their grievances.
Scope of consumer protection:
- Applicable to all types of undertakings, big and small,
- Whether in the private or public sector or in the co-operative sector,
- Whether a manufacturer or a trader,
- Whether supplying goods or providing services.
Consumer:
- A person who buys any goods for consideration or any user of such goods when such use is made with the approval of the buyer.
- A person who hires or avails of service for consideration or any beneficiary of such services when such use is made with the approval of the buyer.
- Consideration here means that the goods or services are either fully paid, partly paid or under a scheme of deferred payment such as an installment scheme.
- This definition does not include people who avail services for some commercial purpose or obtain goods for resale or for some commercial purpose.
Who can file a complaint?
A complaint before the appropriate consumer forum can be made by:
- Any consumer;
- Any registered consumers ‘association;
- The Central Government or any State Government;
- One or more consumers, on behalf of numerous consumers having the same interest; and
- A legal heir or representative of a deceased consumer.
Against whom a complaint can be filed?
Consumer Protection Act, 1986 is applicable to all types of undertakings, whether big or small, private or public, or in the co-operative sector, manufacturer or a trader, wholesaler or retailer, supplying goods or providing services. Thus, a complaint can be filed against:
- The seller, manufacturer, or dealer of defective goods. Defect means any fault, imperfection, or shortcoming in the quality, quantity, or purity of goods.
- The provider of services if they are deficient in any manner. Deficiency means any imperfection, shortcoming, or inadequacy in the quality, nature, and manner of performance of services.
Rights & Responsibilities of Consumer
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
RIGHTS & RESPONSIBILITIES OF CONSUMERS:
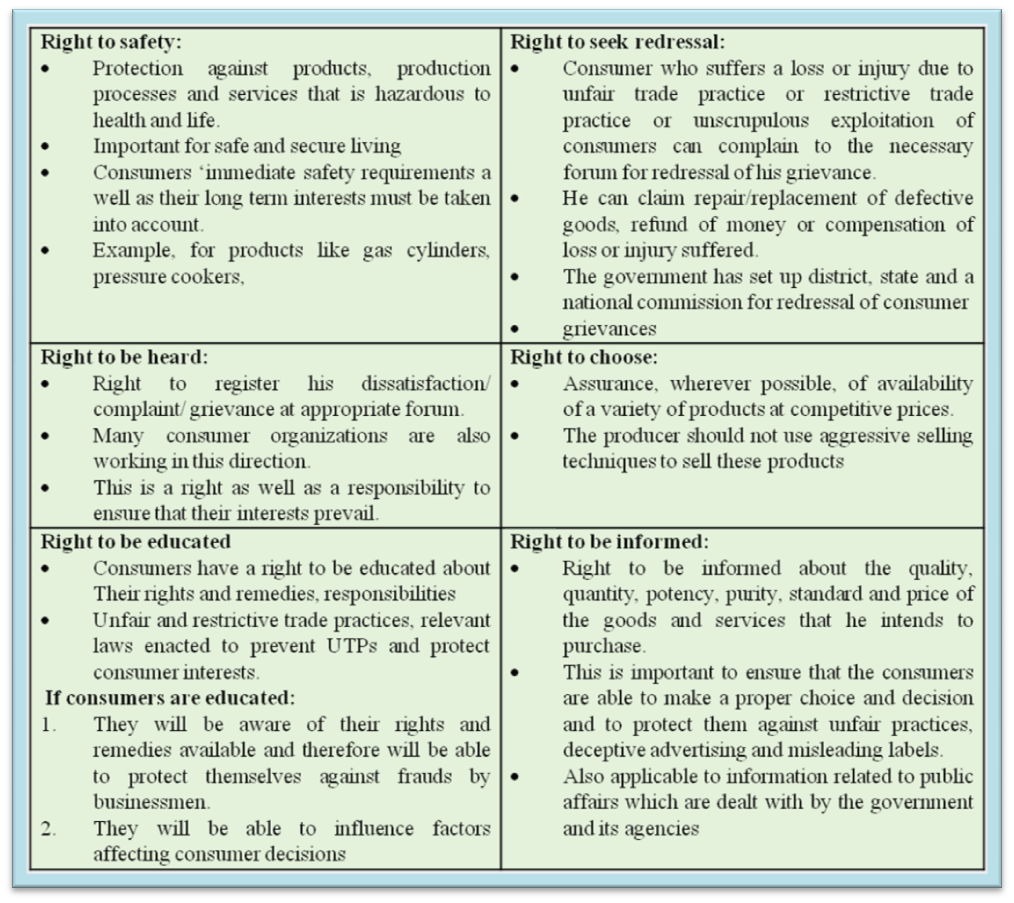
Legal Redressal Forum
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
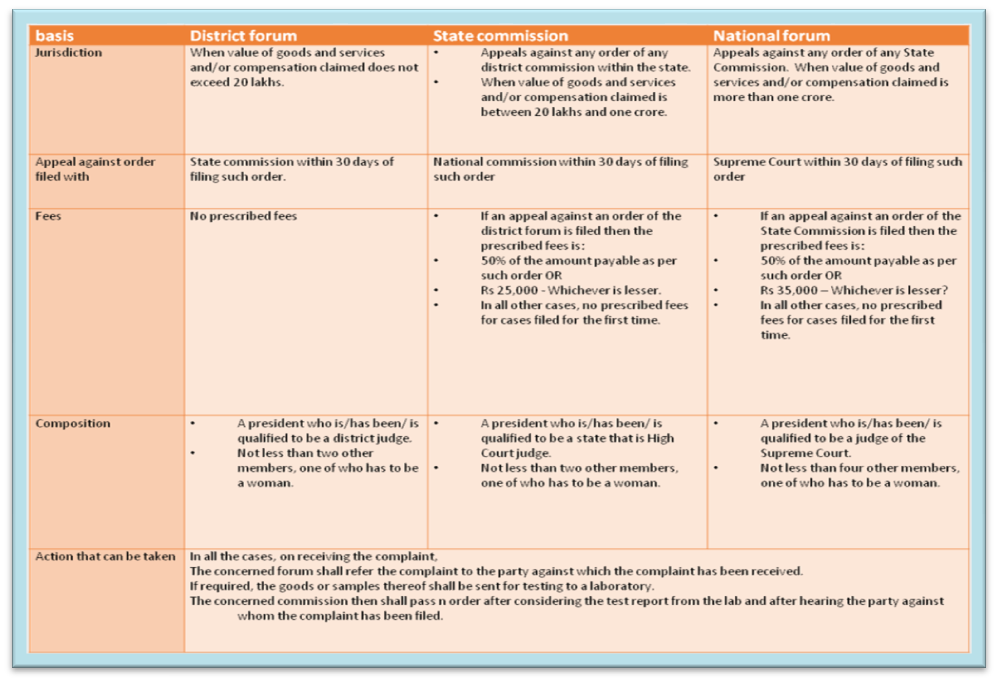
LEGAL REDRESSAL FORUM:
Redressal Agencies under Consumer Protect Act, 1986
Remedies/Relief Available
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
REMEDIES/RELIEFS AVAILABLE
Relief Available
- To remove the defect in goods or the deficiency in service.
- To replace the defective product with a new one, free from any defect.
- To refund the price paid for the product.
- To pay a reasonable amount of compensation for any loss or injury suffered by the consumer due to negligence of the opposite party.
- To pay punitive damages in appropriate circumstances.
- To discontinue the unfair/ restrictive trade practice and not repeat the same in the future.
- Not to offer hazardous goods for sale.
- To withdraw hazardous goods from sale.
- To cease manufacture of hazardous goods.
- To pay any amount (not less than 5% of the value of the defective goods to be credited to the Consumer Welfare Fund or any other organization/person, to be utilized in the prescribed manner.
- To issue corrective advertisements to neutralize the effect of misleading advertisements.
- To pay adequate costs to the appropriate party
Consumer Responsibilities
- Awareness: Aware of various goods and services available in the market to make an intelligent and wise decision.
- Follow instructions: Read labels carefully so as to have information about prices, net weight, manufacturing and expiry dates, etc, and the risks associated with products, and use the products safely
- Honest: be honest in dealings and choose only from legal goods and services and discourage dishonest practices like black-marketing, hoarding, etc.
- Cash memo: Ask for a cash memo on the purchase of goods or services for proof of the purchase made.
- Filing a complaint: File a complaint in an appropriate consumer forum in case of a shortcoming in the quality of goods purchased or services. Do not fail to take any action even when the amount involved is small.
- Environment friendly: Respect the environment. Avoid waste, littering and contributing to pollution.
- Form Consumer Awareness organizations: which can be represented the consumers for their welfare.
- Quality conscious: Buy only standardized goods as they provide quality assurance. ISI mark on electrical goods, FPO mark on food products, Hallmark on jewelry etc.

What kind of quality certification mark will you look for before buying products?

Role of Consumer Organisations & NGOs
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
ROLE OF CONSUMER ORGANISATIONS & NGOs:
- Publishing: periodicals and other publications to impart knowledge about consumer problems, legal reporting, and relief’s available and other matters of interest.
- Assist in Educating: the general public about consumer rights by organizing training programs, seminars and workshops
- Representing: the consumers by Filing complaints in appropriate consumer courts on their behalf
- Carrying: out comparative testing of consumer products in accredited laboratories to test the relative qualities of competing brands and publishing the test results for the benefit of consumers
- Encouraging: consumers to strongly protest and take an action against unscrupulous, exploitative and unfair trade practices of sellers.
- Legal assistance: to consumers by way of providing legal advice

 ABCD CLASSES
ABCD CLASSES
